
Wake-on-LAN is an Ethernet or Token Ring computer networking standard that allows a computer to be turned on or awakened from sleep mode by a network message. It is based upon AMD's Magic Packet Technology, which was co-developed by AMD and Hewlett-Packard, following its proposal as a standard in 1995. The standard saw quick adoption thereafter through IBM, Intel and others.

A secure cryptoprocessor is a dedicated computer-on-a-chip or microprocessor for carrying out cryptographic operations, embedded in a packaging with multiple physical security measures, which give it a degree of tamper resistance. Unlike cryptographic processors that output decrypted data onto a bus in a secure environment, a secure cryptoprocessor does not output decrypted data or decrypted program instructions in an environment where security cannot always be maintained.
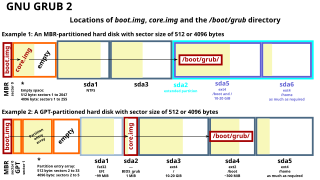
A boot sector is the sector of a persistent data storage device which contains machine code to be loaded into random-access memory (RAM) and then executed by a computer system's built-in firmware.
The Encrypting File System (EFS) on Microsoft Windows is a feature introduced in version 3.0 of NTFS that provides filesystem-level encryption. The technology enables files to be transparently encrypted to protect confidential data from attackers with physical access to the computer.

Unified Extensible Firmware Interface is a specification that defines an architecture for the platform firmware used for booting a computer's hardware and its interface for interaction with the operating system. Examples of firmware that implement the specification are AMI Aptio, Phoenix SecureCore, TianoCore EDK II, InsydeH2O.
Disk encryption software is a computer security software that protects the confidentiality of data stored on computer media by using disk encryption.
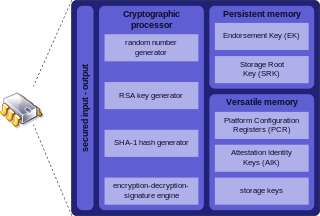
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is an international standard for a secure cryptoprocessor, a dedicated microcontroller designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. The term can also refer to a chip conforming to the standard ISO/IEC 11889. Common uses are to verify platform integrity, and to store disk encryption keys.
Intel Trusted Execution Technology is a computer hardware technology of which the primary goals are:

The Apple–Intel architecture, or Mactel, is an unofficial name used for Macintosh personal computers developed and manufactured by Apple Inc. that use Intel x86 processors, rather than the PowerPC and Motorola 68000 ("68k") series processors used in their predecessors or the ARM-based Apple silicon SoCs used in their successors. As Apple changed the architecture of its products, they changed the firmware from the Open Firmware used on PowerPC-based Macs to the Intel-designed Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI). With the change in processor architecture to x86, Macs gained the ability to boot into x86-native operating systems, while Intel VT-x brought near-native virtualization with macOS as the host OS.

BitLocker is a full volume encryption feature included with Microsoft Windows versions starting with Windows Vista. It is designed to protect data by providing encryption for entire volumes. By default, it uses the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm in cipher block chaining (CBC) or "xor–encrypt–xor (XEX)-based Tweaked codebook mode with ciphertext Stealing" (XTS) mode with a 128-bit or 256-bit key. CBC is not used over the whole disk; it is applied to each individual sector.

The EFIsystem partition or ESP is a partition on a data storage device that is used by computers that have the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). When a computer is booted, UEFI firmware loads files stored on the ESP to start operating systems and various utilities.

The Windows Boot Manager (BOOTMGR) is the bootloader provided by Microsoft for Windows NT versions starting with Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. It is the first program launched by the BIOS or UEFI of the computer and is responsible for loading the rest of Windows. It replaced the NTLDR present in older versions of Windows.
Disk encryption is a technology which protects information by converting it into code that cannot be deciphered easily by unauthorized people or processes. Disk encryption uses disk encryption software or hardware to encrypt every bit of data that goes on a disk or disk volume. It is used to prevent unauthorized access to data storage.
There are a number of security and safety features new to Windows Vista, most of which are not available in any prior Microsoft Windows operating system release.
This is a technical feature comparison of different disk encryption software.
In computer security, a cold boot attack is a type of side channel attack in which an attacker with physical access to a computer performs a memory dump of a computer's random-access memory (RAM) by performing a hard reset of the target machine. Typically, cold boot attacks are used for retrieving encryption keys from a running operating system for malicious or criminal investigative reasons. The attack relies on the data remanence property of DRAM and SRAM to retrieve memory contents that remain readable in the seconds to minutes following a power switch-off.
Hardware-based full disk encryption (FDE) is available from many hard disk drive (HDD/SSD) vendors, including: Hitachi, Integral Memory, iStorage Limited, Micron, Seagate Technology, Samsung, Toshiba, Viasat UK, Western Digital. The symmetric encryption key is maintained independently from the computer's CPU, thus allowing the complete data store to be encrypted and removing computer memory as a potential attack vector.
InstantGo, also known as InstantOn or Modern Standby, is a Microsoft specification for Windows 8 hardware and software that aims to bring smartphone-type power management capabilities to the PC platform, as well as increasing physical security.

VeraCrypt is a free and open-source utility for on-the-fly encryption (OTFE). The software can create a virtual encrypted disk that works just like a regular disk but within a file. It can also encrypt a partition or the entire storage device with pre-boot authentication.

An evil maid attack is an attack on an unattended device, in which an attacker with physical access alters it in some undetectable way so that they can later access the device, or the data on it.










