Related Research Articles
Lips are a visible body part at the mouth of humans and many animals.

The external iliac arteries are two major arteries which bifurcate off the common iliac arteries anterior to the sacroiliac joint of the pelvis. They proceed anterior and inferior along the medial border of the psoas major muscles. They exit the pelvic girdle posterior and inferior to the inguinal ligament about one third laterally from the insertion point of the inguinal ligament on the pubic tubercle at which point they are referred to as the femoral arteries. The external iliac artery is usually the artery used to attach the renal artery to the recipient of a kidney transplant.

The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face.

The maxillary nerve (CN V2) is one of the three branches or divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth (V) cranial nerve. It comprises the principal functions of sensation from the maxillary, nasal cavity, sinuses, the palate and subsequently that of the mid-face, and is intermediate, both in position and size, between the ophthalmic nerve and the mandibular nerve.

The superior thyroid artery arises from the external carotid artery just below the level of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone and ends in the thyroid gland.

The inferior rectal artery is an artery that supplies blood to the lower half of the anal canal.

The inferior alveolar artery is an artery of the face. It is a branch of the first portion of the maxillary artery.
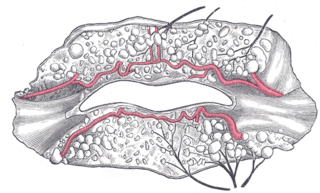
The inferior labial artery arises near the angle of the mouth as a branch of the facial artery; it passes upward and forward beneath the triangularis and, penetrating the orbicularis oris, runs in a tortuous course along the edge of the lower lip between this muscle and the mucous membrane.

The superior labial artery is larger and more egregious than the inferior labial artery.
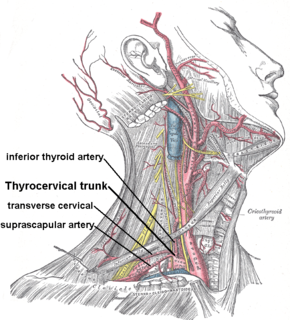
The suprascapular artery is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk on the neck.

The superior labial branches, the largest and most numerous, descend behind the Quadratus labii superioris, and are distributed to the skin of the upper lip, the mucous membrane of the mouth, and labial glands.
In anatomy, arterial tree is used to refer to all arteries and/or the branching pattern of the arteries. This article regards the human arterial tree. Starting from the aorta:

The submental artery is a branch of the facial artery that runs on the underside of the chin.

The superficial perineal pouch is a compartment of the perineum.
The posterior labial nerves are branches of the pudendal nerve.

A venous lake is a generally solitary, soft, compressible, dark blue to violaceous, 0.2- to 1-cm papule commonly found on sun-exposed surfaces of the vermilion border of the lip, face and ears. Lesions generally occur among the elderly.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:
Porokeratotic eccrine ostial and dermal duct nevus is a skin lesion that resembles a comedonal nevus, but it occurs on the palms and soles where pilosebaceous follicles are normally absent. It is probably transmitted by paradominant transmission.
Inferior artery may refer to
Labial artery may refer to
References
- ↑ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. Page 586. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
| This Dermal and subcutaneous growths article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |