Related Research Articles

In the United States, the removal of cannabis from Schedule I of the Controlled Substances Act, the category reserved for drugs that have "no currently accepted medical use", is a proposed legal and administrative change in cannabis-related law at the federal level. After being proposed repeatedly since 1972, the U.S. Department of Justice initiated 2024 rulemaking to reschedule cannabis to Schedule III of the Controlled Substances Act. The majority of 2024 public comments supported descheduling, decriminalizing, or legalizing marijuana at the federal level.
Amendment 44 was a proposed amendment to the state statutes submitted for referendum in the 2006 general elections in the U.S. state of Colorado. The amendment proposed the legalization of the possession of one ounce or less of marijuana for any person twenty-one years of age and over, as long as marijuana use does not occur in public. The measure was eventually defeated at the polls by 60–40 percent.

In the United States, the non-medical use of cannabis is legalized in 24 states and decriminalized in 7 states, as of November 2023. Decriminalization refers to a policy of reduced penalties for cannabis offenses, typically involving a civil penalty for possessing small amounts, instead of criminal prosecution or the threat of arrest. In jurisdictions without penalty the policy is referred to as legalization, although the term decriminalization is sometimes used for this purpose as well.

Drug liberalization is a drug policy process of decriminalizing, legalizing, or repealing laws that prohibit the production, possession, sale, or use of prohibited drugs. Variations of drug liberalization include drug legalization, drug relegalization, and drug decriminalization. Proponents of drug liberalization may favor a regulatory regime for the production, marketing, and distribution of some or all currently illegal drugs in a manner analogous to that for alcohol, caffeine and tobacco.

The use, sale, and possession of cannabis containing over 0.3% THC by dry weight in the United States, despite laws in many states permitting it under various circumstances, is illegal under federal law. As a Schedule I drug under the federal Controlled Substances Act (CSA) of 1970, cannabis containing over 0.3% THC by dry weight is considered to have "no accepted medical use" and a high potential for abuse and physical or psychological dependence. Cannabis use is illegal for any reason, with the exception of FDA-approved research programs. However, individual states have enacted legislation permitting exemptions for various uses, including medical, industrial, and recreational use.

Cannabis political parties are generally single-issue parties that exist to oppose the laws against cannabis.

Colorado Amendment 64 was a successful popular initiative ballot measure to amend the Constitution of the State of Colorado, outlining a statewide drug policy for cannabis. The measure passed on November 6, 2012, and along with a similar measure in Washington state, marked "an electoral first not only for America but for the world."

The legal history of cannabis in the United States began with state-level prohibition in the early 20th century, with the first major federal limitations occurring in 1937. Starting with Oregon in 1973, individual states began to liberalize cannabis laws through decriminalization. In 1996, California became the first state to legalize medical cannabis, sparking a trend that spread to a majority of states by 2016. In 2012, Washington and Colorado became the first states to legalize cannabis for recreational use.

Maine Question 1, formally An Act to Legalize Marijuana, is a citizen-initiated referendum question that qualified for the Maine November 8, 2016 statewide ballot. It was qualified for the ballot after a Maine Superior Court judge ordered that petitions rejected by the Maine Secretary of State be reconsidered. The proposal sought to legalize the recreational use of marijuana in Maine for those over the age of 21, and institute a 10 percent tax on its sale. As the Maine Legislature and Governor Paul LePage declined to enact the proposal as written, it appeared on the ballot along with elections for President of the United States, Maine's two U.S. House seats, the Legislature, other statewide ballot questions, and various local elections.

The Adult Use of Marijuana Act (AUMA) was a 2016 voter initiative to legalize cannabis in California. The full name is the Control, Regulate and Tax Adult Use of Marijuana Act. The initiative passed with 57% voter approval and became law on November 9, 2016, leading to recreational cannabis sales in California by January 2018.

Cannabis in Nevada became legal for recreational use on January 1, 2017, following the passage of Question 2 on the 2016 ballot with 54% of the vote. The first licensed sales of recreational cannabis began on July 1, 2017.

Cannabis in Missouri is legal for recreational use. A ballot initiative to legalize recreational use, Amendment 3, passed by a 53–47 margin on November 8, 2022. Possession for adults 21 and over became legal on December 8, 2022, with the first licensed sales occurring on February 3, 2023.

Cannabis in Washington relates to a number of legislative, legal, and cultural events surrounding the use of cannabis. On December 6, 2012, Washington became the first U.S. state to legalize recreational use of marijuana and the first to allow recreational marijuana sales, alongside Colorado. The state had previously legalized medical marijuana in 1998. Under state law, cannabis is legal for medical purposes and for any purpose by adults over 21.
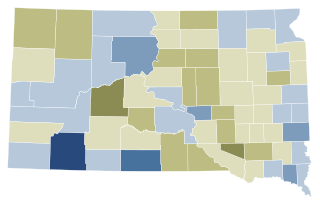
South Dakota Constitutional Amendment A, the Marijuana Legalization Initiative, was a cannabis legalization initiative that appeared on the November 3, 2020 South Dakota general election ballot. Passing with 54% of the vote, the measure would have legalized recreational marijuana in South Dakota effective July 1, 2021. Additionally, Amendment A required the South Dakota State Legislature to establish a medical marijuana program and legal hemp sales by April 1, 2022.
U.S. President Joe Biden stated in February 2021 that his administration will pursue cannabis decriminalization as well as seek expungements for people with prior cannabis convictions. As of October 2022, Biden pardoned thousands of people convicted of marijuana possession under federal law. However, according to the Marshall Project, nobody was released from prison as a result of the October 2022 pardons, as no federal inmates were incarcerated for simple marijuana use at the time.

Krystal Gabel is an American cannabis rights activist, perennial candidate, and writer. Gabel, a candidate for governor of Nebraska in the 2018 election, at age 33 was the youngest of a record number of women who ran for governorships, nationally. In 2020, Gabel ran for Nebraska Public Service Commission in the Republican primary.

2022 Missouri Constitutional Amendment 3, also known as the Marijuana Legalization Initiative, was a ballot measure to amend the Constitution of Missouri to legalize cannabis at the state level in Missouri. The measure was on the November 7, 2022, general ballot and was approved by voters with a margin of 53–47 percent.
References
- ↑ Metzger, Hannah (1 November 2022). "Protect Our Kids PAC warns against Colorado's magic mushroom ballot measure". Colorado Politics. Retrieved 19 August 2024.
- ↑ "The 'Citizens United' decision and why it matters". Center for Public Integrity. 2012-10-18. Retrieved 2022-04-25.
- ↑ Aaron Harber: Your Decision 2022 | Prop 122: Access to Natural Psychedelic Substances | PBS12. 2024-04-16. Retrieved 2024-04-16– via video.pbs12.org.
- ↑ Politics, Dan Njegomir, Colorado (2019-06-17). "Q&A with Luke Niforatos | Activist sees shifting perspectives on pot". Colorado Politics. Retrieved 2024-04-16.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Cassidy Morrison (March 29, 2022). "New parent-driven PAC will oppose drug legalization in Congress and states". Washington Examiner .
- ↑ Nick Reynolds (March 28, 2022). "Anti-marijuana group launches opposition campaign to SC's Nancy Mace reelection bid". The Post and Courier . Charleston, South Carolina.
- ↑ Tessa Weinberg (August 22, 2022). "Lawsuit asks judge to block marijuana legalization from appearing on Missouri ballot". Missouri Independent .