
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, and over six thousand smaller islands. They have a total area of 315,159 km2 (121,684 sq mi) and a combined population of almost 72 million, and include two sovereign states, the Republic of Ireland, and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The Channel Islands, off the north coast of France, are normally taken to be part of the British Isles, even though they do not form part of the archipelago.

The Isle of Man is an island in the Irish Sea, between Great Britain and Ireland in Northern Europe, with a population of almost 85,000. It is a British Crown dependency. It has a small islet, the Calf of Man, to its south. It is located at 54°15′N4°30′W.

The National Trust, formally the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, is a charity and membership organisation for heritage conservation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. In Scotland, there is a separate and independent National Trust for Scotland.

The National Trust for Scotland for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, commonly known as the National Trust for Scotland, is a Scottish conservation organisation. It is the largest membership organisation in Scotland and describes itself as "the conservation charity that protects and promotes Scotland's natural and cultural heritage for present and future generations to enjoy".

The Giant's Causeway is an area of about 40,000 interlocking basalt columns, the result of an ancient volcanic fissure eruption. It is located in County Antrim on the north coast of Northern Ireland, about three miles (5 km) northeast of the town of Bushmills.

Pembrokeshire Coast National Park is a national park along the Pembrokeshire coast in west Wales.

Gateholm or Gateholm Island is a small tidal island off the south west coast of Pembrokeshire, in the community of Marloes and St Brides, in the south west side of Wales, in the west of the UK, and about 8 miles (13 km) west of the port of Milford Haven. It is known for its Romano-British remains. Gateholm is owned by the National Trust as part of their Marloes Sands and Mere estate.

The White Cliffs of Dover is the region of English coastline facing the Strait of Dover and France. The cliff face, which reaches a height of 350 feet (110 m), owes its striking appearance to its composition of chalk accented by streaks of black flint, deposited during the Late Cretaceous. The cliffs, on both sides of the town of Dover in Kent, stretch for eight miles (13 km). The White Cliffs of Dover form part of the North Downs. A section of coastline encompassing the cliffs was purchased by the National Trust in 2016.
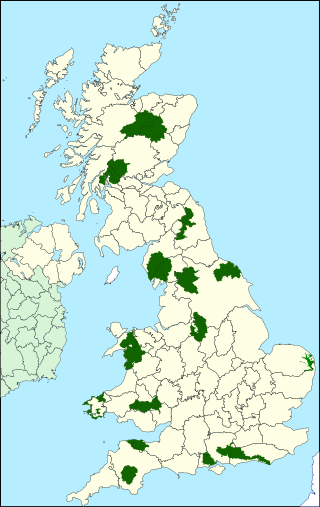
National parks of the United Kingdom are areas of relatively undeveloped and scenic landscape across the country. Despite their name, they are quite different from national parks in many other countries, which are usually owned and managed by governments as protected community resources, and which do not usually include permanent human communities. In the United Kingdom, an area designated as a national park may include substantial settlements and human land uses that are often integral parts of the landscape. Land within national parks remains largely in private ownership. These parks are therefore not "national parks" according to the internationally accepted standard of the IUCN but they are areas of outstanding landscape where planning controls are a little more restrictive than elsewhere.

An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has special rights regarding the exploration and use of marine resources, including energy production from water and wind. It stretches from the outer limit of the territorial sea out to 200 nautical miles (nmi) from the coast of the state in question. It is also referred to as a maritime continental margin and, in colloquial usage, may include the continental shelf. The term does not include either the territorial sea or the continental shelf beyond the 200 nautical mile limit. The difference between the territorial sea and the exclusive economic zone is that the first confers full sovereignty over the waters, whereas the second is merely a "sovereign right" which refers to the coastal state's rights below the surface of the sea. The surface waters, as can be seen in the map, are international waters.
The American Battlefield Trust is a charitable organization whose primary focus is in the preservation of battlefields of the American Civil War, the Revolutionary War and the War of 1812 through acquisition of battlefield land. The American Battlefield Trust was formerly known as the Civil War Trust. On May 8, 2018, the organization announced the creation of the American Battlefield Trust as the umbrella organization for two divisions, the Civil War Trust and the Revolutionary War Trust, which was formerly known as "Campaign 1776."

England comprises most of the central and southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain, in addition to a number of small islands of which the largest is the Isle of Wight. England is bordered to the north by Scotland and to the west by Wales. It is closer to continental Europe than any other part of mainland Britain, divided from France only by a 33 km (21 mi) sea gap, the English Channel. The 50 km (31 mi) Channel Tunnel, near Folkestone, directly links England to mainland Europe. The English/French border is halfway along the tunnel.

Hurricane Katrina's winds and storm surge reached the Mississippi coastline on the morning of August 29, 2005. beginning a two-day path of destruction through central Mississippi; by 10 a.m. CDT on August 29, 2005, the eye of Katrina began traveling up the entire state, only slowing from hurricane-force winds at Meridian near 7 p.m. and entering Tennessee as a tropical storm. Many coastal towns of Mississippi had already been obliterated, in a single night. Hurricane-force winds reached coastal Mississippi by 2 a.m. and lasted over 17 hours, spawning 11 tornadoes and a 28-foot (8.5 m) storm surge flooding 6–12 miles (9.7–19.3 km) inland. Many, unable to evacuate, survived by climbing to attics or rooftops, or swimming to higher buildings and trees. The worst property damage from Katrina occurred in coastal Mississippi, where all towns flooded over 90% in hours, and waves destroyed many historic buildings, with others gutted to the 3rd story. Afterward, 238 people died in Mississippi, and all counties in Mississippi were declared disaster areas, 49 for full federal assistance. Regulations were changed later for emergency centers and casinos. The emergency command centers were moved higher because all 3 coastal centers flooded at 30 ft (9.1 m) above sea level. Casinos were allowed on land rather than limited to floating casino barges as in 2005.
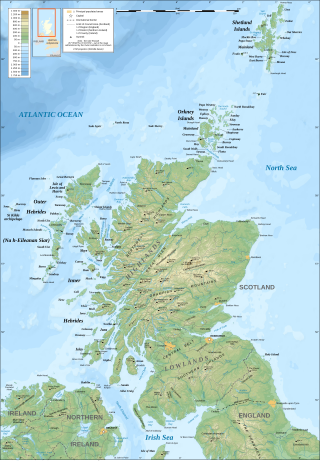
The geography of Scotland is varied, from rural lowlands to unspoilt uplands, and from large cities to sparsely inhabited islands. Located in Northern Europe, Scotland comprises the northern third of the island of Great Britain as well as 790 surrounding islands encompassing the major archipelagos of the Shetland Islands, Orkney Islands and the Inner and Outer Hebrides.

Hurricane Charley was the second hurricane to threaten the East Coast of the United States within a year's timeframe, after Hurricane Gloria of 1985. The third tropical storm and second hurricane of the season, Charley formed as a subtropical low on August 13 along the Florida panhandle. After moving off the coast of South Carolina, the system transitioned into a tropical cyclone and intensified into a tropical storm on August 15. Charley later attained hurricane status before moving across eastern North Carolina. It gradually weakened over the north Atlantic Ocean before transitioning into an extratropical cyclone on August 20. Charley's remnants remained identifiable for over a week, until after crossing Ireland and Great Britain they dissipated on August 30.

The United Kingdom has a network of roads, of varied quality and capacity, totalling about 262,300 miles (422,100 km). Road distances are shown in miles or yards and UK speed limits are indicated in miles per hour (mph) or by the use of the national speed limit (NSL) symbol. Some vehicle categories have various lower maximum limits enforced by speed limiters. A unified numbering system is in place for Great Britain, whilst in Northern Ireland, there is no available explanation for the allocation of road numbers.

The Irish Sea is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Celtic Sea in the south by St George's Channel and to the Inner Seas off the West Coast of Scotland in the north by the North Channel. Anglesey, North Wales, is the largest island in the Irish Sea, followed by the Isle of Man. The term Manx Sea may occasionally be encountered.

The Wales Coast Path is a designated long-distance trail which follows, or runs close to, the coastline of Wales.
The Maine Coast Heritage Trust is a nonprofit land conservation organization.

Ardress House is a country house in Annaghmore, County Armagh, in Northern Ireland. The house was owned by the Clarke, then Ensor families, including the writer and lawyer George Ensor. The estate, which includes orchards, a farm and a dairy, borders the River Tall. Collections within the house include eighteenth-century paintings and furniture. In 1959, the National Trust acquired Ardress from Captain Charles Ensor with support from the Ulster Land Fund.


















