Related Research Articles

The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the wrist is to facilitate effective positioning of the hand and powerful use of the extensors and flexors of the forearm, and the mobility of individual carpal bones increase the freedom of movements at the wrist.

In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as wrist joints. This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum.

The anatomical snuff box or snuffbox or foveola radialis is a triangular deepening on the radial, dorsal aspect of the hand—at the level of the carpal bones, specifically, the scaphoid and trapezium bones forming the floor. The name originates from the use of this surface for placing and then sniffing powdered tobacco, or "snuff." It is sometimes referred to by its French name tabatière.

The trapezoid bone is a carpal bone in tetrapods, including humans. It is the smallest bone in the distal row of carpal bones that give structure to the palm of the hand. It may be known by its wedge-shaped form, the broad end of the wedge constituting the dorsal, the narrow end the palmar surface; and by its having four articular facets touching each other, and separated by sharp edges. It is homologous with the "second distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians.

The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone is the largest bone of the proximal row of wrist bones, its long axis being from above downward, lateralward, and forward. It is approximately the size and shape of a medium cashew.

The capitate bone is found in the center of the carpal bone region, colloquially known as the wrist, which is at the distal end of the radius and ulna bones. It articulates with the third metacarpal bone and forms the third carpometacarpal joint. The capitate bone is the largest of the carpal bones in the human hand. It presents, above, a rounded portion or head, which is received into the concavity formed by the scaphoid and lunate bones; a constricted portion or neck; and below this, the body. The bone is also found in many other mammals, and is homologous with the "third distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians.

The lunate bone is a carpal bone in the human hand. It is distinguished by its deep concavity and crescentic outline. It is situated in the center of the proximal row carpal bones, which lie between the ulna and radius and the hand. The lunate carpal bone is situated between the lateral scaphoid bone and medial triquetral bone.

Kienböck's disease is a disorder of the wrist. It is named for Dr. Robert Kienböck, a radiologist in Vienna, Austria who described osteomalacia of the lunate in 1910.

Arthrodesis, also known as artificial ankylosis or syndesis, is the artificial induction of joint ossification between two bones by surgery. This is done to relieve intractable pain in a joint which cannot be managed by pain medication, splints, or other normally indicated treatments. The typical causes of such pain are fractures which disrupt the joint, severe sprains, and arthritis. It is most commonly performed on joints in the spine, hand, ankle, and foot. Historically, knee and hip arthrodeses were also performed as pain-relieving procedures, but with the great successes achieved in hip and knee arthroplasty, arthrodesis of these large joints has fallen out of favour as a primary procedure, and now is only used as a procedure of last resort in some failed arthroplasties.
The Brunelli Procedure is a surgical procedure that can be used to correct instability in the wrist. Instability in the wrist can be caused by a torn Scapholunate ligament. The Brunelli Procedure does not fix the torn ligament. A hole is drilled through the Scaphoid bone and a part of a tendon taken from the patient is put through this hole and attached to the nearby bones. The procedure usually results in reduced movement of the wrist. Instability in the wrist can, over time, lead to wrist osteoarthritis.

The intercarpal joints can be subdivided into three sets of joints : Those of the proximal row of carpal bones, those of the distal row of carpal bones, and those of the two rows with each other.

The radial styloid process is a projection of bone on the lateral surface of the distal radius bone.

The midcarpal joint is formed by the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetral bones in the proximal row, and the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate bones in the distal row. The distal pole of the scaphoid articulates with two trapezial bones as a gliding type of joint. The proximal end of the scaphoid combines with the lunate and triquetrum to form a deep concavity that articulates with the convexity of the combined capitate and hamate in a form of diarthrodial, almost condyloid joint.
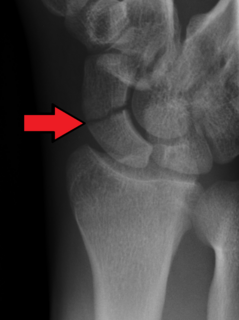
A scaphoid fracture is a break of the scaphoid bone in the wrist. Symptoms generally includes pain at the base of the thumb which is worse with use of the hand. The anatomic snuffbox is generally tender and swelling may occur. Complications may include nonunion of the fracture, avascular necrosis of the proximal part of the bone, and arthritis.

Preiser disease, or (idiopathic) avascular necrosis of the scaphoid, is a rare condition where ischemia and necrosis of the scaphoid bone occurs without previous fracture. It is thought to be caused by repetitive microtrauma or side effects of drugs in conjunction with existing defective vascular supply to the proximal pole of the scaphoid. MRI coupled with CT and X-ray are the methods of choice for diagnosis.

The scapholunate ligament is a ligament of the wrist.
Watson's test is a diagnostic test for instability between the scaphoid and lunate bones of the wrist.

Wrist osteoarthritis is a group of mechanical abnormalities resulting in joint destruction, which can occur in the wrist. These abnormalities include degeneration of cartilage and hypertrophic bone changes, which can lead to pain, swelling and loss of function. Osteoarthritis of the wrist is one of the most common conditions seen by hand surgeons.

Carpal coalition is the abnormal fusion of two or more carpal bones when they fail to segment during intrauterine development. First described by Eduard Sandifort in 1779, carpal coalitions are often an isolated issue which connect two carpal bones in the same row of the wrist. These issues are congenital and occur at various rates throughout the population.