
Gallia Lugdunensis was a province of the Roman Empire in what is now the modern country of France, part of the Celtic territory of Gaul formerly known as Celtica. It is named after its capital Lugdunum, possibly Roman Europe's major city west of Italy, and a major imperial mint. Outside Lugdunum was the Sanctuary of the Three Gauls, where representatives met to celebrate the cult of Rome and Augustus.

Gallia Aquitania, also known as Aquitaine or Aquitaine Gaul, was a province of the Roman Empire. It lies in present-day southwest France, where it gives its name to the modern region of Aquitaine. It was bordered by the provinces of Gallia Lugdunensis, Gallia Narbonensis, and Hispania Tarraconensis.

Germania Superior was an imperial province of the Roman Empire. It comprised an area of today's western Switzerland, the French Jura and Alsace regions, and southwestern Germany. Important cities were Besançon (Vesontio), Strasbourg (Argentoratum), Wiesbaden, and Germania Superior's capital, Mainz (Mogontiacum). It comprised the Middle Rhine, bordering on the Limes Germanicus, and on the Alpine province of Raetia to the south-east. Although it had been occupied militarily since the reign of Augustus, Germania Superior was not made into an official province until c. 85 AD.
Quintus Petillius Cerialis Caesius Rufus, otherwise known as Quintus Petillius Cerialis, was a Roman general and administrator who served in Britain during Boudica's rebellion and went on to participate in the civil wars after the death of Nero. He later crushed the rebellion of Julius Civilis and returned to Britain as its governor.

Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia into two parts: Pannonia Superior and Pannonia Inferior. The province included parts of present-day states of Hungary, Serbia, Croatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina. The province was bordered to the east by a Sarmatian tribe—the Iazyges. Later, the Vandals appeared to the north-east.
Secundus is the Latin word for "second." However, it also had the meaning of "favorable" or "lucky." It functions both as a proper name and a numeral title. It can refer to:
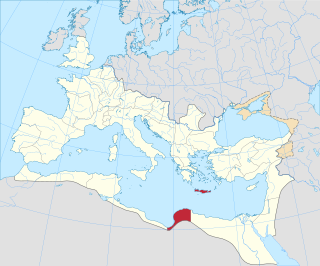
Crete and Cyrenaica was a senatorial province of the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire, established in 67 BC, which included the island of Crete and the region of Cyrenaica in modern-day Libya. These areas were settled by Greek colonists from the eighth to sixth centuries BC. After Alexander the Great's death, his short-lived empire was partitioned between his generals during the Wars of the Diadochi. Cyrenaica ended up under Egyptian rule, except for Crete, which remained independent.

Lucius Junius Quintus Vibius Crispus was a Roman senator and amicus or companion of the Emperors, known for his wit. He was a three-time suffect consul.
Quintus Vibius Secundus was a Roman Senator who was active during the reigns of Domitian and Trajan. He was suffect consul for the nundinium of March to April 86.

The Rheinisches Landesmuseum Bonn, or LVR-LandesMuseum Bonn, is a museum in Bonn, Germany, run by the Rhineland Landscape Association. It is one of the oldest museums in the country. In 2003 it completed an extensive renovation. The museum has a number of notable ancient busts and figures dating back to Roman times.

The gens Caecilia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are mentioned in history as early as the fifth century BC, but the first of the Caecilii who obtained the consulship was Lucius Caecilius Metellus Denter, in 284 BC. The Caecilii Metelli were one of the most powerful families of the late Republic, from the decades before the First Punic War down to the time of Augustus.
Gaius Poppaeus Sabinus was a Roman senator, who served as consul in AD 9 with Quintus Sulpicius Camerinus as his colleague. He enjoyed the friendship of the Emperors Augustus and Tiberius.
The gens Poppaea was a minor plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens first appear under the early Empire, when two brothers served as consuls in AD 9. The Roman empress Poppaea Sabina was a descendant of this family, but few others achieved any prominence in the Roman state. A number of Poppaei are known from inscriptions. The name is sometimes confused with that of Pompeia.
Quintus Poppaeus Q. f. Q. n. Secundus was consul suffectus in AD 9, and one of the authors of the lex Papia Poppaea.

The gens Petillia or Petilia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens first appear in history at the beginning of the second century BC, and the first to obtain the consulship was Quintus Petillius Spurinus in 176 BC.
The gens Seccia, Secia, or Siccia was a minor plebeian family at ancient Rome. Few members of this gens occur in history, but a number are known from inscriptions. The best known members include Lucius Siccius Dentatus, who won martial fame in the fifth century BC, and Gaius Secius Campanus suffect consul under Domitian.
The Stele of Quintus Aemilius Secundus is a first-century Roman tombstone bearing a notable funerary inscription. It records how the dedicatee served in Roman Syria under Publius Sulpicius Quirinius, who was governor of Syria at the time, and there oversaw a census in the town of Apamea.









