Related Research Articles

Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus, surnamed Cunctator, was a Roman statesman and general of the third century BC. He was consul five times and was appointed dictator in 221 and 217 BC. He was censor in 230 BC. His agnomen, Cunctator, usually translated as "the delayer", refers to the strategy that he employed against Hannibal's forces during the Second Punic War. Facing an outstanding commander with superior numbers, he pursued a then-novel strategy of targeting the enemy's supply lines, and accepting only smaller engagements on favourable ground, rather than risking his entire army on direct confrontation with Hannibal himself. As a result, he is regarded as the originator of many tactics used in guerrilla warfare.

Hannibal was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.
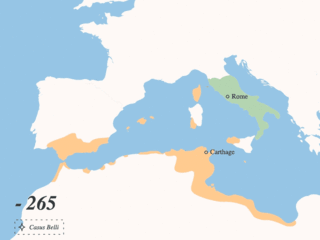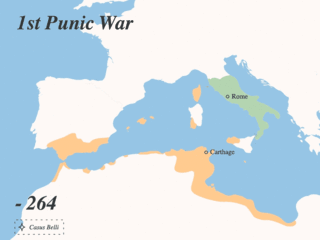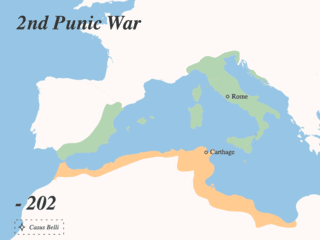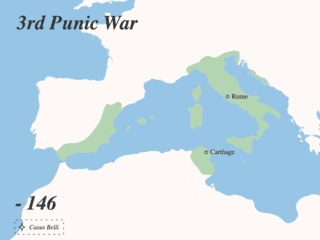
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146 BC fought between the Roman Republic and Ancient Carthage. Three wars took place, on both land and sea, across the western Mediterranean region and involved a total of forty-three years of warfare. The Punic Wars are also considered to include the four-year-long revolt against Carthage which started in 241 BC. Each war involved immense materiel and human losses on both sides.

The Second Punic War was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were once again defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war.
This article concerns the period 219 BC – 210 BC.

The Battle of Lake Trasimene was fought when a Carthaginian force under Hannibal Barca ambushed a Roman army commanded by Gaius Flaminius on 21 June 217 BC, during the Second Punic War. The battle took place on the north shore of Lake Trasimene, to the south of Cortona, and resulted in a heavy defeat for the Romans.
The gens Baebia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. The first member of the gens who obtained the consulship was Gnaeus Baebius Tamphilus, in 182 BC. During the later Republic, the Baebii were frequently connected with the patrician family of the Aemilii.

Hasdrubal Barca, a latinization of ʿAzrubaʿal son of Hamilcar Barca, was a Carthaginian general in the Second Punic War. He was the brother of Hannibal and Mago Barca.
Gaius Terentius Varro was a Roman politician and general active during the Second Punic War. A plebeian son of a butcher, he was a populist politician who was elected consul for the year 216 BC. While holding that office, he was decisively defeated by Hannibal at the Battle of Cannae.

Gaius Claudius Nero was a Roman general active during the Second Punic War against the invading Carthaginian force, led by Hannibal Barca. During a military career that began as legate in 214 BC, he was praetor in 212 BC, propraetor in 211 BC during the siege of Capua, before being sent to Spain that same year. He became consul in 207 BC.
Titus Manlius Torquatus was a politician of the Roman Republic. He had a long and distinguished career, being consul in 235 BC and 224 BC, censor in 231 BC, and dictator in 208 BC. He was an ally of Fabius Maximus "Cunctator".
Quintus Pleminius was a propraetor in 205 BC. He was given command over Locri in Bruttium by Scipio Africanus after its recapture, considered the "outstanding event" in Sicilian operations that year. His governorship, if it should be called that, ended in sacrilege and murder.
Marcus Valerius Laevinus was a Roman consul and commander who rose to prominence during the Second Punic War and corresponding First Macedonian War. A member of the gens Valeria, an old patrician family believed to have migrated to Rome under the Sabine king T. Tatius, Laevinus played an integral role in the containment of the Macedonian threat.

The Battle of Ibera, also known as the Battle of Dertosa, was fought in the spring of 215 BC on the south bank of the Ebro River near the town of Ibera and was part of the Second Punic War. A Roman army, under the command of the brothers Gnaeus and Publius Scipio, defeated a similarly sized Carthaginian army under Hasdrubal Barca. The Romans, under Gnaeus Scipio, had invaded Iberia in late 218 BC and established a foothold after winning the Battle of Cissa. This lodgement, on the north-east Iberian coast, between the Ebro and the Pyrenees, blocked the route of any reinforcements from Iberia for the army of Hannibal, who had invaded Italy from Iberia earlier in the year. Hasdrubal attempted to evict the Romans in 217 BC, but this ended in defeat when the Carthaginian naval contingent was mauled at the Battle of Ebro River.
Lucius Aemilius Papus was a Roman general and statesman. He jointly commanded the Roman armies which defeated the Gauls at the Battle of Telamon in 225 BC; his co-Consul, Gaius Atilius Regulus was killed during the battle. Papus was honoured with a triumph for this victory. He subsequently held several senior positions. He belonged to the patrician gens Aemilia.

The Ebro Treaty was a treaty signed in 226 BC by Hasdrubal the Fair of Carthage and the Roman Republic, which fixed the river Ebro in Iberia as the boundary between the two respective powers. Under the terms of the treaty, Carthage would not expand north of the Ebro, as long as Rome likewise did not expand to the south of the river.

The Battle of the Rhône Crossing was a battle during the Second Punic War in September of 218 BC. Hannibal marched on the Italian Alps, and an army of Gallic Volcae attacked the Carthaginian army on the east bank of the Rhône. The Roman army camped near Massalia. The Volcae tried to prevent the Carthaginians from crossing the Alps and invading Italy.
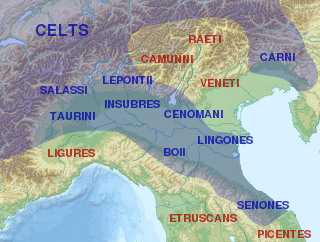
Over the course of nearly four centuries, the Roman Republic fought a series of wars against various Celtic tribes, whom they collectively described as Galli, or Gauls. Among the principal Gallic peoples described as antagonists by Greek and Roman writers were the Senones, Insubres, Boii, and Gaesatae.
Publius Cornelius Scipio Asina was a Roman politician and general who served as consul in 221 BC, and as such campaigned against the Histri, a people in the northern Adriatic. Asina belonged to the Scipionic-Aemilian faction which dominated Roman politics at the beginning of the Second Punic War, and advocated for an aggressive policy against Hannibal. This stance led him to oppose the more prudent strategy of Fabius Maximus. He was notably appointed Interrex in 216 BC, probably in order to manipulate the elections.
The Battle of Silva Litana was an ambush that took place in a forest 75 miles northwest of the Roman city of Ariminum during the Second Punic War in 216 BC. The Gallic Boii surprised and destroyed a Roman army under the consul-elect Lucius Postumius Albinus. Of 25,000 Romans, only 10 survived, with a few being taken prisoner by the Gauls. The corpse of Postumius was decapitated and his skull was made into a gilded ceremonial cup by the Boii. News of this military disaster probably reached Rome after the defeat at Cannae in the fall of 216 BC or the spring election of consuls for 215 BC, triggering a renewed panic. The Romans were compelled to postpone military operations against the Gauls until the conclusion of the Second Punic War, sending only two legions to guard against additional Gallic attacks. However, the Boii and Insubres did not attempt to exploit their victory. Cisalpine Gaul remained in relative peace until 207 BC, when Hasdrubal Barca arrived there with his army from Spain.
References
Unless otherwise noted, dates, offices, and citations of ancient sources from T.R.S. Broughton, The Magistrates of the Roman Republic (American Philological Association, 1951, 1986), vol. 1, pp. 237, 239; vol. 2 (1952), p 537.
- ↑ Livy 21.6; Cicero, Philippics 5.27.
- ↑ MRR1 p. 237.
- ↑ Dexter Hoyos, Hannibal's Dynasty: Power and Politics in the Western Mediterranean, 247–183 BC (Routledge, 2003, reprinted 2005), p. 92 online. The embassy of Valerius and Baebius to Hannibal is discussed at length by Hoyos, Unplanned Wars: The Origins of the First and Second Punic Wars (de Gruyter, 1997), pp. 196–218, limited preview online.
- ↑ The others were Marcus Livius Salinator, Lucius Aemilius Paullus, Gaius Licinius Varus, and either Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus or Marcus Fabius Buteo.
- ↑ Maiores natu, "greater in birth."
- ↑ His presence among them is one piece of evidence for his otherwise shadowy praetorship; see T. Corey Brennan, The Praetorship in the Roman Republic (Oxford University Press, 2000), p. 896, note 18 online.
- ↑ Livy 21.18.1 and 21.19.6 and 20.9; Cassius Dio frg. 55.10; Zonaras 8.22; Polybius 3.20.6 and 9, 33.1–4, 40.2; Frontinus, Stratagems 1.11.4; Silius Italicus 2.1–390; Appian, Iberica 13.
- ↑ H.H. Scullard, "The Carthaginians in Spain," in Cambridge Ancient History: Rome and the Mediterranean to 133 B.C. (Cambridge University Press, 1989, reprinted 2003), 2nd ed., vol. 8, p. 38 online.