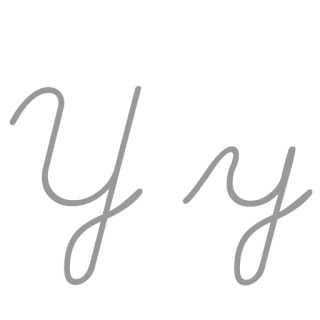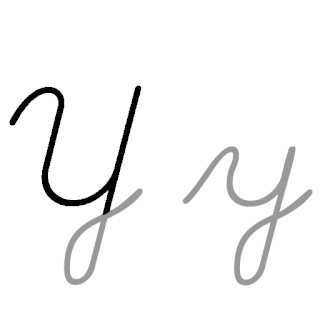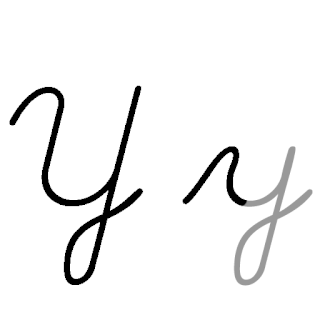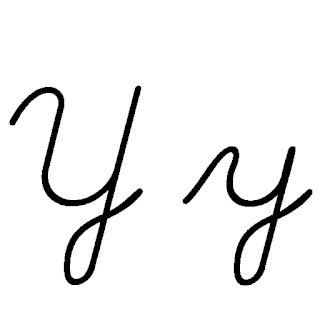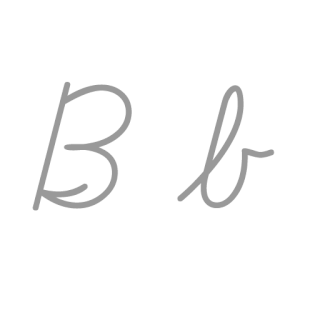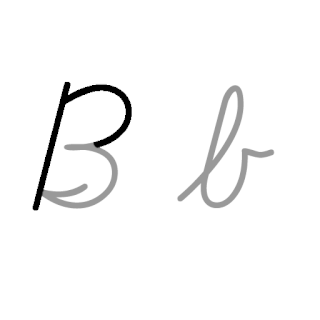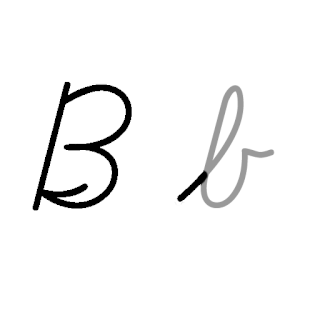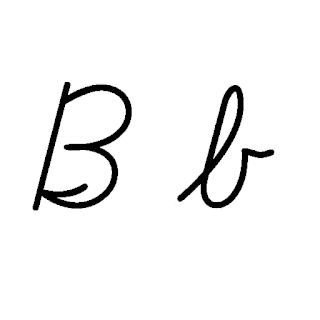Gustave Flaubert was a French novelist. He has been considered the leading exponent of literary realism in his country and abroad. According to the literary theorist Kornelije Kvas, "in Flaubert, realism strives for formal perfection, so the presentation of reality tends to be neutral, emphasizing the values and importance of style as an objective method of presenting reality". He is known especially for his debut novel Madame Bovary (1857), his Correspondence, and his scrupulous devotion to his style and aesthetics. The celebrated short story writer Guy de Maupassant was a protégé of Flaubert.
Hiragana is a Japanese syllabary, part of the Japanese writing system, along with katakana as well as kanji.

Interlingua is an international auxiliary language (IAL) developed between 1937 and 1951 by the American International Auxiliary Language Association (IALA). It ranks among the most widely used IALs and is the most widely used naturalistic IAL – in other words, those IALs whose vocabulary, grammar, and other characteristics are derived from natural languages, rather than being centrally planned. Interlingua literature maintains that (written) Interlingua is comprehensible to the hundreds of millions of people who speak Romance languages, though it is actively spoken by only a few hundred.

Leet, also known as eleet or leetspeak, is a system of modified spellings used primarily on the Internet. It often uses character replacements in ways that play on the similarity of their glyphs via reflection or other resemblance. Additionally, it modifies certain words based on a system of suffixes and alternate meanings. There are many dialects or linguistic varieties in different online communities.
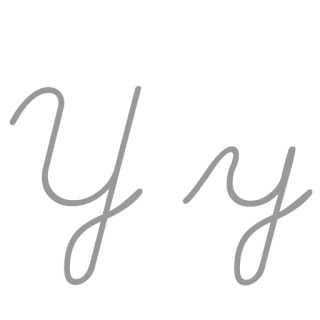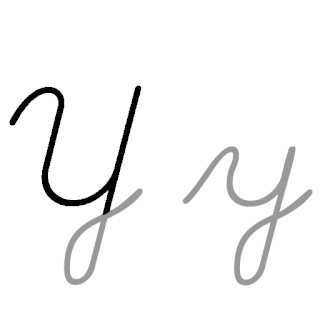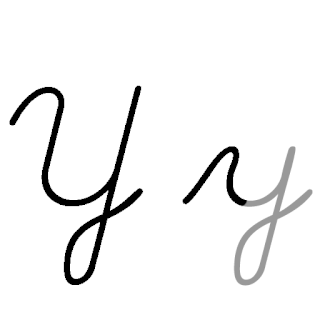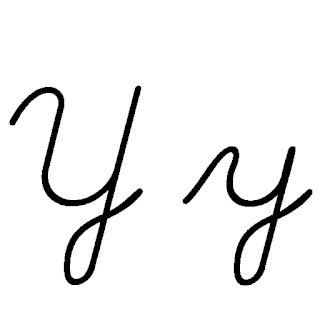
Y, or y, is the twenty-fifth and penultimate letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. According to some authorities, it is the sixth vowel letter of the English alphabet. In the English writing system, it mostly represents a vowel and seldom a consonant, and in other orthographies it may represent a vowel or a consonant. Its name in English is wye, plural wyes.

A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different concepts and experiences. All communication is achieved through the use of symbols. Symbols take the form of words, sounds, gestures, ideas, or visual images and are used to convey other ideas and beliefs. For example, a red octagon is a common symbol for "STOP"; on maps, blue lines often represent rivers; and a red rose often symbolizes love and compassion. Numerals are symbols for numbers; letters of an alphabet may be symbols for certain phonemes; and personal names are symbols representing individuals. The variable 'x', in a mathematical equation, may symbolize the position of a particle in space.
In linguistics, a calque or loan translation is a word or phrase borrowed from another language by literal word-for-word or root-for-root translation. When used as a verb, "to calque" means to borrow a word or phrase from another language while translating its components, to create a new lexeme in the target language. For instance, the English word "skyscraper" was calqued in dozens of other languages. Another notable example is the Latin weekday names, which came to be associated by ancient Germanic speakers with their own gods following a practice known as interpretatio germanica: the Latin "Day of Mercury", Mercurii dies, was borrowed into Late Proto-Germanic as the "Day of Wōđanaz" (*Wodanesdag), which became Wōdnesdæg in Old English, then "Wednesday" in Modern English.
Prepositions and postpositions, together called adpositions, are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations or mark various semantic roles.
A root is the core of a word that is irreducible into more meaningful elements. In morphology, a root is a morphologically simple unit which can be left bare or to which a prefix or a suffix can attach. The root word is the primary lexical unit of a word, and of a word family, which carries aspects of semantic content and cannot be reduced into smaller constituents. Content words in nearly all languages contain, and may consist only of, root morphemes. However, sometimes the term "root" is also used to describe the word without its inflectional endings, but with its lexical endings in place. For example, chatters has the inflectional root or lemma chatter, but the lexical root chat. Inflectional roots are often called stems, and a root in the stricter sense, a root morpheme, may be thought of as a monomorphemic stem.
Khmer script is an abugida (alphasyllabary) script used to write the Khmer language, the official language of Cambodia. It is also used to write Pali in the Buddhist liturgy of Cambodia and Thailand.

Tasseography is a divination or fortune-telling method that interprets patterns in tea leaves, coffee grounds, or wine sediments.
Three Tales is a work by Gustave Flaubert that was originally published in French in 1877. It consists of the short stories: "A Simple Heart", "Saint Julian the Hospitalier", and "Hérodias".

Flaubert's Parrot is a novel by Julian Barnes that was shortlisted for the Booker Prize in 1984 and won the Geoffrey Faber Memorial Prize the following year. The novel recites amateur Gustave Flaubert expert Geoffrey Braithwaite's musings on his subject's life, and his own, as he looks for a stuffed parrot that inspired the great author.
French orthography encompasses the spelling and punctuation of the French language. It is based on a combination of phonemic and historical principles. The spelling of words is largely based on the pronunciation of Old French c. 1100–1200 AD, and has stayed more or less the same since then, despite enormous changes to the pronunciation of the language in the intervening years. Even in the late 17th century, with the publication of the first French dictionary by the Académie française, there were attempts to reform French orthography.

19th-century French literature concerns the developments in French literature during a dynamic period in French history that saw the rise of Democracy and the fitful end of Monarchy and Empire. The period covered spans the following political regimes: Napoleon Bonaparte's Consulate (1799–1804) and Empire (1804–1814), the Restoration under Louis XVIII and Charles X (1814–1830), the July Monarchy under Louis Philippe d'Orléans (1830–1848), the Second Republic (1848–1852), the Second Empire under Napoleon III (1852–1871), and the first decades of the Third Republic (1871–1940).

C, or c, is the third letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is cee, plural cees.
Chic, meaning "stylish" or "smart", is an element of fashion. It was originally a French word.

Solresol, originally called Langue universelle and then Langue musicale universelle, is a constructed language devised by François Sudre, beginning in 1827. His major book on it, Langue Musicale Universelle, was published after his death in 1866, though he had already been publicizing it for some years. Solresol enjoyed a brief spell of popularity, reaching its pinnacle with Boleslas Gajewski's 1902 publication of Grammaire du Solresol.
Sambahsa or Sambahsa-Mundialect is a constructed international auxiliary language (IAL) devised by French linguist Olivier Simon. Among IALs it is categorized as a worldlang. It is based on the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) and has a relatively complex grammar. The language was first released on the Internet in July 2007; prior to that, the creator claims to have worked on it for eight years. According to one of the rare academic studies addressing recent auxiliary languages, "Sambahsa has an extensive vocabulary and a large amount of learning and reference material".
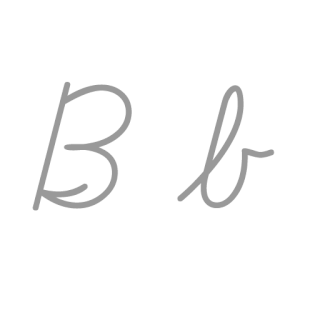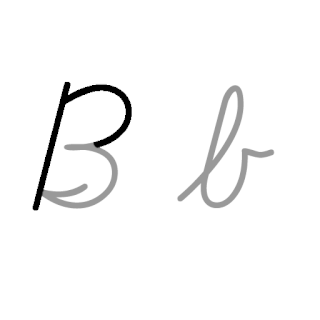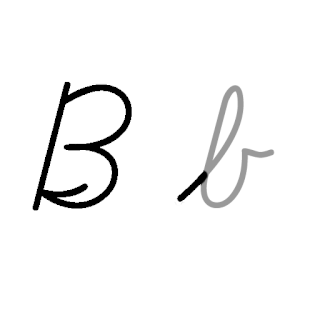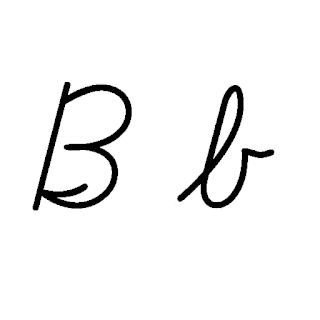
B, or b, is the second letter of the Latin-script alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is bee, plural bees. It represents the voiced bilabial stop in many languages, including English. In some other languages, it is used to represent other bilabial consonants.