
Germanicus Julius Caesar was an ancient Roman general and politician most famously known for his campaigns in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicus was born into an influential branch of the patrician gens Claudia. The agnomen Germanicus was added to his full name in 9 BC when it was posthumously awarded to his father in honor of his victories in Germania. In AD 4 he was adopted by his paternal uncle Tiberius, himself the stepson and heir of Germanicus' great-uncle Augustus; ten years later, Tiberius succeeded Augustus as Roman emperor. As a result of his adoption, Germanicus became an official member of the gens Julia, another prominent family, to which he was related on his mother's side. His connection to the Julii Caesares was further consolidated through a marriage between him and Agrippina the Elder, a granddaughter of Augustus. He was also the father of Caligula, the maternal grandfather of Nero, and the older brother of Claudius.

The 10s decade ran from January 1, AD 10, to December 31, AD 19.
AD 16 (XVI) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Taurus and Libo. The denomination AD 16 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
This article concerns the period 69 BC – 60 BC.

The Cherusci were a Germanic tribe that inhabited parts of the plains and forests of northwestern Germania in the area of the Weser River and present-day Hanover during the first centuries BC and AD. Roman sources reported they considered themselves kin with other Irmino tribes and claimed common descent from an ancestor called Mannus. During the early Roman Empire under Augustus, the Cherusci first served as allies of Rome and sent sons of their chieftains to receive Roman education and serve in the Roman army as auxiliaries. The Cherusci leader Arminius led a confederation of tribes in the ambush that destroyed three Roman legions in the Teutoburg Forest in AD 9. He was subsequently kept from further damaging Rome by disputes with the Marcomanni and reprisal attacks led by Germanicus. After rebel Cherusci killed Arminius in AD 21, infighting among the royal family led to the highly Romanized line of his brother Flavus coming to power. Following their defeat by the Chatti around AD 88, the Cherusci do not appear in further accounts of the German tribes, apparently being absorbed into the late classical groups such as the Saxons, Thuringians, Franks, Bavarians, and Allemanni.
Gnaeus Calpurnius Piso was a Roman statesman during the reigns of Augustus and Tiberius. He served as consul in 7 BC, after which he was appointed governor of Hispania and consul of Africa. Piso is best known for being accused of poisoning and killing Germanicus, the heir of emperor Tiberius.

Nero Julius Caesar was the adopted grandson and heir of the Roman emperor Tiberius, alongside his brother Drusus. Born into the prominent Julio-Claudian dynasty, Nero was the son of Tiberius' general and heir, Germanicus. After the deaths of his father and of Tiberius' son, Drusus the Younger, Nero and his brother Drusus were adopted together by Tiberius in September AD 23. As a result of being heirs of the emperor, he and his brother enjoyed accelerated political careers.

Artabanus II, incorrectly known in older scholarship as Artabanus III, was King of Kings of the Parthian Empire from 12 to 38/41 AD, with a one-year interruption. He was the nephew and successor of Vonones I. His father has been variously identified as a Dahae or Atropatid prince, whilst his mother was a daughter of the Parthian King of Kings Phraates IV.

Vonones I was an Arsacid prince, who ruled as King of Kings of Parthian Empire from 8 to 12, and subsequently as king of Armenia from 12 to 18. He was the eldest son of Phraates IV and was sent to Rome as a hostage in 10/9 BC in order to prevent conflict over the succession of Phraates IV's youngest son, Phraataces.
Lucius Caecilius Metellus was a Roman aristocrat. He was praetor in 71 BC. He succeeded Gaius Verres as governor of Sicily in 70 BC. He died in office as consul in 68 BC. His co-consul was Quintus Marcius Rex.
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Creticus was a politically active member of the Roman upper class. He was praetor in 74 BC and pontifex from 73 BC until his death. He was consul in 69 BC along with Quintus Hortensius Hortalus.
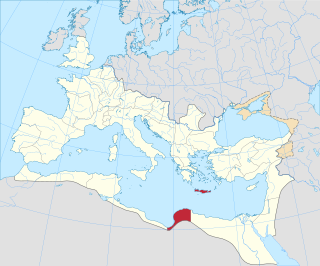
Crete and Cyrenaica was a senatorial province of the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire, established in 67 BC, which included the island of Crete and the region of Cyrenaica in modern-day Libya. These areas were settled by Greek colonists from the eighth to sixth centuries BC. After Alexander the Great's death, his short-lived empire was partitioned between his generals during the Wars of the Diadochi. Cyrenaica ended up under Egyptian rule, except for Crete, which remained independent.

The gens Caecilia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are mentioned in history as early as the fifth century BC, but the first of the Caecilii who obtained the consulship was Lucius Caecilius Metellus Denter, in 284 BC. The Caecilii Metelli were one of the most powerful families of the late Republic, from the decades before the First Punic War down to the time of Augustus.
This section of the timeline of Hispania concerns Spanish and Portuguese history events from the Carthaginian conquests to before the barbarian invasions.
Gnaeus Cornelius Lentulus "Augur" was a politician and general of the early Roman Empire during the reign of Augustus, who became consul in 14 BC as the colleague of Marcus Licinius Crassus Frugi. Enormously wealthy, he reputedly was forced by emperor Tiberius to commit suicide in 25 AD.
Gaius Junius Silanus was a Roman Senator, who was consul in 17 BC as the colleague of Gaius Furnius.
Aulus Licinius Nerva Silianus was a Roman senator who was active during the Principate. He was consul in AD 7 as the colleague of Quintus Caecilius Metellus Creticus Silanus. Silianus was born the second of three sons of Publius Silius Nerva, consul in 20 BC, and was later adopted by Aulus Licinius Nerva. Velleius Paterculus salutes him for his simplicissimus.
Lucilius Longus was a Roman politician and senator of the Roman Empire in the 1st century.