Related Research Articles

A cluster munition is a form of air-dropped or ground-launched explosive weapon that releases or ejects smaller submunitions. Commonly, this is a cluster bomb that ejects explosive bomblets that are designed to kill personnel and destroy vehicles. Other cluster munitions are designed to destroy runways or electric power transmission lines.

The Butterfly Bomb was a German 2-kilogram (4.4 lb) anti-personnel submunition used by the Luftwaffe during the Second World War. It was so named because the thin cylindrical metal outer shell which hinged open when the bomblet deployed gave it the superficial appearance of a large butterfly. The design was very distinctive and easy to recognise. SD 2 bomblets were not dropped individually, but were packed into containers holding between 6 and 108 submunitions e.g. the AB 23 SD 2 and AB 250-3 submunition dispensers. The SD 2 submunitions were released after the container was released from the aircraft and had burst open. Because SD 2s were always dropped in groups the discovery of one unexploded SD 2 was a reliable indication that others had been dropped nearby. This bomb type was one of the first cluster bombs ever used in combat and it proved to be a highly effective weapon. The bomb containers that carried the SD 2 bomblets and released them in the air were nicknamed the "Devil's Eggs" by Luftwaffe air and ground crew.

The Mk 20 Rockeye II, CBU-99 Rockeye II, and CBU-100 Rockeye II comprise an American cluster bomb family which are employed primarily in an anti-tank mode against armored vehicles.

BLU-3 Pineapple was a cluster bomblet, 360 were deployed from the CBU-2A cluster bomb. It was used extensively in the Vietnam War by American forces. It was named "Pineapple" because of its appearance. On some Arc Light missions, the B-52Ds carried two SUU-24 dispensers in the bomb bay, containing a total of 10,656 bomblets.
The CBU-87 Combined Effects Munition (CEM) is a cluster bomb used by the United States Air Force, developed by Aerojet General/Honeywell and introduced in 1986 to replace the earlier cluster bombs used in the Vietnam War. CBU stands for Cluster Bomb Unit. When the CBU-87 is used in conjunction with the Wind Corrected Munitions Dispenser guidance tail kit, it becomes much more accurate, and is designated CBU-103.

The BLU-97/B Combined Effects Bomb is the submunition used in several cluster bomb type weapon systems, mainly the CBU-87 and its precision-guided version CBU-103. When the bomblets fall, they separate from the main bomb and independently free fall to the ground. They contain an inflatable bag (ballute) on the top of them, which slows them down and spreads them out. Once the bomblets reach a force of 6 Gs they arm themselves. As the bomblets fall, they are also spinning. Arming takes about 2.6 seconds. They have a combined shaped charge, fragmentation and incendiary effect on the target. It is very effective against and mainly used for anti-personnel, anti-materiel, and anti-armor.

The M33 cluster bomb, also known as the (M33) Brucella cluster bomb, was a U.S. biological cluster bomb developed in the early 1950s and deployed in 1952. It was the first standardized biological weapon in the U.S. arsenal.

The M34 cluster bomb was the first mass-produced United States Army weapon meant to deliver the chemical agent sarin (GB). A large stockpile of M34s was destroyed between 1973 and 1976.
The M138 bomblet was a sub-munition of the U.S. chemical weapon, the M43 BZ cluster bomb. The bomblet contained BZ, an incapacitating agent and was developed with the M43 in 1962. The M138s, along with all other U.S. BZ weapons were destroyed during the 1980s.
The E61 anthrax bomblet was an American biological sub-munition for the E133 cluster bomb. This anti-personnel weapon was developed in the early 1950s and carried 35 milliliters of anthrax spores or another pathogen.
The M125 bomblet was a U.S. chemical sub-munition designed to deliver the nerve agent sarin. It was brought into service in 1954 with the M34 cluster bomb as part of the first U.S. air-delivered nerve agent weapon.
This is a glossary of acronyms and initials used for aircraft weapons in the Russian Federation and formerly the USSR. The Latin-alphabet names are phonetic representations of the Cyrillic originals, and variations are inevitable.

The M69 incendiary bomblet was used in air raids on Japan and China during World War II, including the firebombing of Tokyo in 1945. It was created by the Standard Oil Development Company, whose work was funded by the Office of Scientific Research and Development. They were nicknamed "Tokyo calling cards". The M69 was a plain steel pipe with a hexagonal cross section 3 inches (76 mm) in diameter and 20 inches (510 mm) long. It weighed about 6 pounds (2.7 kg).

The Fairchild AU-23 Peacemaker is an American armed gunship, counter-insurgency, utility transport aircraft developed from the Pilatus PC-6 Porter for the United States Air Force. A total of 35 were built under license in the United States by Fairchild Industries, for use during the Vietnam War in the early 1970s. All aircraft were later sold to the Royal Thai Air Force.
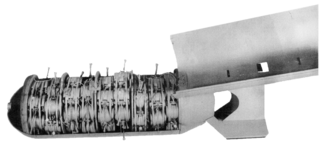
The M29 cluster bomb was a 500-pound (230 kg) cluster bomb used by the United States Air Force during World War II against troops, unarmoured vehicles and artillery. The weapon contained ninety 4-pound (1.8 kg) M83 fragmentation submunitions - a direct copy of the earlier German Butterfly Bomb - in 9 ten-bomb "wafers". The M28 was a 100-pound (45 kg) equivalent of the M29 containing 24 bomblets.
RBK-500 is a Russian 500 kg cluster bomb. It carries 15 "Motiv-3" SPBE-D antitank submunitions developed by NPO Bazalt with dual-mode infrared homing system. It entered service with the Soviet Air Force in 1987.
The bombing of Barcs was an air attack of the Yugoslav Air Force on the Hungarian border town of Barcs that occurred on 27 October 1991.
Soviet Union and Russian Federation developed a range of aerial bombs for use on its aircraft.
References
- ↑ Pike, John. "RBK cluster bombs". www.globalsecurity.org.
- ↑ The New York Times, 21 December 2012: Cluster bombs in Syria