Related Research Articles

Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and anaphylaxis. Symptoms may include red eyes, an itchy rash, sneezing, coughing, a runny nose, shortness of breath, or swelling. Note that food intolerances and food poisoning are separate conditions.
An allergen is a type of antigen that produces an abnormally vigorous immune response in which the immune system fights off a perceived threat that would otherwise be harmless to the body. Such reactions are called allergies.

The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay is a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a ligand in a liquid sample using antibodies directed against the ligand to be measured. ELISA has been used as a diagnostic tool in medicine, plant pathology, and biotechnology, as well as a quality control check in various industries.
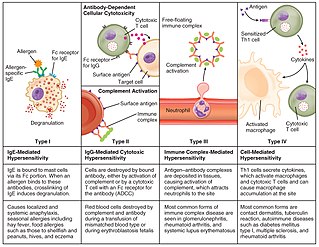
Hypersensitivity is an abnormal physiological condition in which there is an undesirable and adverse immune response to antigen. It is an abnormality in the immune system that causes immune diseases including allergies and autoimmunity. It is caused by many types of particles and substances from the external environment or from within the body that are recognized by the immune cells as antigens. The immune reactions are usually referred to as an over-reaction of the immune system and they are often damaging and uncomfortable.
A radioallergosorbent test (RAST) is a blood test using radioimmunoassay test to detect specific IgE antibodies in order to determine the substances a subject is allergic to. This is different from a skin allergy test, which determines allergy by the reaction of a person's skin to different substances.
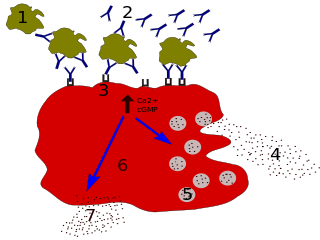
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody that has been found only in mammals. IgE is synthesised by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains and two light chains, with the ε chain containing four Ig-like constant domains (Cε1–Cε4). IgE is thought to be an important part of the immune response against infection by certain parasitic worms, including Schistosoma mansoni, Trichinella spiralis, and Fasciola hepatica. IgE is also utilized during immune defense against certain protozoan parasites such as Plasmodium falciparum. IgE may have evolved as a defense to protect against venoms.
Haptens are small molecules that elicit an immune response only when attached to a large carrier such as a protein; the carrier may be one that also does not elicit an immune response by itself. The mechanisms of absence of immune response may vary and involve complex immunological interactions, but can include absent or insufficient co-stimulatory signals from antigen-presenting cells.
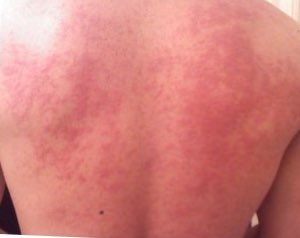
A food allergy is an abnormal immune response to food. The symptoms of the allergic reaction may range from mild to severe. They may include itchiness, swelling of the tongue, vomiting, diarrhea, hives, trouble breathing, or low blood pressure. This typically occurs within minutes to several hours of exposure. When the symptoms are severe, it is known as anaphylaxis. A food intolerance and food poisoning are separate conditions, not due to an immune response.
Serology is the scientific study of serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the diagnostic identification of antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection, against other foreign proteins, or to one's own proteins. In either case, the procedure is simple.

A radioimmunoassay (RIA) is an immunoassay that uses radiolabeled molecules in a stepwise formation of immune complexes. A RIA is a very sensitive in vitro assay technique used to measure concentrations of substances, usually measuring antigen concentrations by use of antibodies.

The hook effect refers to the prozone phenomenon, also known as antibody excess or the Postzone phenomenon, also known as antigen excess. It is an immunologic phenomenon whereby the effectiveness of antibodies to form immune complexes can be impaired when concentrations of an antibody or an antigen are very high. The formation of immune complexes stops increasing with greater concentrations and then decreases at extremely high concentrations, producing a hook shape on a graph of measurements. An important practical relevance of the phenomenon is as a type of interference that plagues certain immunoassays and nephelometric assays, resulting in false negatives or inaccurately low results. Other common forms of interference include antibody interference, cross-reactivity and signal interference. The phenomenon is caused by very high concentrations of a particular analyte or antibody and is most prevalent in one-step (sandwich) immunoassays.

Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) or extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) is a syndrome caused by the repetitive inhalation of antigens from the environment in susceptible or sensitized people. Common antigens include molds, bacteria, bird droppings, bird feathers, agricultural dusts, bioaerosols and chemicals from paints or plastics. People affected by this type of lung inflammation (pneumonitis) are commonly exposed to the antigens by their occupations, hobbies, the environment and animals. The inhaled antigens produce a hypersensitivity immune reaction causing inflammation of the airspaces (alveoli) and small airways (bronchioles) within the lung. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis may eventually lead to interstitial lung disease.
Cross-reactivity, in a general sense, is the reactivity of an observed agent which initiates reactions outside the main reaction expected. This has implications for any kind of test or assay, including diagnostic tests in medicine, and can be a cause of false positives. In immunology, the definition of cross-reactivity refers specifically to the reaction of the immune system to antigens. There can be cross-reactivity between the immune system and the antigens of two different pathogens, or between one pathogen and proteins on non-pathogens, which in some cases can be the cause of allergies.

Ouchterlony double immunodiffusion is an immunological technique used in the detection, identification and quantification of antibodies and antigens, such as immunoglobulins and extractable nuclear antigens. The technique is named after Örjan Ouchterlony, the Swedish physician who developed the test in 1948 to evaluate the production of diphtheria toxins from isolated bacteria.
The use of podiatry drills, in the absence of engineering controls and personal protective equipment, is an occupational hazard to the healthcare provider. Nail dust collected during foot care procedures performed in office settings has been found to contain keratin, keratin hydrolysates, microbial debris, and viable fungal elements, including dermatophytes and saprotrophs. Exposure to nail dust and the associated risk will vary with the policies and practices in place, the type of podiatry drill used, therapy technique, frequency of procedures, personal protective equipment utilized and the use of ventilation systems.

Type III hypersensitivity, in the Gell and Coombs classification of allergic reactions, occurs when there is accumulation of immune complexes that have not been adequately cleared by innate immune cells, giving rise to an inflammatory response and attraction of leukocytes. There are three steps that lead to this response. The first step is immune complex formation, which involves the binding of antigens to antibodies to form mobile immune complexes. The second step is immune complex deposition, during which the complexes leave the plasma and are deposited into tissues. Finally, the third step is the inflammatory reaction, during which the classical pathway is activated and macrophages and neutrophils are recruited to the affected tissues. Such reactions may progress to immune complex diseases.

Allergic symptoms are caused by an initial systemic histamine release by activated basophils and mast cells, that may lead to shock with laryngeal edema, lower-airway obstruction and hypotension. This is why basophils are considered with mast cells to be the key cells in allergic diseases.

Anti-double stranded DNA (Anti-dsDNA) antibodies are a group of anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA) the target antigen of which is double stranded DNA. Blood tests such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunofluorescence are routinely performed to detect anti-dsDNA antibodies in diagnostic laboratories. They are highly diagnostic of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and are implicated in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis.

Ara h 1 is a seed storage protein from Arachis hypogaea (peanuts). It is a heat stable 7S vicilin-like globulin with a stable trimeric form that comprises 12-16% of the total protein in peanut extracts. Ara h 1 is known because sensitization to it was found in 95% of peanut-allergic patients from North America. In spite of this high percentage, peanut-allergic patients of European populations have fewer sensitizations to Ara h 1.
Antigen-antibody interaction, or antigen-antibody reaction, is a specific chemical interaction between antibodies produced by B cells of the white blood cells and antigens during immune reaction. The antigens and antibodies combine by a process called agglutination. It is the fundamental reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign molecules, such as pathogens and their chemical toxins. In the blood, the antigens are specifically and with high affinity bound by antibodies to form an antigen-antibody complex. The immune complex is then transported to cellular systems where it can be destroyed or deactivated.
References
- ↑ Heidelberger, Michael; Kendall, Forrest E. (30 November 1929). "A Quantitative Study of the Precipitin Reaction Between Type III Pneumococcus Polysaccharide and Purified Homologous Antibody". Journal of Experimental Medicine. 50 (6): 809–823. doi:10.1084/jem.50.6.809. ISSN 1540-9538. PMC 2131658 . PMID 19869667.
- 1 2 Witter, Richard L. (1962). "The Diagnosis of Infectious Bronchitis of Chickens by the Agar Gel Precipitin Test". Avian Diseases. 6 (4): 478–492. doi:10.2307/1587924. ISSN 0005-2086. JSTOR 1587924.
- 1 2 Lau, Kevin S. K.; Yeung, Chantane; Carlsten, Chris (2020-09-03). "Stability of serum precipitins to Aspergillus fumigatus for the diagnosis of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis". Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology. 16 (1): 78. doi: 10.1186/s13223-020-00476-4 . ISSN 1710-1492. PMC 7491339 . PMID 32944032.