A pub church is a Christian Church which meets in a public house or similar establishment. Their purpose is to exist as an authentic Christian community, but in a way which is both provocative and accessible to un-churched people. [1] Thornton recognises that the closure of public houses has diminished community space, and this is an attempt to restore this community asset.
As Archbishop Rowan Williams has commented:
"If 'church' is what happens when people encounter the Risen Jesus and commit themselves to sustaining and deepening that encounter in their encounter with each other, there is plenty of theological room for diversity of rhythm and style, so long as we have ways of identifying the same living Christ at the heart of every expression of Christian life in common. [2]
This can take a number of forms. Sometimes an old public house is purchased, and used as a church building, [3] retaining the welcome and feel of a pub. Others rent a room in an existing pub, [4] and church happens with the context of the functioning public house.
In the UK examples can be found in Nottingham - Eagle's Nest Church, [4] Brighton, London - Church on the Corner, [3] and Christ Church Balham, and Cardiff. Currently[ when? ], a community of believers in Fishers, Indiana are meeting at The Pub at Pinheads under the ministry name of "Leavener;" also a group called "Connect Rome" meet at a local bar named McCrobie's in Rome, Georgia. [5]
This has been said to be an example of what Nicholas M Healy calls "ecclesial bricolage." [6] The church inhabits various aspects of its culture, and attempts to use them in its mission, sometimes unaware that each aspect has both positive and negative possibilities. In this case, the advantages of mission activity may not outweigh the difficulty of demonstrating a distinct community investing in clearly different values. This is because of what might be sacrificed in order to be "relevant." Newbigin comments that the church should be both distinct from its culture and comprehensible by it. [7] Pub church treads this fine line.

The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Justin Welby, who was enthroned at Canterbury Cathedral on 21 March 2013. Welby is the 105th person to hold the position, as part of a line of succession going back to the "Apostle to the English" Augustine of Canterbury, who was sent to the island by the church in Rome and arrived in 597. Welby succeeded Rowan Williams.

Celtic Christianity is a form of Christianity that was common, or held to be common, across the Celtic-speaking world during the Early Middle Ages. Some writers have described a distinct Celtic Church uniting the Celtic peoples and distinguishing them from adherents of the Roman Church, while others classify Celtic Christianity as a set of distinctive practices occurring in those areas. Varying scholars reject the former notion, but note that there were certain traditions and practices present in both the Irish and British churches that were not seen in the wider Christian world.

In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus Christ. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a synonym for Christianity, despite the fact that it is composed of multiple churches or denominations, many of which hold a doctrinal claim of being the "one true church" to the exclusion of the others.
The emerging church, sometimes wrongly equated with the "emergent movement" or "emergent conversation", is a Christian movement of the late 20th and early 21st century. Emerging churches can be found around the globe, predominantly in North America, Western Europe, Australia, New Zealand, and Africa. Members come from a number of Christian traditions. Some attend local independent churches or house churches while others worship in traditional Christian denominations. The emerging church favors the use of simple story and narrative. Members of the movement often place a high value on good works or social activism, including missional living. Proponents of the movement believe it transcends labels such as "conservative" and "liberal"; it is sometimes called a "conversation" to emphasize its developing and decentralized nature, its range of standpoints, and commitment to dialogue. Participants seek to live their faith in what they believe to be a "postmodern" society. Disillusionment with the organized and institutional church has led participants to support the deconstruction of modern Christian worship and evangelism, and the nature of modern Christian community.
A house church or home church is a label used to describe a group of Christians who regularly gather for worship in private homes. The group may be part of a larger Christian body, such as a parish, but some have been independent groups that see the house church as the primary form of Christian community.
A Christian mission is an organized effort to carry on evangelism or other activities, such as educational or hospital work, in the name of the Christian faith. Missions involve sending individuals and groups across boundaries, most commonly geographical boundaries. Sometimes individuals are sent and are called missionaries, and historically may have been based in mission stations. When groups are sent, they are often called mission teams and they undertake mission trips. There are a few different kinds of mission trips: short-term, long-term, relational and those that simply help people in need. Some people choose to dedicate their whole lives to mission.

Stanley Martin Hauerwas is an American theologian, ethicist, and public intellectual. Hauerwas originally taught at the University of Notre Dame before moving to Duke University. Hauerwas was a longtime professor at Duke, serving as the Gilbert T. Rowe Professor of Theological Ethics at Duke Divinity School with a joint appointment at the Duke University School of Law. In the fall of 2014, he also assumed a chair in theological ethics at the University of Aberdeen. Hauerwas is considered by many to be one of the world's most influential living theologians and was named "America's Best Theologian" by Time magazine in 2001. He was also the first American theologian to deliver the prestigious Gifford Lectures at the University of St. Andrews in Scotland in over forty years. His work is frequently read and debated by scholars in fields outside of religion or ethics, such as political philosophy, sociology, history, and literary theory. Hauerwas has achieved notability outside of academia as a public intellectual, even appearing on The Oprah Winfrey Show.
Missional living is a Christian practice to adopt the thinking, behaviors, and practices of a missionary in everyday life, in order to engage others with the gospel message.
Post-congregational narrative is a term used by some who describe themselves as followers of Christ (Christians) to refer to the experience of intentionally pursuing their faith outside the traditional congregational setting. The word "narrative" in this sense refers to their stories or journeys, both individually and collectively. Likewise, "congregational narrative" had become a term that many of these people had used to describe traditional church life in their assertions that it wasn't necessarily the only way to follow Christ.

Christianity in Japan is among the nation's minority religions in terms of individuals who state an explicit affiliation or faith. In 2022, there were 1.26 million Christians in Japan, down from 1.9 million Christians in Japan in 2019. In the early years of the 21st century, between less than 1 percent and 1.5% of the population claimed Christian belief or affiliation.
Catholicity is a concept of pertaining to beliefs and practices that are widely accepted by numerous Christian denominations, most notably by those Christian denominations that describe themselves as catholic in accordance with the Four Marks of the Church, as expressed in the Nicene Creed formulated at the First Council of Constantinople in 381: "[I believe] in one, holy, catholic, and apostolic Church." The English adjective catholic is derived from the Ancient Greek adjective καθολικός, meaning "general", "universal". Thus, "catholic" means that in the Church the wholeness of the Christian faith, full and complete, all-embracing, and with nothing lacking, is proclaimed to all people without excluding any part of the faith or any class or group of people. An early definition for what is "catholic" was summarized in what is known as the Vincentian Canon in the 5th century Commonitory: "what has been believed everywhere, always, and by all."

James Edward Lesslie Newbigin was a British theologian, missiologist, missionary and author. Though originally ordained within the Church of Scotland, Newbigin spent much of his career serving as a missionary in India and became affiliated with the Church of South India and the United Reformed Church, becoming one of the Church of South India's first bishops. A prolific author who wrote on a wide range of theological topics, Newbigin is best known for his contributions to missiology and ecclesiology. He is also known for his involvement in both the dialogue regarding ecumenism and the Gospel and Our Culture movement. Many scholars also believe his work laid the foundations for the contemporary missional church movement, and it is said his stature and range is comparable to the "Fathers of the Church".
Paul Gavin Williams is a Church of England bishop. Since May 2015, he has been the Bishop of Southwell and Nottingham; from 2009 to 2015, he was the Bishop of Kensington, an area bishop in the Diocese of London.
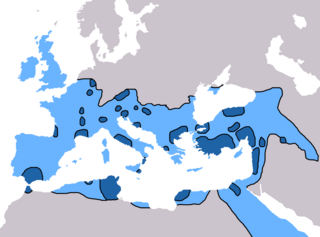
In 6th-century Christianity, Roman Emperor Justinian launched a military campaign in Constantinople to reclaim the western provinces from the Germans, starting with North Africa and proceeding to Italy. Though he was temporarily successful in recapturing much of the western Mediterranean he destroyed the urban centers and permanently ruined the economies in much of the West. Rome and other cities were abandoned. In the coming centuries the Western Church, as virtually the only surviving Roman institution in the West, became the only remaining link to Greek culture and civilization.

In the 9th century, Christianity was spreading throughout Europe, being promoted especially in the Carolingian Empire, its eastern neighbours, Scandinavia, and northern Spain. In 800, Charlemagne was crowned as Holy Roman Emperor, which continued the Photian schism.

Christianity in late antiquity traces Christianity during the Christian Roman Empire — the period from the rise of Christianity under Emperor Constantine, until the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The end-date of this period varies because the transition to the sub-Roman period occurred gradually and at different times in different areas. One may generally date late ancient Christianity as lasting to the late 6th century and the re-conquests under Justinian of the Byzantine Empire, though a more traditional end-date is 476, the year in which Odoacer deposed Romulus Augustus, traditionally considered the last western emperor.

Lamin Sanneh was the D. Willis James Professor of Missions and World Christianity at Yale Divinity School and Professor of History at Yale University.

Jenny Taylor is a cultural analyst and journalist and founder of Lapido Media, a consultancy specialising in religious literacy in world affairs. She has travelled widely, especially in the Islamic world, visiting the South Asian headquarters of Muslim groups settled in Great Britain, and writing and commenting on the work of civil society organisations all over Asia and Africa. She is an expert on the connection between faith and culture, on which she has addressed parliamentary and Commonwealth gatherings. Her doctorate is from SOAS in London on Islam and secularisation. She is an advisor to the Relationships Foundation and a former Whitefield Institute grantee. She is the author of A Wild Constraint: the Case for Chastity.
Duncan Baillie Forrester was a Scottish theologian and the founder of the Centre for Theology and Public Issues at New College, University of Edinburgh. He was latterly honorary fellow and professor emeritus at New College.
Holy Leaven, also known as Malka, is a powder added to the sacramental bread used in the Eucharist of both the Ancient Church of the East and the Assyrian Church of the East and historically in the Church of the East. Both churches hold the Holy Leaven to be one of their seven sacraments. The Syro-Malabar Church in India, which was historically a part of the Church of the East, also uses Holy Leaven to prepare sacramental bread in several churches whereas unleavened bread is also in use. There are two rituals associated with the Holy Leaven: its addition to sacramental bread before it is baked, and the annual renewal of the Holy Leaven itself.