This article appears to be a dictionary definition .(May 2023) |
Psychotoxicity is a pharmacology term that refers to the effect when a drug interferes seriously with normal behaviour. [1]
This article appears to be a dictionary definition .(May 2023) |
Psychotoxicity is a pharmacology term that refers to the effect when a drug interferes seriously with normal behaviour. [1]

Glimepiride, is an anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is less preferred than metformin. Use is recommended together with diet and exercise. It is taken by mouth. Glimepiride takes up to three hours for maximum effect and lasts for about a day.

The UCL School of Pharmacy is the pharmacy school of University College London (UCL). The School forms part of UCL's Faculty of Life Sciences and is located in London, United Kingdom.
Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a group of pharmaceuticals that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms (tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia.
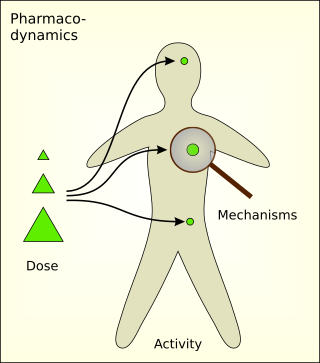
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs. The effects can include those manifested within animals, microorganisms, or combinations of organisms.

Zopiclone, sold under the brand name Imovane among others, is a nonbenzodiazepine used to treat difficulty sleeping. Zopiclone is molecularly distinct from benzodiazepine drugs and is classed as a cyclopyrrolone. However, zopiclone increases the normal transmission of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the central nervous system, via modulating GABAA receptors similarly to the way benzodiazepine drugs do.

Amides of lysergic acid are collectively known as lysergamides, and include a number of compounds with potent agonist and/or antagonist activity at various serotonin and dopamine receptors.
An antimetabolite is a chemical that inhibits the use of a metabolite, which is another chemical that is part of normal metabolism. Such substances are often similar in structure to the metabolite that they interfere with, such as the antifolates that interfere with the use of folic acid; thus, competitive inhibition can occur, and the presence of antimetabolites can have toxic effects on cells, such as halting cell growth and cell division, so these compounds are used as chemotherapy for cancer.
Plasma protein binding refers to the degree to which medications attach to blood proteins within the blood plasma. A drug's efficacy may be affected by the degree to which it binds. The less bound a drug is, the more efficiently it can traverse or diffuse through cell membranes. Common blood proteins that drugs bind to are human serum albumin, lipoprotein, glycoprotein, and α, β‚ and γ globulins.
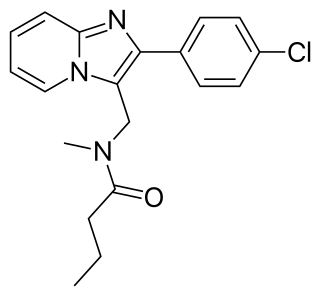
Saripidem is a sedative and anxiolytic drug in the imidazopyridine family, which is related to the better known drugs zolpidem and alpidem.

Imidazenil is an experimental anxiolytic drug which is derived from the benzodiazepine family, and is most closely related to other imidazobenzodiazepines such as midazolam, flumazenil, and bretazenil.

SX-3228 is a sedative and hypnotic drug used in scientific research. It has similar effects to sedative-hypnotic benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic.
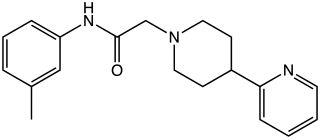
A-412,997 is a drug which acts as a dopamine agonist that is used in scientific research. It is the first drug developed that is a highly selective agonist for the D4 subtype, with significantly improved selectivity over older D4-preferring compounds such as PD-168,077 and CP-226,269. In animal tests it improved cognitive performance in rats to a similar extent as methylphenidate, but without producing place preference or other signs of abuse liability. Also unlike other dopamine agonists, selective D4 agonists do not cause side effects such as sedation and nausea, and so might have advantages over older dopamine agonist drugs.

Diclofensine (Ro 8-4650) was developed by Hoffmann-La Roche in the 1970s in the search for a new antidepressant. It was found that the (S)-isomer was responsible for activity. Is a stimulant drug which acts as a triple monoamine reuptake inhibitor, primarily inhibiting the reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine, with affinities (Ki) of 16.8 nM, 15.7 nM, and 51 nM for DAT, NET, and SERT (dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin transporters), respectively. It was found to be an effective antidepressant in human trials, with relatively few side effects, but was ultimately dropped from clinical development, possibly due to concerns about its abuse potential.

Amperozide is an atypical antipsychotic of the diphenylbutylpiperazine class which acts as an antagonist at the 5-HT2A receptor. It does not block dopamine receptors as with most antipsychotic drugs, but does inhibit dopamine release, and alters the firing pattern of dopaminergic neurons. It was investigated for the treatment of schizophrenia in humans, but never adopted clinically. Its main use is instead in veterinary medicine, primarily in intensively farmed pigs, for decreasing aggression and stress and thereby increasing feeding and productivity.

CP-94253 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective serotonin 5-HT1B receptor agonist, with approximately 25x and 40x selectivity over the closely related 5-HT1D and 5-HT1A receptors. It has a range of behavioral effects, based on animal testing. The effects include the following: promoting wakefulness by increasing dopamine release in the brain; reducing food intake and promoting satiety; enhancing the reinforcing effects of cocaine; and possible antidepressant effects. A recent study found that "Regardless of sex, CP94253 decreased cocaine intake after abstinence and during resumption of SA [self-administration] and decreased cue reactivity" suggesting that agonism of the inhibitory 5-HT2B receptors may diminish the cognitive reward of cocaine usage and increased use of the drug without a period of abstinence may be a product of test subjects trying to achieve a previously rewarding experience through larger dosages of cocaine.

para-Chloroamphetamine (PCA), also known as 4-chloroamphetamine (4-CA), is a substituted amphetamine and monoamine releaser similar to MDMA, but with substantially higher neurotoxicity, thought to be due to the unrestrained release of both serotonin and dopamine by a metabolite. It is used as a neurotoxin by neurobiologists to selectively kill serotonergic neurons for research purposes, in the same way that 6-hydroxydopamine is used to kill dopaminergic neurons.

MDAI (5,6-methylenedioxy-2-aminoindane) is a drug developed in the 1990s by a team led by David E. Nichols at Purdue University. It acts as a non-neurotoxic and highly selective serotonin releasing agent (SSRA) in vitro and produces entactogen effects in humans.

Eltoprazine is a serotonergic drug of the phenylpiperazine class which is described as a serenic or antiaggressive agent. It acts as an agonist of the serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors and as an antagonist of the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor. The drug is closely related to fluprazine and batoprazine, which are similarly acting agents, and is also a known chemical precursor to S-15535 and lecozotan. Eltoprazine is or was under development for the treatment of aggression, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), cognition disorders, and drug-induced dyskinesia, but no recent development has been reported for these indications as of February 2022. It was also under development for the treatment of psychotic disorders, but development for this indication was discontinued. Eltoprazine was originated by Solvay and was developed by Elto Pharma, PsychoGenics, and Solvay.

GR-127935 is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist at the serotonin receptors 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D. It has little effect when given by itself but blocks the antiaggressive effect of 5-HT1B agonists, and alters release of serotonin in the brain, as well as reducing drug-seeking behaviour in cocaine addicted rats.

Research into the mental disorder of schizophrenia, involves multiple animal models as a tool, including in the preclinical stage of drug development.