Bioleaching is the extraction of metals from their ores through the use of living organisms. This is much cleaner than the traditional heap leaching using cyanide. Bioleaching is one of several applications within biohydrometallurgy and several methods are used to recover copper, zinc, lead, arsenic, antimony, nickel, molybdenum, gold, silver, and cobalt.

Yellowcake is a type of uranium concentrate powder obtained from leach solutions, in an intermediate step in the processing of uranium ores. It is a step in the processing of uranium after it has been mined but before fuel fabrication or uranium enrichment. Yellowcake concentrates are prepared by various extraction and refining methods, depending on the types of ores. Typically, yellowcakes are obtained through the milling and chemical processing of uranium ore, forming a coarse powder that has a pungent odor, is insoluble in water, and contains about 80% uranium oxide, which melts at approximately 2880 °C.

Copper extraction refers to the methods used to obtain copper from its ores. The conversion of copper consists of a series of physical and electrochemical processes. Methods have evolved and vary with country depending on the ore source, local environmental regulations, and other factors.
The nirvana fallacy is the informal fallacy of comparing actual things with unrealistic, idealized alternatives. It can also refer to the tendency to assume there is a perfect solution to a particular problem. A closely related concept is the "perfect solution fallacy".
Hydrometallurgy is a technique within the field of extractive metallurgy, the obtaining of metals from their ores. Hydrometallurgy involve the use of aqueous solutions for the recovery of metals from ores, concentrates, and recycled or residual materials. Processing techniques that complement hydrometallurgy are pyrometallurgy, vapour metallurgy, and molten salt electrometallurgy. Hydrometallurgy is typically divided into three general areas:

Gold extraction refers to the processes required to extract gold from its ores. The great majority of gold is extracted from dilute ores using a combination of chemical processes. About 2000 tons are obtained from the earth annually, plus another 300 tons from recycling.
Carbon in pulp (CIP) is an extraction technique for recovery of gold which has been liberated into a cyanide solution as part of the gold cyanidation process.

Heap leaching is an industrial mining process used to extract precious metals, copper, uranium, and other compounds from ore using a series of chemical reactions that absorb specific minerals and re-separate them after their division from other earth materials. Similar to in situ mining, heap leach mining differs in that it places ore on a liner, then adds the chemicals via drip systems to the ore, whereas in situ mining lacks these liners and pulls pregnant solution up to obtain the minerals. Heap leaching is widely used in modern large-scale mining operations as it produces the desired concentrates at a lower cost compared to conventional processing methods such as flotation, agitation, and vat leaching.
Dump leaching is an industrial process to extract precious metals and copper from ores.
Uranyl sulfate describes a family of inorganic compounds with the formula UO2SO4(H2O)n. These salts consist of sulfate, the uranyl ion, and water. They are lemon-yellow solids. Uranyl sulfates are intermediates in some extraction methods used for uranium ores. These compounds can also take the form of an anhydrous salt.

Sodium diuranate, Na2U2O7·6H2O, is a uranium salt also known as the yellow oxide of uranium. Sodium diuranate is commonly referred to by the initials SDU. Along with ammonium diuranate it was a component in early yellowcakes. The ratio of the two compounds is determined by process conditions; however, yellowcake is now largely a mix of uranium oxides.
Magnesium diuranate (MgU2O7) is a compound of uranium. It is known in the uranium refining industry as "MDU" and forms the major part of some yellowcake mixtures. Yellowcakes are an intermediate product in the uranium refining process.
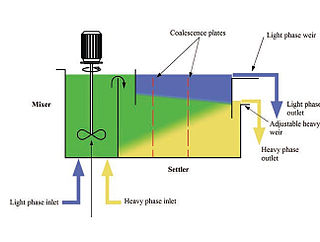
Mixer settlers are a class of mineral process equipment used in the solvent extraction process. A mixer settler consists of a first stage that mixes the phases together followed by a quiescent settling stage that allows the phases to separate by gravity.

In-situ leaching (ISL), also called in-situ recovery (ISR) or solution mining, is a mining process used to recover minerals such as copper and uranium through boreholes drilled into a deposit, in situ. In situ leach works by artificially dissolving minerals occurring naturally in a solid state. For recovery of material occurring naturally in solution, see: Brine mining.
In metallurgical processes tank leaching is a hydrometallurgical method of extracting valuable material from ore.

In agriculture, leaching is the loss of water-soluble plant nutrients from the soil, due to rain and irrigation. Soil structure, crop planting, type and application rates of fertilizers, and other factors are taken into account to avoid excessive nutrient loss. Leaching may also refer to the practice of applying a small amount of excess irrigation where the water has a high salt content to avoid salts from building up in the soil. Where this is practiced, drainage must also usually be employed, to carry away the excess water.
The Honeymoon Mine was Australia's second operating in-situ recovery uranium mine, beginning production in 2011. It is located in South Australia and is 80 kilometres (50 mi) northwest of Broken Hill, New South Wales.

Cobalt extraction refers to the techniques used to extract cobalt from its ores and other compound ores. Several methods exist for the separation of cobalt from copper and nickel. They depend on the concentration of cobalt and the exact composition of the ore used.
Heterogeneous metal catalyzed cross-coupling is a subset of metal catalyzed cross-coupling in which a heterogeneous metal catalyst is employed. Generally heterogeneous cross-coupling catalysts consist of a metal dispersed on an inorganic surface or bound to a polymeric support with ligands. Heterogeneous catalysts provide potential benefits over homogeneous catalysts in chemical processes in which cross-coupling is commonly employed—particularly in the fine chemical industry—including recyclability and lower metal contamination of reaction products. However, for cross-coupling reactions, heterogeneous metal catalysts can suffer from pitfalls such as poor turnover and poor substrate scope, which have limited their utility in cross-coupling reactions to date relative to homogeneous catalysts. Heterogeneous metal catalyzed cross-couplings, as with homogeneous metal catalyzed ones, most commonly use Pd as the cross-coupling metal.







