Knowledge representation and reasoning is the field of artificial intelligence (AI) dedicated to representing information about the world in a form that a computer system can use to solve complex tasks such as diagnosing a medical condition or having a dialog in a natural language. Knowledge representation incorporates findings from psychology about how humans solve problems and represent knowledge, in order to design formalisms that will make complex systems easier to design and build. Knowledge representation and reasoning also incorporates findings from logic to automate various kinds of reasoning.

Medicine is the science and practice of caring for patients, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others.

A physician, medical practitioner, medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the study, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of disease, injury, and other physical and mental impairments. Physicians may focus their practice on certain disease categories, types of patients, and methods of treatment—known as specialities—or they may assume responsibility for the provision of continuing and comprehensive medical care to individuals, families, and communities—known as general practice. Medical practice properly requires both a detailed knowledge of the academic disciplines, such as anatomy and physiology, underlying diseases, and their treatment, which is the science of medicine, and a decent competence in its applied practice, which is the art or craft of the profession.
The history of anatomy extends from the earliest examinations of sacrificial victims to the sophisticated analyses of the body performed by modern anatomists and scientists. Written descriptions of human organs and parts can be traced back thousands of years to ancient Egyptian papyri, where attention to the body was necessitated by their highly elaborate burial practices.
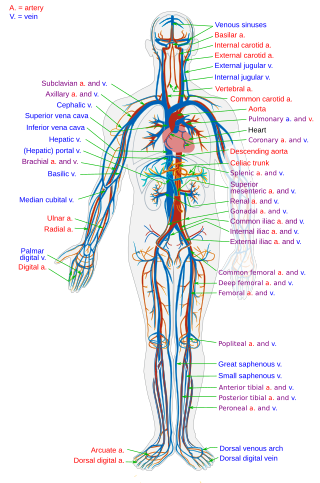
The circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels. The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms cardiovascular system and vascular system interchangeably with circulatory system.

William Cullen was a Scottish physician, chemist and agriculturalist, and professor at the Edinburgh Medical School. Cullen was a central figure in the Scottish Enlightenment: He was David Hume's physician, and was friends with Joseph Black, Henry Home, Adam Ferguson, John Millar, and Adam Smith, among others.
This article presents a timeline of hypertext technology, including "hypermedia" and related human–computer interaction projects and developments from 1945 on. The term hypertext is credited to the author and philosopher Ted Nelson.

Health informatics is the study and implementation of computer structures and algorithms to improve communication, understanding, and management of medical information. It can be viewed as a branch of engineering and applied science.
Inslaw, Inc. is a Washington, D.C. based information technology company that markets case management software for corporate and government users. Inslaw is known for developing PROMIS, an early case management software system. It is also known for a lawsuit that it brought against the United States Department of Justice (DOJ) in 1986 over PROMIS, alleging that the Justice Department had dishonestly conspired to "drive Inslaw out of business 'through trickery, fraud and deceit'" by withholding payments to Inslaw and then pirating the software.

Sir Charles Bell was a Scottish surgeon, anatomist, physiologist, neurologist, artist, and philosophical theologian. He is noted for discovering the difference between sensory nerves and motor nerves in the spinal cord. He is also noted for describing Bell's palsy.

The World Squash Federation (WSF) is the international federation for squash, an indoor racket sport which was formerly called "squash rackets". The WSF is recognised by the International Olympic Committee (IOC) as the International Federation (IF) for squash, and is also a member of the Global Association of International Sports Federations and the Association of the IOC Recognised International Sports Federations (ARISF).

Byzantine medicine encompasses the common medical practices of the Byzantine Empire from c. 400 AD to 1453 AD. Byzantine medicine was notable for building upon the knowledge base developed by its Greco-Roman predecessors. In preserving medical practices from antiquity, Byzantine medicine influenced Islamic medicine and fostered the Western rebirth of medicine during the Renaissance. The concept of the hospital appeared in Byzantine Empire as an institution to offer medical care and possibility of a cure for the patients because of the ideals of Christian charity.

First Databank (FDB) is a major provider of drug and medical device databases that help inform healthcare professionals to make decisions. FDB partners with information system developers to deliver useful medication- and medical device-related information to clinicians, business associates, and patients. FDB is part of Hearst and the Hearst Health network.
Drug discovery and development requires the integration of multiple scientific and technological disciplines. These include chemistry, biology, pharmacology, pharmaceutical technology and extensive use of information technology. The latter is increasingly recognised as Pharmacoinformatics. Pharmacoinformatics relates to the broader field of bioinformatics.

Information is an abstract concept that refers to something which has the power to inform. At the most fundamental level, it pertains to the interpretation of that which may be sensed, or their abstractions. Any natural process that is not completely random and any observable pattern in any medium can be said to convey some amount of information. Whereas digital signals and other data use discrete signs to convey information, other phenomena and artifacts such as analogue signals, poems, pictures, music or other sounds, and currents convey information in a more continuous form. Information is not knowledge itself, but the meaning that may be derived from a representation through interpretation.
PROMIS or Promis may refer to:

Serapion the Younger wrote a medicinal-botany book titled The Book of Simple Medicaments. The book is dated to the 12th or 13th century. He is called "the Younger" to distinguish him from Serapion the Elder, aka Yahya ibn Sarafyun, an earlier medical writer with whom he was often confused. Serapion the Younger's Simple Medicaments was likely written in Arabic, but no Arabic copy survives, and there is no record of knowledge of the book among medieval Arabic authors. The book was translated to Latin in the late 13th century and was widely circulated in late medieval Latin medical circles. Portions of the Latin text make a good match with portions of a surviving Arabic text Kitab al-Adwiya al-Mufrada attributed to Ibn Wafid. The entire Latin text is very heavily reliant on medieval Arabic medicinal literature; and it is essentially just a compilation of such literature. It is exceedingly clear that the book was not originally written in a Latin language.
Henry Daniel was a Dominican friar and author of widely circulating medieval medical and scientific treatises. He is credited with introducing important Latin medical terms and concepts into Middle English.
The Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) provides clinicians and researchers access to reliable, valid, and flexible measures of health status that assess physical, mental, and social well–being from the patient perspective. PROMIS measures are standardized, allowing for assessment of many patient-reported outcome domains—including pain, fatigue, emotional distress, physical functioning and social role participation—based on common metrics that allow for comparisons across domains, across chronic diseases, and with the general population. Further, PROMIS tools allow for computer adaptive testing, efficiently achieving precise measurement of health status domains with few items. There are PROMIS measures for both adults and children. PROMIS was established in 2004 with funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) as one of the initiatives of the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research.
Martin Marc Cummings, MD (1920-2011), was director of the National Library of Medicine (NLM) from 1964 to 1983, and subsequently Distinguished Professor at Georgetown University School of Medicine. During his two decades at the NLM, it was transformed into a unique international biomedical communications center, tr and one of the most advanced scientific libraries in the world. During this time, NLM was established as a new, civilian entity on the National Institutes of Health campus in Bethesda, Maryland. [it was already a civilian agency, and already on campus, but became an official component of NIH in 1968].











