
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization, management, and storage format that is usually chosen for efficient access to data. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data, i.e., it is an algebraic structure about data.
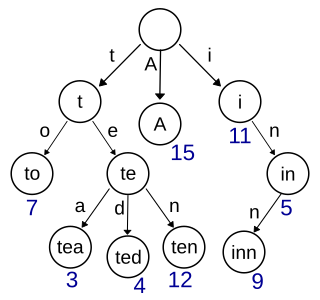
In computer science, a trie, also called digital tree or prefix tree, is a type of k-ary search tree, a tree data structure used for locating specific keys from within a set. These keys are most often strings, with links between nodes defined not by the entire key, but by individual characters. In order to access a key, the trie is traversed depth-first, following the links between nodes, which represent each character in the key.

A distributed hash table (DHT) is a distributed system that provides a lookup service similar to a hash table. Key–value pairs are stored in a DHT, and any participating node can efficiently retrieve the value associated with a given key. The main advantage of a DHT is that nodes can be added or removed with minimum work around re-distributing keys. Keys are unique identifiers which map to particular values, which in turn can be anything from addresses, to documents, to arbitrary data. Responsibility for maintaining the mapping from keys to values is distributed among the nodes, in such a way that a change in the set of participants causes a minimal amount of disruption. This allows a DHT to scale to extremely large numbers of nodes and to handle continual node arrivals, departures, and failures.
Kademlia is a distributed hash table for decentralized peer-to-peer computer networks designed by Petar Maymounkov and David Mazières in 2002. It specifies the structure of the network and the exchange of information through node lookups. Kademlia nodes communicate among themselves using UDP. A virtual or overlay network is formed by the participant nodes. Each node is identified by a number or node ID. The node ID serves not only as identification, but the Kademlia algorithm uses the node ID to locate values.

In computer science, a suffix tree is a compressed trie containing all the suffixes of the given text as their keys and positions in the text as their values. Suffix trees allow particularly fast implementations of many important string operations.
In distributed data storage, a P-Grid is a self-organizing structured peer-to-peer system, which can accommodate arbitrary key distributions, still providing storage load-balancing and efficient search by using randomized routing.

In computer science, a radix tree is a data structure that represents a space-optimized trie in which each node that is the only child is merged with its parent. The result is that the number of children of every internal node is at most the radix r of the radix tree, where r is a positive integer and a power x of 2, having x ≥ 1. Unlike regular trees, edges can be labeled with sequences of elements as well as single elements. This makes radix trees much more efficient for small sets and for sets of strings that share long prefixes.

In cryptography and computer science, a hash tree or Merkle tree is a tree in which every "leaf" (node) is labelled with the cryptographic hash of a data block, and every node that is not a leaf is labelled with the cryptographic hash of the labels of its child nodes. A hash tree allows efficient and secure verification of the contents of a large data structure. A hash tree is a generalization of a hash list and a hash chain.
In computer science, a ternary search tree is a type of trie where nodes are arranged in a manner similar to a binary search tree, but with up to three children rather than the binary tree's limit of two. Like other prefix trees, a ternary search tree can be used as an associative map structure with the ability for incremental string search. However, ternary search trees are more space efficient compared to standard prefix trees, at the cost of speed. Common applications for ternary search trees include spell-checking and auto-completion.
BitVault is a content-addressable distributed storage system, developed by Microsoft Research in China. BitVault uses peer-to-peer technology to distribute the tasks of storing and managing data. As such, there is no central authority responsible for management of the system. Rather, it is self-managing, provides high availability, reliability and scales up in a self-organizing manner, with low administrative overhead, which is almost constant irrespective of the size of the distributed overlay network.
Pastry is an overlay network and routing network for the implementation of a distributed hash table (DHT) similar to Chord. The key–value pairs are stored in a redundant peer-to-peer network of connected Internet hosts. The protocol is bootstrapped by supplying it with the IP address of a peer already in the network and from then on via the routing table which is dynamically built and repaired. It is claimed that because of its redundant and decentralized nature there is no single point of failure and any single node can leave the network at any time without warning and with little or no chance of data loss. The protocol is also capable of using a routing metric supplied by an outside program, such as ping or traceroute, to determine the best routes to store in its routing table.
The Luleå algorithm of computer science, designed by Degermark et al. (1997), is a technique for storing and searching internet routing tables efficiently. It is named after the Luleå University of Technology, the home institute/university of the technique's authors. The name of the algorithm does not appear in the original paper describing it, but was used in a message from Craig Partridge to the Internet Engineering Task Force describing that paper prior to its publication.
A hash array mapped trie (HAMT) is an implementation of an associative array that combines the characteristics of a hash table and an array mapped trie. It is a refined version of the more general notion of a hash tree.
In the BitTorrent file distribution system, a torrent file or meta-info file is a computer file that contains metadata about files and folders to be distributed, and usually also a list of the network locations of trackers, which are computers that help participants in the system find each other and form efficient distribution groups called swarms. Torrent files are normally named with the extension .torrent.
In computer science, an x-fast trie is a data structure for storing integers from a bounded domain. It supports exact and predecessor or successor queries in time O(log log M), using O(n log M) space, where n is the number of stored values and M is the maximum value in the domain. The structure was proposed by Dan Willard in 1982, along with the more complicated y-fast trie, as a way to improve the space usage of van Emde Boas trees, while retaining the O(log log M) query time.
In computer science, a hash tree is a persistent data structure that can be used to implement sets and maps, intended to replace hash tables in purely functional programming. In its basic form, a hash tree stores the hashes of its keys, regarded as strings of bits, in a trie, with the actual keys and (optional) values stored at the trie's "final" nodes.
The HAT-trie is a type of radix trie that uses array nodes to collect individual key–value pairs under radix nodes and hash buckets into an associative array. Unlike a simple hash table, HAT-tries store key–value in an ordered collection. The original inventors are Nikolas Askitis and Ranjan Sinha. Askitis & Zobel showed that building and accessing the HAT-trie key/value collection is considerably faster than other sorted access methods and is comparable to the array hash which is an unsorted collection. This is due to the cache-friendly nature of the data structure which attempts to group access to data in time and space into the 64 byte cache line size of the modern CPU.
Elliptics is a distributed key–value data storage with open source code. By default it is a classic distributed hash table (DHT) with multiple replicas put in different groups. Elliptics was created to meet requirements of multi-datacenter and physically distributed storage locations when storing huge amount of medium and large files.





