Related Research Articles
A utility cooperative is a type of cooperative that is tasked with the delivery of a public utility such as electricity, water or telecommunications to its members. Profits are either reinvested for infrastructure or distributed to members in the form of "patronage" or "capital credits", which are dividends paid on a member's investment in the cooperative.
The Stability Pact for Southeastern Europe was an institution aimed at strengthening peace, democracy, human rights and economy in the countries of South Eastern Europe from 1999 to 2008. It was replaced by the Regional Cooperation Council (RCC) in February 2008. The RCC replaced it because it is more "regionally owned" than the Stability Pact, which was driven more by outside partners such as the EU.

The Southeast European Cooperative Initiative (SECI) is a multilateral regional initiative that has been initiated by the European Union, the United States of America and the countries of Southeast Europe within the framework of the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) as a support to the implementation of the Dayton Accords in December 1996 at the inaugural session at Geneva on the basis of Final Points of Common EU-USA Understanding.

Ballot Initiative 937 is a clean energy initiative passed in the US state of Washington, appearing on the ballot in the November 2006 elections. It passed with 52 percent of the vote.

The energy policy of the European Union focuses on energy security, sustainability, and integrating the energy markets of member states. A key energy policy adopted in 2009 are the 20/20/20 objectives, binding for all EU Member States. The target involved increasing the share of renewable energy in its final energy use to 20%, reduce greenhouse gases by 20% and increase energy efficiency by 20%. After this target was met, new targets for 2030 were set at a 55% reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 as part of the European Green Deal. After the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the EU's energy policy turned more towards energy security in their REPowerEU policy package, which boosts both renewable deployment and fossil fuel infrastructure for alternative suppliers.
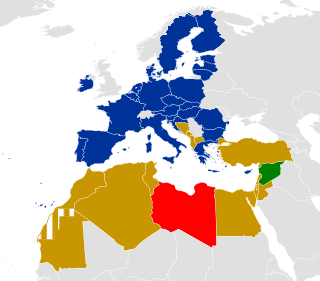
The Union for the Mediterranean is an intergovernmental organization of 43 member states from Europe and the Mediterranean Basin: the 27 EU member states and 16 Mediterranean partner countries from North Africa, Western Asia and Southern Europe. It was founded on 13 July 2008 at the Paris Summit for the Mediterranean, with an aim of reinforcing the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership (Euromed) that was set up in 1995 as the Barcelona Process. Its general secretariat is located in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain.
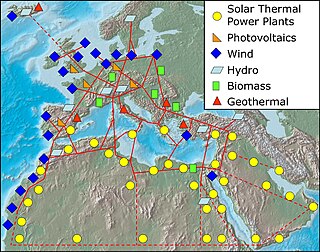
The European super grid is a possible future super grid that would ultimately interconnect the various European countries and the regions around Europe's borders – including North Africa, Kazakhstan, and Turkey – with a high-voltage direct current (HVDC) power grid.

The Renewable Energy Directive 2018 is a Directive in EU law that requires 32 percent of the energy consumed within the European Union to be renewable by 2030. This target is pooled among the member states.

The North Seas Energy Cooperation (NSEC) officially the Political Declaration on energy cooperation between the North Seas Countries previously the, North Seas Countries Offshore Grid Initiative (NSCOGI), is a collaboration between EU member-states and Norway to create an integrated offshore energy grid which links wind farms and other renewable energy sources across the northern seas of Europe. It is one of several proposed European super grid schemes.
Elia is a Belgian transmission system operator for high-voltage electricity, located in Brussels, Belgium. It operates in Belgium and Germany. The company transmits electricity from generators to distribution system operators, which then supply SMEs and homes. Elia also has contracts with major industrial users that directly connect to its high-voltage grid.
Ecopower is a Belgian cooperative founded in 1991, financing renewable energy projects in Flanders.

Som Energia is a Spanish renewable energies cooperative that was officially founded in December 2010 in Girona, Catalonia, making it the first of its kind in Spain. The project to create the cooperative was begun in November 2009 by a group of former students and lecturers at University of Girona and other contributors, with the objective of setting up something similar to initiatives such as Ecopower (Belgium) or Enercoop (France). Som Energia intends to offer its members the possibility of consuming energy from sources that are 100% renewable at a price similar to conventional energy, as well as developing its own renewable energy projects. In January 2019, the cooperative had over 54.300 members, had invested over 13 million euro in renewable energy production projects had produced over 11.80 GWh and employed 47 people.
A National Renewable Energy Action Plan (NREAP) is a detailed report submitted by countries outlining commitments and initiatives to develop renewable energy that all member states of the European Union were obliged to notify to the European Commission by 30 June 2010. The plan provides a detailed road map of how the member state expects to reach its legally binding 2020 target for the share of renewable energy in their total energy consumption, as required by article 4 of the Renewable Energy Directive 2009/28/EC. In the plan, the member state sets out sectoral targets, the technology mix they expect to use, the trajectory they will follow, and the measures and reforms they will undertake to overcome the barriers to developing renewable energy.
REScoop.eu is the European federation of renewable energy cooperatives, founded in 2011.

Energy4All facilitates the creation and development of community energy in the United Kingdom, based on the experience gained in the creation of the UK's first wind co-op, Baywind Energy Co-operative. It has gone on to raise over £40m on behalf of the co-operatives and community benefit societies through community share offerings.

Green Planet Energy is a German electric utility in the form of a registered association. The stated goal of the cooperative is the provision of environmentally friendly energy to the electrical grid.
REScoop Vlaanderen is the energy cooperative for renewable energy in Flanders, Belgium.
Wase Wind is a Flemish energy cooperative, active in the production of renewable energy and the supply of electricity from wind turbines.
The kerosene tax is an ecotax on the kerosene-based jet fuel in commercial aviation, which can be levied within and by the European Union. The legal basis for it is the Energy Taxation Directive (2003/96/EG) of 27 October 2003, which proves the member states with the option of introducing a tax on turbine fuel for commercial domestic flights and flights between member states.
Stop Bloody Energy project is a global initiative of Ukrainian energy companies aimed at refusing to buy Russian energy resources and cooperating with Russia in the energy sector due to its war against Ukraine. The project was launched by Rinat Akhmetov's private company DTEK and the state-owned companies Naftogaz and Ukrenergo.
References
- ↑ "REScoop.be | REScoop.eu". rescoop.eu. Archived from the original on 2012-08-05.