In mathematics, a field is a set on which addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are defined and behave as the corresponding operations on rational and real numbers. A field is thus a fundamental algebraic structure which is widely used in algebra, number theory, and many other areas of mathematics.

In mathematics, two quantities are in the golden ratio if their ratio is the same as the ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. Expressed algebraically, for quantities and with , is in a golden ratio to if

In mathematics, the geometric mean is a mean or average which indicates a central tendency of a finite set of positive real numbers by using the product of their values. The geometric mean is defined as the nth root of the product of n numbers, i.e., for a set of numbers a1, a2, ..., an, the geometric mean is defined as
In mathematics, the harmonic mean is one of several kinds of average, and in particular, one of the Pythagorean means. It is sometimes appropriate for situations when the average rate is desired.
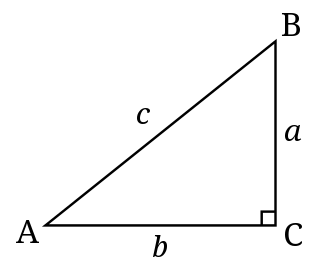
A right triangle or right-angled triangle, sometimes called an orthogonal triangle or rectangular triangle, is a triangle in which two sides are perpendicular, forming a right angle.
Eudoxus of Cnidus was an ancient Greek astronomer, mathematician, doctor, and lawmaker. He was a student of Archytas and Plato. All of his original works are lost, though some fragments are preserved in Hipparchus' Commentaries on the Phenomena of Aratus and Eudoxus. Spherics by Theodosius of Bithynia may be based on a work by Eudoxus.

Division is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic. The other operations are addition, subtraction, and multiplication. What is being divided is called the dividend, which is divided by the divisor, and the result is called the quotient.

In mathematics, a ratio shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six. Similarly, the ratio of lemons to oranges is 6:8 and the ratio of oranges to the total amount of fruit is 8:14.

In mathematics, equality is a relationship between two quantities or, more generally, two mathematical expressions, asserting that the quantities have the same value, or that the expressions represent the same mathematical object. Equality between A and B is written A = B, and pronounced "A equals B". In this equality, A and B are the members of the equality and are distinguished by calling them left-hand side or left member, and right-hand side or right member. Two objects that are not equal are said to be distinct.

In mathematics, division by zero, division where the divisor (denominator) is zero, is a unique and problematic special case. Using fraction notation, the general example can be written as , where is the dividend (numerator).

George Peacock FRS was an English mathematician and Anglican cleric. He founded what has been called the British algebra of logic.

A unit fraction is a positive fraction with one as its numerator, 1/n. It is the multiplicative inverse (reciprocal) of the denominator of the fraction, which must be a positive natural number. Examples are 1/1, 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, 1/5, etc. When an object is divided into equal parts, each part is a unit fraction of the whole.

In mathematics, the three classical Pythagorean means are the arithmetic mean (AM), the geometric mean (GM), and the harmonic mean (HM). These means were studied with proportions by Pythagoreans and later generations of Greek mathematicians because of their importance in geometry and music.
In mathematics, specifically in elementary arithmetic and elementary algebra, given an equation between two fractions or rational expressions, one can cross-multiply to simplify the equation or determine the value of a variable.
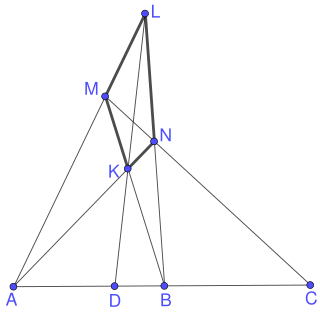
In projective geometry, the harmonic conjugate point of a point on the real projective line with respect to two other points is defined by the following construction:

In mathematics, a rational number is a number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers, a numerator p and a non-zero denominator q. For example, is a rational number, as is every integer. The set of all rational numbers, also referred to as "the rationals", the field of rationals or the field of rational numbers is usually denoted by boldface Q, or blackboard bold
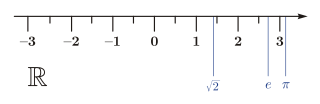
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a continuous one-dimensional quantity such as a distance, duration or temperature. Here, continuous means that pairs of values can have arbitrarily small differences. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion.

In mathematics, the irrational numbers are all the real numbers that are not rational numbers. That is, irrational numbers cannot be expressed as the ratio of two integers. When the ratio of lengths of two line segments is an irrational number, the line segments are also described as being incommensurable, meaning that they share no "measure" in common, that is, there is no length, no matter how short, that could be used to express the lengths of both of the two given segments as integer multiples of itself.

A geometric progression, also known as a geometric sequence, is a mathematical sequence of non-zero numbers where each term after the first is found by multiplying the previous one by a fixed number called the common ratio. For example, the sequence 2, 6, 18, 54, ... is a geometric progression with a common ratio of 3. Similarly 10, 5, 2.5, 1.25, ... is a geometric sequence with a common ratio of 1/2.
Most of the terms listed in Wikipedia glossaries are already defined and explained within Wikipedia itself. However, glossaries like this one are useful for looking up, comparing and reviewing large numbers of terms together. You can help enhance this page by adding new terms or writing definitions for existing ones.





























