
In optics, the refractive index of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
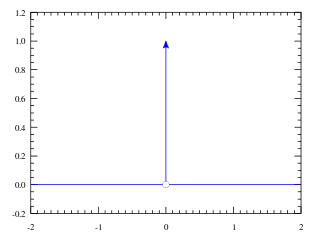
In mathematical physics, the Dirac delta distribution, also known as the unit impulse, is a generalized function or distribution over the real numbers, whose value is zero everywhere except at zero, and whose integral over the entire real line is equal to one.
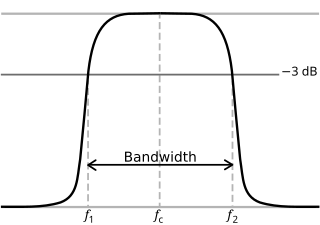
In physics and electrical engineering, a cutoff frequency, corner frequency, or break frequency is a boundary in a system's frequency response at which energy flowing through the system begins to be reduced rather than passing through.
The propagation constant of a sinusoidal electromagnetic wave is a measure of the change undergone by the amplitude and phase of the wave as it propagates in a given direction. The quantity being measured can be the voltage, the current in a circuit, or a field vector such as electric field strength or flux density. The propagation constant itself measures the change per unit length, but it is otherwise dimensionless. In the context of two-port networks and their cascades, propagation constant measures the change undergone by the source quantity as it propagates from one port to the next.
Refractive index contrast, in an optical waveguide, such as an optical fiber, is a measure of the relative difference in refractive index of the core and cladding. The refractive index contrast, Δ, is often given by , where n1 is the maximum refractive index in the core and n2 is the refractive index of the cladding. The criterion n2 < n1 must be satisfied in order to sustain a guided mode by total internal reflection. Alternative formulations include and . Normal optical fibers, constructed of different glasses, have very low refractive index contrast (Δ<<1) and hence are weakly-guiding. The weak guiding will cause a greater portion of the cross-sectional Electric field profile to reside within the cladding as compared to strongly-guided waveguides. Integrated optics can make use of higher core index to obtain Δ>1 allowing light to be efficiently guided around corners on the micro-scale, where popular high-Δ material platform is silicon-on-insulator. High-Δ allows sub-wavelength core dimensions and so greater control over the size of the evanescent tails. The most efficient low-loss optical fibers require low Δ to minimise losses to light scattered outwards.
In mathematics, particularly in linear algebra, tensor analysis, and differential geometry, the Levi-Civita symbol or Levi-Civita epsilon represents a collection of numbers; defined from the sign of a permutation of the natural numbers 1, 2, ..., n, for some positive integer n. It is named after the Italian mathematician and physicist Tullio Levi-Civita. Other names include the permutation symbol, antisymmetric symbol, or alternating symbol, which refer to its antisymmetric property and definition in terms of permutations.

In optics, a Fabry–Pérot interferometer (FPI) or etalon is an optical cavity made from two parallel reflecting surfaces. Optical waves can pass through the optical cavity only when they are in resonance with it. It is named after Charles Fabry and Alfred Perot, who developed the instrument in 1899. Etalon is from the French étalon, meaning "measuring gauge" or "standard".
The laser diode rate equations model the electrical and optical performance of a laser diode. This system of ordinary differential equations relates the number or density of photons and charge carriers (electrons) in the device to the injection current and to device and material parameters such as carrier lifetime, photon lifetime, and the optical gain.

The Mach–Zehnder interferometer is a device used to determine the relative phase shift variations between two collimated beams derived by splitting light from a single source. The interferometer has been used, among other things, to measure phase shifts between the two beams caused by a sample or a change in length of one of the paths. The apparatus is named after the physicists Ludwig Mach and Ludwig Zehnder; Zehnder's proposal in an 1891 article was refined by Mach in an 1892 article. Demonstrations of Mach–Zehnder interferometry with particles other than photons had been demonstrated as well in multiple experiments.

A zone plate is a device used to focus light or other things exhibiting wave character. Unlike lenses or curved mirrors, zone plates use diffraction instead of refraction or reflection. Based on analysis by French physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel, they are sometimes called Fresnel zone plates in his honor. The zone plate's focusing ability is an extension of the Arago spot phenomenon caused by diffraction from an opaque disc.
In general relativity, the Gibbons–Hawking–York boundary term is a term that needs to be added to the Einstein–Hilbert action when the underlying spacetime manifold has a boundary.
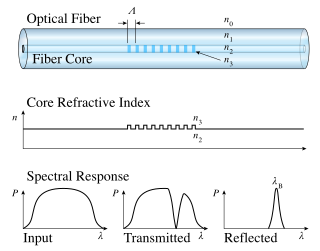
A fiber Bragg grating (FBG) is a type of distributed Bragg reflector constructed in a short segment of optical fiber that reflects particular wavelengths of light and transmits all others. This is achieved by creating a periodic variation in the refractive index of the fiber core, which generates a wavelength-specific dielectric mirror. Hence a fiber Bragg grating can be used as an inline optical fiber to block certain wavelengths, can be used for sensing applications, or it can be used as wavelength-specific reflector.
Angular distance or angular separation, also known as apparent distance or apparent separation, denoted , is the angle between the two sightlines, or between two point objects as viewed from an observer.
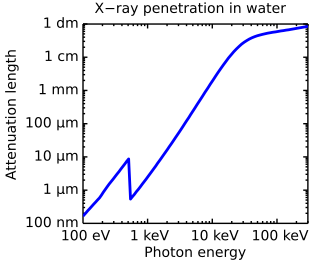
Penetration depth is a measure of how deep light or any electromagnetic radiation can penetrate into a material. It is defined as the depth at which the intensity of the radiation inside the material falls to 1/e of its original value at the surface.

In number theory, the divisor summatory function is a function that is a sum over the divisor function. It frequently occurs in the study of the asymptotic behaviour of the Riemann zeta function. The various studies of the behaviour of the divisor function are sometimes called divisor problems.

Athermalization, in the field of optics, is the process of achieving optothermal stability in optomechanical systems. This is done by minimizing variations in optical performance over a range of temperatures.

Acousto-optics is a branch of physics that studies the interactions between sound waves and light waves, especially the diffraction of laser light by ultrasound through an ultrasonic grating.

The primary line constants are parameters that describe the characteristics of conductive transmission lines, such as pairs of copper wires, in terms of the physical electrical properties of the line. The primary line constants are only relevant to transmission lines and are to be contrasted with the secondary line constants, which can be derived from them, and are more generally applicable. The secondary line constants can be used, for instance, to compare the characteristics of a waveguide to a copper line, whereas the primary constants have no meaning for a waveguide.
Krippendorff's alpha coefficient, named after academic Klaus Krippendorff, is a statistical measure of the agreement achieved when coding a set of units of analysis. Since the 1970s, alpha has been used in content analysis where textual units are categorized by trained readers, in counseling and survey research where experts code open-ended interview data into analyzable terms, in psychological testing where alternative tests of the same phenomena need to be compared, or in observational studies where unstructured happenings are recorded for subsequent analysis.

The Van der Meer formula is a formula for calculating the required stone weight for armourstone under the influence of (wind) waves. This is necessary for the design of breakwaters and shoreline protection. Around 1985 it was found that the Hudson formula in use at that time had considerable limitations. That is why the Dutch government agency Rijkswaterstaat commissioned Deltares to start research for a more complete formula. This research, conducted by Jentsje van der Meer, resulted in the Van der Meer formula in 1988, as described in his dissertation. This formula reads




















