
Qinghai is a landlocked province in Northwestern China. As one of the largest province-level administrative divisions of China by area, the province is ranked fourth-largest in area and has the third-smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xining.
The Bonan people are an ethnic group living in Gansu and Qinghai provinces in Northwestern China. They are one of the "titular nationalities" of Gansu's Jishishan Bonan, Dongxiang and Salar Autonomous County, which is located south of the Yellow River, near Gansu's border with Qinghai.

Xining is the capital of Qinghai province in western China, and the largest city on the Tibetan Plateau. It has 2,208,708 inhabitants at the 2010 census of whom 1,198,304 live in the built up area made of 4 urban districts.

Qinghai Lake, also known by other names, is the largest lake in China. Located in an endorheic basin in Qinghai Province, to which it gave its name, Qinghai Lake is classified as an alkaline salt lake. The lake has fluctuated in size, shrinking over much of the 20th century but increasing since 2004. It had a surface area of 4,317 km2 (1,667 sq mi), an average depth of 21 m (69 ft), and a maximum depth of 25.5 m (84 ft) in 2008.
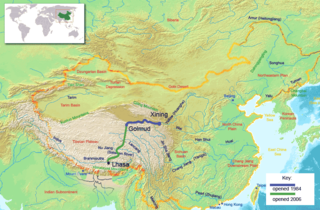
The Qinghai–Tibet railway or Qingzang railway, is a high-elevation railway that connects Xining, Qinghai Province, to Lhasa, Tibet Autonomous Region of China.

China National Highway 109 connects Beijing with Lhasa. It runs westwards of Beijing via Datong, Yinchuan and Xining to Golmud before turning southwest to Lhasa. The portion of the highway from Xining to Lhasa is known as the Qinghai-Tibet Highway. The total distance of the highway is 3,901 km.

Qinghai University is a university located in Xining city, the capital of Qinghai province, China. Established in 1958, the university awards bachelor's degrees in the areas of economics and management, agriculture and stockbreeding, science and technology, engineering, veterinary sciences, adult education, and architecture. Qinghai University also offers 3 master's degrees in the agriculture and stockbreeding field. The university has a student enrollment of approximately 5,187. It is the only university in Qinghai province listed in the Project 211 program. It is a Chinese Ministry of Education Double First Class Discipline University, with Double First Class status in certain disciplines.

Zhao Leji is a senior leader of the Communist Party of China and the Secretary of the Central Commission for Discipline Inspection, the party's top anti-corruption body. Additionally, he is a member of the Politburo Standing Committee, the party's top decision making body.

Haidong is a prefecture-level city of Qinghai province in Western China. Its name literally means "east of the (Qinghai) Lake." On 8 February 2013 Haidong was upgraded from a prefecture (海东地区) into a prefecture-level city. Haidong is the third largest city in Qinghai after Xining and Golmud.
The Tour of Qinghai Lake is an annual professional road bicycle racing stage race held in the Qinghai province of China since 2002, named after Qinghai Lake. The race is sanctioned by the International Cycling Union (UCI) as a 2.HC race as part of the UCI Asia Tour. The race will become part of the new UCI ProSeries in 2020.

Xining railway station is the main railway station serving the city of Xining in Qinghai, China. It is the first station on the Qinghai–Tibet Railway which connects the city with Lhasa in Tibet.
The Politics of Qinghai Province in the People's Republic of China are structured in a dual party-government system like all other governing institutions in mainland China.

Datong Hui and Tu Autonomous County is an autonomous county of Hui and Tu peoples in Qinghai Province, China, it is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Xining, the capital of Qinghai.

Wumatang railway station is a station on the Chinese Qinghai–Tibet Railway.

The Yushu Batang Airport is the airport serving Yushu City in Qinghai Province, China. It is located 18 kilometers to the south of the city center, Gyêgu, at the 3,890 meters elevation about the sea level, which makes it the highest civilian airport in Qinghai Province, and one of the highest in the world.

The Sino-Tibetan War was a war that began in 1930 when the Tibetan Army under the 13th Dalai Lama invaded Xikang and Yushu in Qinghai in a dispute over monasteries. Ma clique warlord Ma Bufang secretly sent a telegram to Sichuan warlord Liu Wenhui and the leader of the Republic of China, Chiang Kai-shek, suggesting a joint attack on the Tibetan forces. Their armies rapidly overwhelmed and defeated the Tibetan Army.
The Qinghai–Tibet War was a conflict that took place during the Sino-Tibetan War. A rebellion led by the Dalai Lama with British support wanted to expand the original conflict taking place between the Tibetan Army and Liu Wenhui in Xikang, to attack Qinghai, a region northeast of Tibet. Using a dispute over a monastery in Yushu in Qinghai as an excuse in 1932, the Tibetan army attacked. Qinghai Muslim General Ma Bufang overran the Tibetan armies and recaptured several counties in Xikang province. Shiqu, Dege and other counties were seized from the Tibetans. The war against the Tibetan army was led by the Muslim General Ma Biao. The Tibetans were pushed back to the other side of the Jinsha river. The Qinghai army recaptured counties that had been controlled by the Tibetan army since 1919. The victory on the part of the Qinghai army threatened the supply lines to Tibetan forces in Garze and Xinlong. As a result, this part of the Tibetan army was forced to withdraw. Ma and Liu warned Tibetan officials not to dare cross the Jinsha river again. By August the Tibetans lost so much territory to Liu Wenhui and Ma Bufang's forces that the Dalai Lama telegraphed the British government of India for assistance. British pressure led China to declare a cease-fire. Separate truces were signed by Ma and Liu with the Tibetans in 1933, ending the fighting. The British had backed up the Tibetans during the war. After their war the victory over the Tibetans was celebrated by Xikang and Qinghai soldiers.

The Ngolok rebellions (1917–1949) were a series of military campaigns against unconquered Ngolok (Golok) tribal Tibetan areas of Qinghai (Amdo), undertaken by two Hui commanders, Gen. Ma Qi and Gen. Ma Bufang, on behalf of the Beiyang and Kuomintang governments of the Republic of China. The campaigns lasted between 1917 and 1949.

Qinghai Television (QHTV), Chinese: 青海卫视; pinyin: Qīnghǎi Diànshìtái) is a television network under Hunan Broadcasting System (HBS) in the Xining city and Qinghai province area. It was founded on January 1, 1971. QHTV currently broadcasts in Chinese, Mongolian, Tibetan and Salar.
Huanghe Hydropower's Golmud Solar park is a 200 megawatt (MW) photovoltaic power station located in Golmud, Qinghai Province, China. Construction began in August 2009, and it was commissioned on October 29, 2011. 80 MW was provided by Yingli. The project won the 2012 China Quality Power Project Award. Output is expected to be 317 GWh per year.














