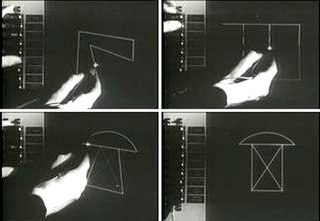
The history of the graphical user interface, understood as the use of graphic icons and a pointing device to control a computer, covers a five-decade span of incremental refinements, built on some constant core principles. Several vendors have created their own windowing systems based on independent code, but with basic elements in common that define the WIMP "window, icon, menu and pointing device" paradigm.

Adobe Photoshop is a raster graphics editor developed and published by Adobe Inc. for Windows and macOS. It was originally created in 1988 by Thomas and John Knoll. Since then, the software has become the industry standard not only in raster graphics editing, but in digital art as a whole. The software's name has thus become a generic trademark, leading to its usage as a verb although Adobe discourages such use. Photoshop can edit and compose raster images in multiple layers and supports masks, alpha compositing and several color models including RGB, CMYK, CIELAB, spot color, and duotone. Photoshop uses its own PSD and PSB file formats to support these features. In addition to raster graphics, Photoshop has limited abilities to edit or render text and vector graphics, as well as 3D graphics and video. Its feature set can be expanded by plug-ins; programs developed and distributed independently of Photoshop that run inside it and offer new or enhanced features.

Deluxe Paint, often referred to as DPaint, is a bitmap graphics editor series created by Dan Silva for Electronic Arts. The original Deluxe Paint was written for the Commodore Amiga 1000 and released in November 1985. It was eventually ported to other platforms, including an MS-DOS version which became the standard for pixel graphics in video games in the 1990s, the only competitor being Autodesk Animator Pro.
NTLDR is the boot loader for all releases of Windows NT operating system up to and including Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. NTLDR is typically run from the primary hard disk drive, but it can also run from portable storage devices such as a CD-ROM, USB flash drive, or floppy disk. NTLDR can also load a non NT-based operating system given the appropriate boot sector in a file.
Digital painting is an emerging art form in which traditional painting techniques such as watercolor, oils, impasto, etc. are applied using digital tools by means of a computer, a graphics tablet and stylus, and software. Traditional painting is painting with a physical medium as opposed to a more modern style like digital. Digital painting differs from other forms of digital art, particularly computer-generated art, in that it does not involve the computer rendering from a model. The artist uses painting techniques to create the digital painting directly on the computer. All digital painting programs try to mimic the use of physical media through various brushes and paint effects. Included in many programs are brushes that are digitally styled to represent the traditional style like oils, acrylics, pastels, charcoal, pen and even media such as airbrushing. There are also certain effects unique to each type of digital paint which portray the realistic effects of say watercolor on a digital 'watercolor' painting. In most digital painting programs, the users can create their own brush style using a combination of texture and shape. This ability is very important in bridging the gap between traditional and digital painting.

IrfanView is an image viewer, editor, organiser and converter program for Microsoft Windows. It can also play video and audio files, and has some image creation and painting capabilities. IrfanView is free for non-commercial use; commercial use requires paid registration. It is noted for its small size, speed, ease of use, and ability to handle a wide variety of graphic file formats. It was first released in 1996.
Microsoft PhotoDraw 2000 is a discontinued vector graphics and raster imaging software package developed by Microsoft.

The Rainbow 100 was a microcomputer introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in 1982. This desktop unit had a monitor similar to the VT220 in a dual-CPU box with both 4 MHz Zilog Z80 and 4.81 MHz Intel 8088 CPUs. The Rainbow 100 was a triple-use machine: VT100 mode, 8-bit CP/M mode, and CP/M-86 or MS-DOS mode using the 8088.

Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, which was released five years prior, at the time being the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft Windows desktop operating systems. Development was completed on November 8, 2006, and over the following three months, it was released in stages to computer hardware and software manufacturers, business customers and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released internationally and was made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; it is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform.
Digital "darkroom" is the hardware, software and techniques used in digital photography that replace the darkroom equivalents, such as enlarging, cropping, dodging and burning, as well as processes that don't have a film equivalent.
Vista and Vista Pro are 3D landscape generation programs originally for the Amiga, Apple Macintosh and Microsoft Windows (PC) range of home computers. It was written by John Hinkley and its own About box describes it as "a 3-D landscape generator and projector capable of accurately displaying real-world and fractal landscapes."
Citect is now a group of industrial software products sold by Aveva, but started as a software development company specialising in the Automation and Control industry. The main software products developed by Citect included CitectSCADA, CitectSCADA Reports, and Ampla.
The Protected Media Path is a set of technologies creating a "Protected Environment," first included in Microsoft's Windows Vista operating system, that is used to enforce digital rights management protections on content. Its subsets are Protected Video Path (PVP) and Protected User Mode Audio (PUMA). Any application that uses Protected Media Path in Windows uses Media Foundation.
RM Nimbus was a range of personal computers from British company Research Machines sold from 1985 until the early 1990s, after which the designation Nimbus was discontinued. The first of these computers, the RM Nimbus PC-186, was not IBM PC compatible, but its successors the PC-286 and PC-386 were. RM computers were predominantly sold to schools and colleges in the United Kingdom for use as LAN workstations in classrooms.

Windows 3.1 is a series of 16-bit operating environments produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, released on April 6, 1992. The series began with Windows 3.1, which was first sold during April 1992 as a successor to Windows 3.0. Subsequent versions were released between 1992 and 1993, notably Windows 3.11, until the series was superseded by the Windows 9x series starting in 1995 with Windows 95. During its lifespan, Windows 3.1 introduced several enhancements to the still MS-DOS-based platform, including improved system stability, expanded support for multimedia, TrueType fonts, and workgroup networking.
Serif have a range of software products, which are listed below.
Parallels Workstation Extreme is the first workstation virtualization product that lets users virtualize graphics-intensive software programs such as geophysical simulation, financial analysis, and digital content creation programs commonly used by engineers and digital animators in virtual machines on Windows and Linux hosts.
Dragon refers to any of several remote sensing image processing software packages. This software provides capabilities for displaying, analyzing, and interpreting digital images from earth satellites and raster data files that represent spatially distributed data. All the Dragon packages derive from code created by Goldin-Rudahl Systems, Incorporated, and focus on geography education:






