Related Research Articles

A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder of an individual's sleep patterns. Some sleep disorders are severe enough to interfere with normal physical, mental, social and emotional functioning. Sleep disorders are frequent and can have serious consequences on patients' health and quality of life. Polysomnography and actigraphy are tests commonly ordered for diagnosing sleep disorders.

Parkinsonism is a clinical syndrome characterized by tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. These are the four motor symptoms found in Parkinson's disease (PD) – after which it is named – dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), Parkinson's disease dementia (PDD), and many other conditions. This set of symptoms occurs in a wide range of conditions and may have many causes, including neurodegenerative conditions, drugs, toxins, metabolic diseases, and neurological conditions other than PD.
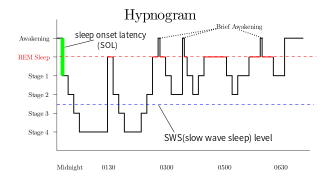
Rapid eye movement sleep is a unique phase of sleep in mammals and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream vividly.

Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is a type of dementia characterized by changes in sleep, behavior, cognition, movement, and regulation of automatic bodily functions. Memory loss is not always an early symptom. The disease worsens over time and is usually diagnosed when cognitive impairment interferes with normal daily functioning. Together with Parkinson's disease dementia, DLB is one of the two Lewy body dementias. It is a common form of dementia, but the prevalence is not known accurately and many diagnoses are missed. The disease was first described by Kenji Kosaka in 1976.

Restless legs syndrome (RLS), also known as Willis–Ekbom disease (WED), is generally a long-term disorder that causes a strong urge to move one's legs. There is often an unpleasant feeling in the legs that improves somewhat by moving them. This is often described as aching, tingling, or crawling in nature. Occasionally, arms may also be affected. The feelings generally happen when at rest and therefore can make it hard to sleep. Due to the disturbance in sleep, people with RLS may be sleepy during the day, have low energy, and feel irritable or depressed. Additionally, many have limb twitching during sleep, a condition known as periodic limb movement disorder. RLS is not the same as habitual foot-tapping or leg-rocking.

Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder or REM behavior disorder (RBD) is a sleep disorder in which people act out their dreams. It involves abnormal behavior during the sleep phase with rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. The major feature of RBD is loss of muscle atonia during otherwise intact REM sleep. The loss of motor inhibition leads to sleep behaviors ranging from simple limb twitches to more complex integrated movements that can be violent or result in injury to either the individual or their bedmates.

Chorea-acanthocytosis is a rare hereditary disease caused by a mutation in a gene that directs structural proteins in red blood cells. It belongs to a group of four diseases characterized under the name neuroacanthocytosis. When a patient's blood is viewed under a microscope, some of the red blood cells appear thorny. These thorny cells are called acanthocytes.

Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) is a late-onset neurodegenerative disease involving the gradual deterioration and death of specific volumes of the brain. The condition leads to symptoms including loss of balance, slowing of movement, difficulty moving the eyes, and cognitive impairment. PSP may be mistaken for other types of neurodegeneration such as Parkinson's disease, frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer's disease. The cause of the condition is uncertain, but involves the accumulation of tau protein within the brain. Medications such as levodopa and amantadine may be useful in some cases.
Periodic limb movement disorder (PLMD) is a sleep disorder where the patient moves limbs involuntarily and periodically during sleep, and has symptoms or problems related to the movement. PLMD should not be confused with restless legs syndrome (RLS), which is characterized by a voluntary response to an urge to move legs due to discomfort. PLMD on the other hand is involuntary, and the patient is often unaware of these movements altogether. Periodic limb movements (PLMs) occurring during daytime period can be found but are considered as a symptom of RLS; only PLMs during sleep can suggest a diagnosis of PLMD.
Hypokinesia is one of the classifications of movement disorders, and refers to decreased bodily movement. Hypokinesia is characterized by a partial or complete loss of muscle movement due to a disruption in the basal ganglia. Hypokinesia is a symptom of Parkinson's disease shown as muscle rigidity and an inability to produce movement. It is also associated with mental health disorders and prolonged inactivity due to illness, amongst other diseases.
Parasomnias are a category of sleep disorders that involve abnormal movements, behaviors, emotions, perceptions, and dreams that occur while falling asleep, sleeping, between sleep stages, or during arousal from sleep. Parasomnias are dissociated sleep states which are partial arousals during the transitions between wakefulness, NREM sleep, and REM sleep, and their combinations.
Rhythmic movement disorder (RMD) is a neurological disorder characterized by repetitive movements of large muscle groups immediately before and during sleep often involving the head and neck. It was independently described first in 1905 by Zappert as jactatio capitis nocturna and by Cruchet as rhythmie du sommeil. The majority of RMD episodes occur during NREM sleep, although REM movements have been reported. RMD is often associated with other psychiatric conditions or mental disabilities. The disorder often leads to bodily injury from unwanted movements. Because of these incessant muscle contractions, patients' sleep patterns are often disrupted. It differs from restless legs syndrome in that RMD involves involuntary muscle contractions before and during sleep while restless legs syndrome is the urge to move before sleep. RMD occurs in both males and females, often during early childhood with symptoms diminishing with age. Many affected individuals also have other sleep related disorders, like sleep apnea. The disorder can be differentially diagnosed into small subcategories, including sleep related bruxism, thumb sucking, hypnagogic foot tremor, and rhythmic sucking, to name a few. In order to be considered pathological, the ICSD-II requires that in the sleep-related rhythmic movements should “markedly interfere with normal sleep, cause significant impairment in daytime function, or result in self-inflicted bodily injury that requires medical treatment ”.

A sleep study is a test that records the activity of the body during sleep. There are five main types of sleep studies that use different methods to test for different sleep characteristics and disorders. These include simple sleep studies, polysomnography, multiple sleep latency tests (MSLTs), maintenance of wakefulness tests (MWTs), and home sleep tests (HSTs). In medicine, sleep studies have been useful in identifying and ruling out various sleep disorders. Sleep studies have also been valuable to psychology, in which they have provided insight into brain activity and the other physiological factors of both sleep disorders and normal sleep. This has allowed further research to be done on the relationship between sleep and behavioral and psychological factors.
Signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease are varied. Parkinson's disease affects movement, producing motor symptoms. Non-motor symptoms, which include dysautonomia, cognitive and neurobehavioral problems, and sensory and sleep difficulties, are also common. When other diseases mimic Parkinson's disease, they are categorized as parkinsonism.
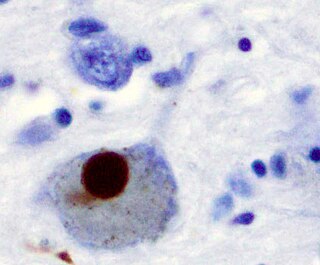
Synucleinopathies are neurodegenerative diseases characterised by the abnormal accumulation of aggregates of alpha-synuclein protein in neurons, nerve fibres or glial cells. There are three main types of synucleinopathy: Parkinson's disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and multiple system atrophy (MSA). Other rare disorders, such as various neuroaxonal dystrophies, also have α-synuclein pathologies. Additionally, autopsy studies have shown that around 6% of sporadic Alzheimer's Disease exhibit α-synuclein positive Lewy pathology, and are sub-classed as Alzheimer's Disease with Amygdalar Restricted Lewy Bodies (AD/ALB).
Parkinson's disease dementia (PDD) is dementia that is associated with Parkinson's disease (PD). Together with dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), it is one of the Lewy body dementias characterized by abnormal deposits of Lewy bodies in the brain.
The REM Sleep Behavior Disorder Single-Question Screen (RBD1Q) is a one-question screening tool for dream enactment behaviors associated with the parasomnia REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD). It screens for RBD with a simple yes/no response.
The Cambridge Behavioural Inventory (CBI) and its revised version, Cambridge Behavioural Inventory-Revised (CBI-R), are informant-based questionnaires that evaluate the emergence of behavioural symptoms in neurodegenerative brain disorders, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), Huntington's disease (HD), Parkinson's disease (PD), and frontotemporal dementia (FTD).
Rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder and Parkinson's disease is rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder (RBD) that is associated with Parkinson's disease. RBC is linked genetically and neuropathologically to α- synuclein, a presynaptic neuronal protein that exerts deleterious effects on neighbouring proteins, leading to neuronal death. This pathology is linked to numerous other neurodegenerative disorders, such as Lewy bodies dementia, and collectively these disorders are known as synucleinopathies. Numerous reports over the past few years have stated the frequent association of synucleinopathies with REM sleep behaviour disorder (RBD). In particular, the frequent association of RBD with Parkinson's. In the general population the incidence of RBD is around 0.5%, compared to the prevalence of RBD in PD patients, which has been reported to be between 38% and 60%. The diagnosis and symptom onset of RBD typically precedes the onset of motor or cognitive symptoms of PD by a number of years, typically ranging anywhere from 2 to 15 years prior. Hence, this link could provide an important window of opportunity in the implementation of therapies and treatments, that could prevent or slow the onset of PD.

Yo-El Ju is the Barbara Burton and Reuben Morriss III Professor of Neurology at the Washington University School of Medicine. She co-directs the Center on Biological Rhythms and Sleep (COBRAS) and is a member of the Hope Center for Neurological Diseases at Washington University. Clinically, she sees patients at Barnes-Jewish Hospital for parasomnia, narcolepsy, restless legs syndrome, and obstructive sleep apnea. Ju's team has made multiple significant contributions to the field of sleep medicine and neurology in unveiling the complex relationship between sleep, amyloid deposition and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, opening new possibilities for clinical treatment. As of April 2023, the most cited work from her lab is their 2017 paper in Brain: A Journal of Neurology that showed cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) amyloid-beta protein level increases due to slow-wave sleep disruption.
References
- 1 2 Stiasny-Kolster K, Mayer G, Schäfer S, Möller JC, Heinzel-Gutenbrunner M, Oertel WH (2007). "The REM Sleep Behavior Disorder Screening Questionnaire—A New Diagnostic Instrument". Movement Disorders. 22 (16): 2386–2393. doi:10.1002/mds.21740. PMID 17894337. S2CID 24235371.
- ↑ Atlas Task Force of the American Sleep Disorders Association (ASDA) (2005). "The International Classification of Sleep Disorders— Diagnostic and Coding Manual". Minnesota: Rochester.
- ↑ Nomura, Takashi; Inoue, Yuichi; Kagimura, Tatsuo; Uemura, Yusuke; Nakashima, Kenji (August 2011). "Utility of the REM sleep behavior disorder screening questionnaire (RBDSQ) in Parkinson's disease patients". Sleep Medicine. 12 (7): 711–713. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2011.01.015. PMID 21700495.
- ↑ Miyamoto, Tomoyuki; Miyamoto, Masayuki; Iwanami, Masaoki; Kobayashi, Mina; Nakamura, Masaki; Inoue, Yuichi; Ando, Chiharu; Hirata, Koichi (December 2009). "The REM sleep behavior disorder screening questionnaire: Validation study of a Japanese version". Sleep Medicine. 10 (10): 1151–1154. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2009.05.007. PMID 19604719.
- ↑ Nihei, Yoshihiro; Takahashi, Kazushi; Koto, Atsuo; Mihara, Ban; Morita, Yoko; Isozumi, Kazuo; Ohta, Kouichi; Muramatsu, Kazuhiro; Gotoh, Jun; Yamaguchi, Keiji; Tomita, Yutaka; Sato, Hideki; Seki, Morinobu; Iwasawa, Satoko; Suzuki, Norihiro (10 January 2012). "REM sleep behavior disorder in Japanese patients with Parkinson's disease: a multicenter study using the REM sleep behavior disorder screening questionnaire". Journal of Neurology. 259 (8): 1606–1612. doi:10.1007/s00415-011-6386-1. PMID 22231870. S2CID 10980181.