Related Research Articles

In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". Prominent examples include celiac disease, diabetes mellitus type 1, Henoch–Schönlein purpura, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Graves' disease, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, Addison's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, and multiple sclerosis. Autoimmune diseases are very often treated with steroids.
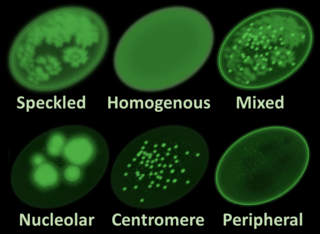
Antinuclear antibodies are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human proteins (autoantigens). In some cases, antibodies to human antigens are produced; these are known as autoantibodies.

Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs) are a group of autoantibodies, mainly of the IgG type, against antigens in the cytoplasm of neutrophils and monocytes. They are detected as a blood test in a number of autoimmune disorders, but are particularly associated with systemic vasculitis, so called ANCA-associated vasculitides (AAV).
An autoantibody is an antibody produced by the immune system that is directed against one or more of the individual's own proteins. Many autoimmune diseases are associated with such antibodies.

Citrullination or deimination is the conversion of the amino acid arginine in a protein into the amino acid citrulline. Citrulline is not one of the 20 standard amino acids encoded by DNA in the genetic code. Instead, it is the result of a post-translational modification. Citrullination is distinct from the formation of the free amino acid citrulline as part of the urea cycle or as a byproduct of enzymes of the nitric oxide synthase family.
Extractable nuclear antigens (ENAs) are over 100 different soluble cytoplasmic and nuclear antigens. They are known as "extractable" because they can be removed from cell nuclei using saline and represent six main proteins: Ro, La, Sm, RNP, Scl-70, Jo1. Most ENAs are part of spliceosomes or nucleosomes complexes and are a type of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNPS). The location in the nucleus and association with spliceosomes or nucleosomes results in these ENAs being associated with additional RNA and proteins such as polymerases. This quality of ENAs often makes it difficult to purify and quantify their presence for clinical use.
Mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) is a systemic autoimmune disease that shares characteristics with at least two other systemic autoimmune diseases, including systemic sclerosis (Ssc), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), polymyositis/dermatomyositis (PM/DM), and rheumatoid arthritis. The idea behind the "mixed" disease is that this specific autoantibody is also present in other autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, polymyositis, scleroderma, etc. MCTD was characterized as an individual disease in 1972 by Sharp et al., and the term was introduced by Leroy in 1980.
Gideon Dreyfuss is an American biochemist, the Isaac Norris Professor of Biochemistry and Biophysics at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine, and an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. He was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 2012.
Anti-transglutaminase antibodies (ATA) are autoantibodies against the transglutaminase protein. Detection is considered abnormal, and may indicate one of several conditions.

Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins A2/B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HNRNPA2B1 gene.

snRNP70 also known as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 70 kDa is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNRNP70 gene. snRNP70 is a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein that associates with U1 spliceosomal RNA, forming the U1snRNP a core component of the spliceosome. The U1-70K protein and other components of the spliceosome complex form detergent-insoluble aggregates in both sporadic and familial human cases of Alzheimer's disease. U1-70K co-localizes with Tau in neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease.

Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HNRNPL gene.

60 kDa SS-A/Ro ribonucleoprotein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TROVE2 gene.
RNA-binding protein Raly is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RALY gene.

Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) are autoantibodies that are directed against peptides and proteins that are citrullinated. They are present in the majority of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clinically, cyclic citrullinated peptides (CCP) are frequently used to detect these antibodies in patient serum or plasma.

Anti-double stranded DNA (Anti-dsDNA) antibodies are a group of anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA) the target antigen of which is double stranded DNA. Blood tests such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunofluorescence are routinely performed to detect anti-dsDNA antibodies in diagnostic laboratories. They are highly diagnostic of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and are implicated in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis.
Anti-nRNP is a type of antibody.
Detection of autoantibodies against mutated citrullinated vimentin is part of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) diagnostics, especially in sera negative for rheumatoid factor. Anti-MCV antibodies are a member of the ACPA family, a group of the so-called antibodies to citrullinated protein/peptide antigens.
Rheumatoid lung disease is a disease of the lung associated with RA, rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatoid lung disease is characterized by pleural effusion, pulmonary fibrosis, lung nodules and pulmonary hypertension. Common symptoms associated with the disease include shortness of breath, cough, chest pain and fever. It is estimated that about one quarter of people with rheumatoid arthritis develop this disease, which are more likely to develop among elderly men with a history of smoking.

Anti-SSA autoantibodies are a type of anti-nuclear autoantibodies that are associated with many autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), SS/SLE overlap syndrome, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE), neonatal lupus and primary biliary cirrhosis. They are often present in Sjögren's syndrome (SS). Additionally, Anti-Ro/SSA can be found in other autoimmune diseases such as systemic sclerosis (SSc), polymyositis/dermatomyositis (PM/DM), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), and are also associated with heart arrhythmia.
References
- ↑ Hassfeld et al.: Demonstration of a new antinuclear antibody (anti-RA33) that is highly specific for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 1989; 32:1515-20.
- ↑ Steiner et al.: Purification and partial sequencing of the nuclear autoantigen RA33 shows that it is indistinguishable from the A2 protein of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1992; 90:1061-66
- ↑ Steiner et al.: Autoantibodies to the A/B proteins of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex: Novel tools for the diagnosis of rheumatic diseases. International Archives of Allergology and Immunology 1996;111:314-19.
- ↑ Fritsch et al.: Characterization of autoreactive T cells to the autoantigens RA33 (hnRNP A2) and filaggrin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Immunology 2002 169:1068-76