
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term exon refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. In RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons are covalently joined to one another as part of generating the mature RNA. Just as the entire set of genes for a species constitutes the genome, the entire set of exons constitutes the exome.
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word intron is derived from the term intragenic region, i.e., a region inside a gene. The term intron refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and the corresponding RNA sequence in RNA transcripts. The non-intron sequences that become joined by this RNA processing to form the mature RNA are called exons.

RNA splicing is a process in molecular biology where a newly-made precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) transcript is transformed into a mature messenger RNA (mRNA). It works by removing all the introns and splicing back together exons. For nuclear-encoded genes, splicing occurs in the nucleus either during or immediately after transcription. For those eukaryotic genes that contain introns, splicing is usually needed to create an mRNA molecule that can be translated into protein. For many eukaryotic introns, splicing occurs in a series of reactions which are catalyzed by the spliceosome, a complex of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs). There exist self-splicing introns, that is, ribozymes that can catalyze their own excision from their parent RNA molecule. The process of transcription, splicing and translation is called gene expression, the central dogma of molecular biology.

Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final RNA product of the gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different splice variants. In the case of protein-coding genes, the proteins translated from these splice variants may contain differences in their amino acid sequence and in their biological functions.

A spliceosome is a large ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex found primarily within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. The spliceosome is assembled from small nuclear RNAs (snRNA) and numerous proteins. Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) molecules bind to specific proteins to form a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex, which in turn combines with other snRNPs to form a large ribonucleoprotein complex called a spliceosome. The spliceosome removes introns from a transcribed pre-mRNA, a type of primary transcript. This process is generally referred to as splicing. An analogy is a film editor, who selectively cuts out irrelevant or incorrect material from the initial film and sends the cleaned-up version to the director for the final cut.

A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have unique functions. A set of protein isoforms may be formed from alternative splicings, variable promoter usage, or other post-transcriptional modifications of a single gene; post-translational modifications are generally not considered. Through RNA splicing mechanisms, mRNA has the ability to select different protein-coding segments (exons) of a gene, or even different parts of exons from RNA to form different mRNA sequences. Each unique sequence produces a specific form of a protein.

UniProt is a freely accessible database of protein sequence and functional information, many entries being derived from genome sequencing projects. It contains a large amount of information about the biological function of proteins derived from the research literature. It is maintained by the UniProt consortium, which consists of several European bioinformatics organisations and a foundation from Washington, DC, USA.
The European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) is an intergovernmental organization (IGO) which, as part of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) family, focuses on research and services in bioinformatics. It is located on the Wellcome Genome Campus in Hinxton near Cambridge, and employs over 600 full-time equivalent (FTE) staff. Institute leaders such as Rolf Apweiler, Alex Bateman, Ewan Birney, and Guy Cochrane, an adviser on the National Genomics Data Center Scientific Advisory Board, serve as part of the international research network of the BIG Data Center at the Beijing Institute of Genomics.
RNA-binding proteins are proteins that bind to the double or single stranded RNA in cells and participate in forming ribonucleoprotein complexes. RBPs contain various structural motifs, such as RNA recognition motif (RRM), dsRNA binding domain, zinc finger and others. They are cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins. However, since most mature RNA is exported from the nucleus relatively quickly, most RBPs in the nucleus exist as complexes of protein and pre-mRNA called heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein particles (hnRNPs). RBPs have crucial roles in various cellular processes such as: cellular function, transport and localization. They especially play a major role in post-transcriptional control of RNAs, such as: splicing, polyadenylation, mRNA stabilization, mRNA localization and translation. Eukaryotic cells express diverse RBPs with unique RNA-binding activity and protein–protein interaction. According to the Eukaryotic RBP Database (EuRBPDB), there are 2961 genes encoding RBPs in humans. During evolution, the diversity of RBPs greatly increased with the increase in the number of introns. Diversity enabled eukaryotic cells to utilize RNA exons in various arrangements, giving rise to a unique RNP (ribonucleoprotein) for each RNA. Although RBPs have a crucial role in post-transcriptional regulation in gene expression, relatively few RBPs have been studied systematically.It has now become clear that RNA–RBP interactions play important roles in many biological processes among organisms.

Transcriptional modification or co-transcriptional modification is a set of biological processes common to most eukaryotic cells by which an RNA primary transcript is chemically altered following transcription from a gene to produce a mature, functional RNA molecule that can then leave the nucleus and perform any of a variety of different functions in the cell. There are many types of post-transcriptional modifications achieved through a diverse class of molecular mechanisms.
InterPro is a database of protein families, protein domains and functional sites in which identifiable features found in known proteins can be applied to new protein sequences in order to functionally characterise them.
In molecular biology, small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are a class of small RNA molecules that primarily guide chemical modifications of other RNAs, mainly ribosomal RNAs, transfer RNAs and small nuclear RNAs. There are two main classes of snoRNA, the C/D box snoRNAs, which are associated with methylation, and the H/ACA box snoRNAs, which are associated with pseudouridylation. SnoRNAs are commonly referred to as guide RNAs but should not be confused with the guide RNAs that direct RNA editing in trypanosomes or the guide RNAs (gRNAs) used by Cas9 for CRISPR gene editing.

Bone morphogenetic protein 1, also known as BMP1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the BMP1 gene. There are seven isoforms of the protein created by alternate splicing.
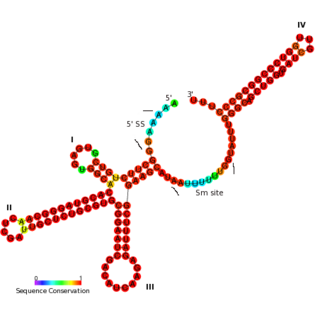
The U11 snRNA is an important non-coding RNA in the minor spliceosome protein complex, which activates the alternative splicing mechanism. The minor spliceosome is associated with similar protein components as the major spliceosome. It uses U11 snRNA to recognize the 5' splice site while U12 snRNA binds to the branchpoint to recognize the 3' splice site.

U12 minor spliceosomal RNA is formed from U12 small nuclear (snRNA), together with U4atac/U6atac, U5, and U11 snRNAs and associated proteins, forms a spliceosome that cleaves a divergent class of low-abundance pre-mRNA introns. Although the U12 sequence is very divergent from that of U2, the two are functionally analogous.

U1 spliceosomal RNA is the small nuclear RNA (snRNA) component of U1 snRNP, an RNA-protein complex that combines with other snRNPs, unmodified pre-mRNA, and various other proteins to assemble a spliceosome, a large RNA-protein molecular complex upon which splicing of pre-mRNA occurs. Splicing, or the removal of introns, is a major aspect of post-transcriptional modification, and takes place only in the nucleus of eukaryotes.

Fast skeletal muscle troponin T (fTnT) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNNT3 gene.

GRINL1A complex locus protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRINL1A gene.
SNED1 is an extracellular matrix (ECM) protein expressed at low levels in a wide range of tissues. The gene encoding SNED1 is located in the human chromosome 2 at locus q37.3. The corresponding mRNA isolated from the spleen and is 6834bp in length, and the corresponding protein is 1413 amino-acid long. The mouse ortholog of SNED1 was cloned in 2004 from the embryonic kidney by Leimester et al. SNED1 present domains characteristic of ECM proteins, including an amino-terminal NIDO domain, several calcium binding EGF-like domains (EGF_CA), a Sushi domain also known as complement control protein (CCP) domain, and three type III fibronectin (FN3) domains in the carboxy-terminal region.
WormBase is an online biological database about the biology and genome of the nematode model organism Caenorhabditis elegans and contains information about other related nematodes. WormBase is used by the C. elegans research community both as an information resource and as a place to publish and distribute their results. The database is regularly updated with new versions being released every two months. WormBase is one of the organizations participating in the Generic Model Organism Database (GMOD) project.











