
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and led to heavy, fairly immobile siege engines. As technology improved, lighter, more mobile field artillery cannons developed for battlefield use. This development continues today; modern self-propelled artillery vehicles are highly mobile weapons of great versatility generally providing the largest share of an army's total firepower.

Shrapnel shells were anti-personnel artillery munitions which carried many individual bullets close to a target area and then ejected them to allow them to continue along the shell's trajectory and strike targets individually. They relied almost entirely on the shell's velocity for their lethality. The munition has been obsolete since the end of World War I for anti-personnel use; high-explosive shells superseded it for that role. The functioning and principles behind Shrapnel shells are fundamentally different from high-explosive shell fragmentation. Shrapnel is named after Lieutenant-General Henry Shrapnel (1761–1842), a British artillery officer, whose experiments, initially conducted on his own time and at his own expense, culminated in the design and development of a new type of artillery shell.

Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action". It includes surface based, subsurface, and air-based weapon systems, associated sensor systems, command and control arrangements, and passive measures. It may be used to protect naval, ground, and air forces in any location. However, for most countries the main effort has tended to be homeland defence. NATO refers to airborne air defence as counter-air and naval air defence as anti-aircraft warfare. Missile defence is an extension of air defence, as are initiatives to adapt air defence to the task of intercepting any projectile in flight.
Indirect fire is aiming and firing a projectile without relying on a direct line of sight between the gun and its target, as in the case of direct fire. Aiming is performed by calculating azimuth and inclination, and may include correcting aim by observing the fall of shot and calculating new angles.

Technology during World War I (1914–1918) reflected a trend toward industrialism and the application of mass-production methods to weapons and to the technology of warfare in general. This trend began at least fifty years prior to World War I during the American Civil War of 1861–1865, and continued through many smaller conflicts in which soldiers and strategists tested new weapons.

In military science, suppressive fire is "fire that degrades the performance of an enemy force below the level needed to fulfill its mission". When used to protect exposed friendly troops advancing on the battlefield, it is commonly called covering fire. Suppression is usually only effective for the duration of the fire. It is one of three types of fire support, which is defined by NATO as "the application of fire, coordinated with the maneuver of forces, to destroy, neutralise or suppress the enemy".

World War I was the first major conflict involving the large-scale use of aircraft. Tethered observation balloons had already been employed in several wars, and would be used extensively for artillery spotting. Germany employed Zeppelins for reconnaissance over the North Sea and Baltic and also for strategic bombing raids over Britain and the Eastern Front.

The Ordnance QF 18-pounder, or simply 18-pounder gun, was the standard British Empire field gun of the First World War-era. It formed the backbone of the Royal Field Artillery during the war, and was produced in large numbers. It was used by British Forces in all the main theatres, and by British troops in Russia in 1919. Its calibre (84 mm) and shell weight were greater than those of the equivalent field guns in French (75 mm) and German (77 mm) service. It was generally horse drawn until mechanisation in the 1930s.

An artillery observer,artillery spotter or forward observer (FO) is responsible for directing artillery and mortar fire onto a target. It may be a forward air controller (FAC) for close air support and spotter for naval gunfire support. Also known as fire support specialist (FiSTer), an artillery observer usually accompanies a tank or infantry maneuver unit. Spotters ensure that indirect fire hits targets which the troops at the fire support base cannot see.

A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a director, and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs the same task as a human gunner firing a weapon, but attempts to do so faster and more accurately.
Counter-battery fire is a battlefield tactic employed to defeat the enemy's indirect fire elements, including their target acquisition, as well as their command and control components. Counter-battery arrangements and responsibilities vary between nations but involve target acquisition, planning and control, and counter-fire. Counter-battery fire rose to prominence in World War I.

Field artillery is a category of mobile artillery used to support armies in the field. These weapons are specialized for mobility, tactical proficiency, short range, long range, and extremely long range target engagement.

The QF 3.7-inch AA was Britain's primary heavy anti-aircraft gun during World War II. It was roughly the equivalent of the German Flak 8.8 cm and American 90 mm, but with a slightly larger calibre of 3.7 inches, approximately 94 mm. Production began in 1937 and it was used throughout World War II in all theatres except the Eastern Front. It remained in use after the war until AA guns were replaced by guided missiles beginning in 1957.

Gun laying is the process of aiming an artillery piece or turret, such as a gun, howitzer, or mortar, on land, in air, or at sea, against surface or aerial targets. It may be laying for direct fire, where the gun is aimed similarly to a rifle, or indirect fire, where firing data is calculated and applied to the sights. The term includes automated aiming using, for example, radar-derived target data and computer-controlled guns.
In land warfare, artillery sound ranging is a method of determining the coordinates of a hostile battery using data derived from the sound of its guns firing. The same methods can also be used to direct artillery fire at a position with known coordinates.

A fire control tower is a structure located near the coastline, used to detect and locate enemy vessels offshore, direct fire upon them from coastal batteries, or adjust the aim of guns by spotting shell splashes. Fire control towers came into general use in coastal defence systems in the late 19th century, as rapid development significantly increased the range of both naval guns and coastal artillery. This made fire control more complex. These towers were used in a number of countries' coastal defence systems through 1945, much later in a few cases such as Sweden. The Atlantic Wall in German-occupied Europe during World War II included fire control towers.
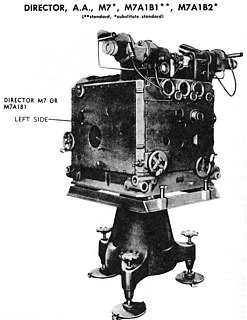
A director, also called an auxiliary predictor, is a mechanical or electronic computer that continuously calculates trigonometric firing solutions for use against a moving target, and transmits targeting data to direct the weapon firing crew.

The 13 pounder 9 cwt anti-aircraft gun became the standard mobile British anti-aircraft gun of the World War I era, especially in theatres outside Britain.

Georg Bruchmüller was a German artillery officer who greatly influenced the development of modern artillery tactics. He was nicknamed Durchbruchmüller, a combination of the German word Durchbruch (breakthrough) with his name.

In military usage, a barrage is massed sustained artillery fire (shelling) aimed at a series of points along a line. In addition to attacking any enemy in the kill zone, a barrage intends to suppress enemy movements and deny access across that line of barrage. The impact points along the line may be 20–30 yards/meters apart, with the total line length of the barrage zone anything from a few hundred to several thousand yards/meters long. Barrages can consist of multiple such lines, usually about 100 yards/meters apart, with the barrage shifting from one line to the next over time, or several lines may be targeted simultaneously.

















