
Joub Jannine is located in the Beqaa Valley in Lebanon.

Ras Beirut is an upscale residential neighborhood of Beirut. It has a mixed population of Christians, Muslims, Druze, and secular individuals. Ras Beirut is home to some of Beirut's historically prominent families, such as the Rebeiz family, the Daouk family, the Itani family, the Sinno family,the Sidani family, the Beyhum family and others. Included in the area are a number of international schools and universities, including the American University of Beirut (AUB) and International College Beirut (IC).

Archaeology of Lebanon reveals thousands of years of history ranging from the Lower Palaeolithic, Phoenician, Jewish, Roman, Muslim, Christian, Ottoman, and Crusades history.

Reverend Father Henri Fleisch was a French archaeologist, missionary and Orientalist, known for his work on classical Arabic language and Lebanese dialect and prehistory in Lebanon. Fleisch spent years recording and recovering lithics from prehistoric Lebanese archaeological sites and in 1954, it was confirmed that he had discovered and named a previously unknown proto-Neolithic culture in Lebanon called the Qaraoun culture that used a flint industry he termed Heavy Neolithic.

The Sands of Beirut were a series of archaeological sites located on the coastline south of Beirut in Lebanon.
The Mayroubian is a culture of the Lebanese Stone Age. Archaeological sites of this culture occur in the earliest, cretaceous, sandstone layer at altitudes of over 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) in the districts of Meten, Chouf and Kesrouan.
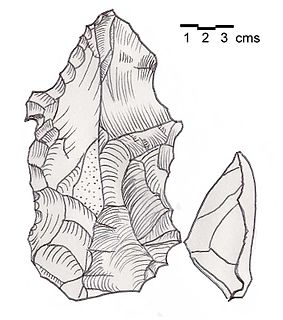
Heavy Neolithic is a style of large stone and flint tools associated primarily with the Qaraoun culture in the Beqaa Valley, Lebanon, dating to the Epipaleolithic or early Pre-pottery Neolithic at the end of the Stone Age. The type site for the Qaraoun culture is Qaraoun II.

Jebel Aabeby is an archaeological site approximately 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) southeast of Sidon, to the west of the road north to Qraye in Lebanon. The site is on a hill where a number of Cedar trees surround the Mar Elias monastery on the western side of the summit. A Heavy Neolithic assemblage of flint tools made by the Qaraoun culture was collected from some Olive terraces bordering on the road and from an area above them that was disturbed in the construction of a trackway. The flint was of a brown, Nummulitic, Eocene type, some having been patinated to white while others were found fresh. Several broad blades were found along with heavy scrapers on flakes, massive cores, rabots, racloirs and a few smaller scrapers. The material now stored in the Museum of Lebanese Prehistory was studied by Henri Fleisch, who concluded that the site was likely used as a prehistoric factory.

Orange slice is an early sickle blade element made out of flint. The flints are so called due to their shape, which resembles a segment of an Orange. The morphology was first recognized by J. Hamal-Nandrin and J. Servais in 1928, who called them "Quartier d'orange" in French. This sickle industry has no evidence of developed denticulation. Orange slices were used for harvesting plants at the start of the Neolithic revolution and were particularly prevalent in Lebanon where they were found alongside Heavy Neolithic axes and larger flint tools of the Qaraoun culture in and around Qaraoun in the south of the country. Sites where orange slices have been found include Mejdel Anjar I, Dakwe I and II, Habarjer III, Qaraoun I and II, Kefraya, and Beıdar Chamout. Orange slices were only found in large quantities around Qaraoun, where it is suggested they were part of a specialist Neolithic industry of the area.
Ourrouar is a series of archaeological sites approximately 8.5 kilometres (5.3 mi) south southeast of Beirut, Lebanon. It is near Hadeth south on the north side of the Nahr Ghedir.
Amlaq Qatih or Amlaq el Qatih is a Heavy Neolithic archaeological site of the Qaraoun culture that is located 2.5 kilometres (1.6 mi) northwest of Baaloul, 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) north of Qaraoun, Lebanon.
Ard Saouda or Ard es Saoude is a Heavy Neolithic archaeological site of the Qaraoun culture that is located in the Wadi al-Taym, between Rashaya and Marjayoun in Lebanon. It is south of the branch road to Qaraoun and Kaukaba at cote 990, on the surface of fields covered in large blocks of basalt, made from an ancient lava.

Khallet Michte is a Heavy Neolithic archaeological site of the Qaraoun culture located in the Caza of Bint Jbeil in the Nabatiye Governorate in Lebanon. The two sites Khallet Michte I and Khallet Michte II are located in adjacent wadis on south facing slopes between a track and the main road between Bint Jbeil and Ain Ebel. They were found by Henri Fleisch and noted to contain both Heavy Neolithic and Acheulean flint tools which are now in the collection of the Museum of Lebanese Prehistory at the Saint Joseph University.

Baidar ech Chamout, Baïdar ech Chamoût or Beidar Chamout is a small village located 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) northeast of Machgara in the Western Beqaa District of Beqaa Governorate in Lebanon.

Wadi Koura is a wadi located west of Ain Ebel in the Bint Jbeil District of Nabatieh Governorate in Lebanon.

Wadi Yaroun, Wadi Yarun, Wadi Jarun, Wadi Hanine, Jarun or Jareon is a wadi located south of Ain Ebel in the Bint Jbeil District of Nabatieh Governorate in Lebanon. After it reaches Yaroun it is called the Wadi Nahle or Wadi Nalesh and after reaching Debel it is called the Wadi Ayun et Tannour.

Flaoui or Fleywe or Flaoueh is a small village located 17 kilometres (11 mi) northwest of Baalbek, Lebanon in Baalbek District, Baalbek-Hermel Governorate, Lebanon. It is located near the north-south road that runs from Bodai to Chlifa.

Khallet el Hamra or Khallet Hamra is a ravine or wadi joining the larger Wadi Yaroun located 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) southeast of Ain Ebelin the Bint Jbeil District of Nabatieh Governorate in Lebanon.

Douwara is a Heavy Neolithic archaeological site of the Qaraoun culture located 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) southwest of Ain Ebel in the Bint Jbeil District of Nabatieh Governorate in Lebanon. It is located on slopes north of the road from Ain Ebel to Rmaich.










