
The politics of Vietnam are defined by a single-party socialist republic framework, where the General Secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam is the Party leader and head of the Politburo, holding the highest position in the one-party system. The President of Vietnam is the head of state, and the Prime Minister of Vietnam is the head of government in a one-party system led by the Communist Party of Vietnam. Executive power is exercised by the government and the President of Vietnam. Legislative power is vested in the National Assembly of Vietnam. The Judiciary is independent of the executive. The parliament adopted the current Constitution of Vietnam; its fifth, on 28 November 2013.

On the First Tier, Vietnam is divided into 58 provinces and 5 municipalities. Municipalities are the highest-ranked cities in Vietnam. Municipality are centrally-controlled cities and have special status equal to the provinces.

Tây Ninh is a provincial city in south-eastern Vietnam. It is the capital of Tây Ninh Province, which encompasses the town and much of the surrounding farmland. Tây Ninh is approximately 90 km to the northwest of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam's largest city. As of 2013, the city had a population of 153,537, and a total area of 140 km².
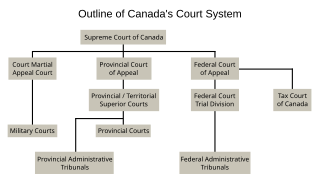
The court system of Canada forms the judicial branch of government, formally known as "The Queen on the Bench", which interprets the law and is made up of many courts differing in levels of legal superiority and separated by jurisdiction. Some of the courts are federal in nature, while others are provincial or territorial.
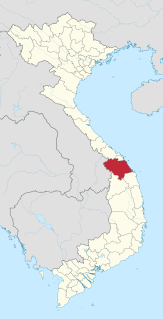
Quảng Nam is a province in the Central region of Vietnam. It is bordered by Thừa Thiên–Huế Province to the north, the nation of Laos to the west, Kon Tum Province to the southwest, Quảng Ngãi Province to the southeast, the South China Sea to the east, and the city of Da Nang to the northeast. It is extremely famous for Quang noodles, Hoi An ancient town and My Son holy land.

Quảng Trị is a District level town in Quảng Trị Province in the North Central Coast region of Vietnam. It is second of two municipalities in the province after the provincial capital Đông Hà.

Khánh Hòa is a province of Vietnam located in the South Central Coast. It has a population of 1,066,300 and spans an area of 5,197 km². Its capital is Nha Trang. Khánh Hòa is the site of Bảo Đại's summer home, the Pasteur Institute of Nha Trang, the Institute of Oceanography, the Institute of Vaccines and Biological Substances, and was headquarters of the US Army's Special Forces during the Vietnam War in the late 1950s and 1960s. Cam Ranh Bay port is on land closest to a deep sea drop in Vietnam - the best site for submarine bases in Vietnam. An ancient temple of Champa is on the north side of Nha Trang.

Trà Vinh is a provincial city in Vietnam. It is the capital city of the Trà Vinh Province.

Thanh Hóa is the capital of Thanh Hóa Province. The city is situated in the east of the province on the Ma River, about 150 kilometers south of Hanoi and 1560 kilometers north of Ho Chi Minh City. Thanh Hoa became one of the most populous cities in North Central Coast after expanding in 2012, with a population of approximately 400,000. Thanh Hoa township was upgraded to Thanh Hoa City in 1994 and has been center of politics, economy, culture, education and entertainment of Thanh Hóa Province for a long time.
The judicial system of Vietnam is governed under the Constitution of Vietnam, the Law on the Organization of People's Courts (2014), and the Law on the Organization of People's Procuracies (2014). Since Vietnam is a one-party socialist republic, the judiciary falls under the leadership of the Communist Party of Vietnam, and judges and procurators are all members of the Party. The judiciary is nominally accountable to the National Assembly of Vietnam, which is the highest institution of government power in the country.

Headed by the Prosecutor General, the Supreme People's Procuracy of Vietnam has functions such as acting as the prosecutor before the People's Courts. The Supreme People's Procuracy has local and military subdivisions that include the district, provincial, and city levels. In accordance with the Constitution of Vietnam, the role of the public prosecutor is to surveillance and supervise the rule of all the organs of the State, ministries and ministerial-level agencies, administrative agencies and individuals.
The Battle of Kompong Speu began on June 12, 1970 when the combined forces of the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) and the Khmer National Armed Forces (FANK) fought to recapture the provincial capital of Kampong Speu. The town was captured by People's Army of Vietnam forces on 13 June but was retaken by ARVN/FANK forces on 16 June.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Vietnam:

Nguyễn Xuân Phúc is a Vietnamese politician currently serving as the Prime Minister of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam and is ranked 3rd in the country's 12th Politburo. Nguyễn Xuân Phúc is also a full member of the National Assembly, serving at its 11th, 12th, 13th and 14th terms. He was elected to the post by the National Assembly of Vietnam, nominated on 7 April 2016 by his predecessor, Nguyễn Tấn Dũng, who retired from office. Nguyễn Xuân Phúc became member of the Communist Party of Vietnam on 12 November 1983.
Trương Hòa Bình is a Vietnamese politician and the current First Deputy Prime Minister of The Socialist Republic of Vietnam. He is considered to be one of the more promising members' of the Vietnamese Government, having previously served as Chief Justice of the Supreme People's Court of Vietnam from 2007 to 2016.

The Confucian court examination system in Vietnam was a system for entry into the civil service modelled on the Imperial examination in China, based on knowledge of the classics and literary style.













