
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as wrist joints. This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum.

The trapezoid bone is a carpal bone in tetrapods, including humans. It is the smallest bone in the distal row of carpal bones that give structure to the palm of the hand. It may be known by its wedge-shaped form, the broad end of the wedge constituting the dorsal, the narrow end the palmar surface; and by its having four articular facets touching each other, and separated by sharp edges. It is homologous with the "second distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians.

The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone is the largest bone of the proximal row of wrist bones, its long axis being from above downward, lateralward, and forward. It is approximately the size and shape of a medium cashew.

The capitate bone is found in the center of the carpal bone region, colloquially known as the wrist, which is at the distal end of the radius and ulna bones. It articulates with the third metacarpal bone and forms the third carpometacarpal joint. The capitate bone is the largest of the carpal bones in the human hand. It presents, above, a rounded portion or head, which is received into the concavity formed by the scaphoid and lunate bones; a constricted portion or neck; and below this, the body. The bone is also found in many other mammals, and is homologous with the "third distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians.
An osteotomy is a surgical operation whereby a bone is cut to shorten or lengthen it or to change its alignment. It is sometimes performed to correct a hallux valgus, or to straighten a bone that has healed crookedly following a fracture. It is also used to correct a coxa vara, genu valgum, and genu varum. The operation is done under a general anaesthetic.

A bone fracture is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of a bone. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several pieces. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture.

Avascular necrosis (AVN), also called osteonecrosis or bone infarction, is death of bone tissue due to interruption of the blood supply. Early on, there may be no symptoms. Gradually joint pain may develop which may limit the ability to move. Complications may include collapse of the bone or nearby joint surface.

Kienböck's disease is a disorder of the wrist. It is named for Dr. Robert Kienböck, a radiologist in Vienna, Austria who described osteomalacia of the lunate in 1910.
Arthroplasty is an orthopedic surgical procedure where the articular surface of a musculoskeletal joint is replaced, remodeled, or realigned by osteotomy or some other procedure. It is an elective procedure that is done to relieve pain and restore function to the joint after damage by arthritis or some other type of trauma.
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis is a medical term referring to a fracture through the growth plate (physis), which results in slippage of the overlying end of the femur (metaphysis).
Osteochondrosis is a family of orthopedic diseases of the joint that occur in children, adolescents and rapidly growing animals, particularly pigs, horses, dogs, and broiler chickens. They are characterized by interruption of the blood supply of a bone, in particular to the epiphysis, followed by localized bony necrosis, and later, regrowth of the bone. This disorder is defined as a focal disturbance of endochondral ossification and is regarded as having a multifactorial cause, so no one thing accounts for all aspects of this disease.

Madelung's deformity is usually characterized by malformed wrists and wrist bones and is often associated with Léri-Weill dyschondrosteosis. It can be bilateral or just in the one wrist. It has only been recognized within the past hundred years. Named after Otto Wilhelm Madelung (1846–1926), a German surgeon, who described it in detail, it was noted by others. Guillaume Dupuytren mentioned it in 1834, Auguste Nélaton in 1847, and Joseph-François Malgaigne in 1855.
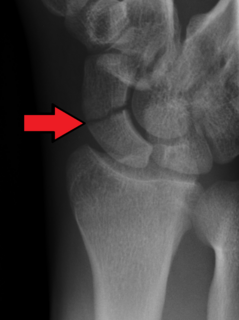
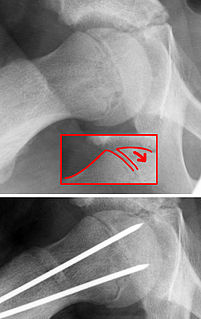
A scaphoid fracture is a break of the scaphoid bone in the wrist. Symptoms generally includes pain at the base of the thumb which is worse with use of the hand. The anatomic snuffbox is generally tender and swelling may occur. Complications may include nonunion of the fracture, avascular necrosis of the proximal part of the bone, and arthritis.

In radiology, the crescent sign is a finding on conventional radiographs that is associated with avascular necrosis. It usually occurs later in the disease, in stage III of the four-stage Ficat classification system. It appears as a curved subchondral radiolucent line that is often found on the proximal femoral or humeral head. Usually, this sign indicates a high likelihood of collapse of the affected bone. The crescent sign may be best seen in an abducted (frog-legged) position.
Four corner fusion, or partial wrist arthrodesis, is a procedure which involves resection/removal of the scaphoid bone and fixation of the remaining wrist bones with a plate or wires. The procedure is usually performed due to wrist arthritis or due to scaphoid collapse. This surgical intervention is often needed as treatment for patients with wrist osteoarthritis.

An ulna fracture is a break in the ulna bone, one of the two bones in the forearm. It is often associated with a fracture of the other forearm bone, the radius.

Wrist osteoarthritis is a group of mechanical abnormalities resulting in joint destruction, which can occur in the wrist. These abnormalities include degeneration of cartilage and hypertrophic bone changes, which can lead to pain, swelling and loss of function. Osteoarthritis of the wrist is one of the most common conditions seen by hand surgeons.
Orthopedic surgery is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal injuries, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, bone tumours, and congenital limb deformities. Trauma surgery and traumatology is a sub-specialty dealing with the operative management of fractures, major trauma and the multiply-injured patient.
An occult fracture is a fracture that is not readily visible, generally in regard to projectional radiography ("X-ray"). Radiographically, occult and subtle fractures are a diagnostic challenge. They may be divided into 1) high energy trauma fracture, 2) fatigue fracture from cyclical and sustained mechanical stress, and 3) insufficiency fracture occurring in weakened bone. Independently of the cause, the initial radiographic examination can be negative either because the findings seem normal or are too subtle. Advanced imaging tools such as computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and scintigraphy are highly valuable in the early detection of these fractures.
Dieterich's disease, also known as avascular necrosis of the metacarpal head, is an extremely rare condition characterized by temporary or permanent loss of blood supply to the metacarpal head of the metacarpal bone, resulting in loss of bone tissue. The five metacarpal bones are long bones located between the carpals of the wrist and phalanges of the fingers. Collectively, the metacarpals are referred to as the "metacarpus."














