Related Research Articles

The Linksys WRT54G Wi-Fi series is a series of Wi-Fi–capable residential gateways marketed by Linksys, a subsidiary of Cisco, from 2003 until acquired by Belkin in 2013. A residential gateway connects a local area network to a wide area network.
Realtek Semiconductor Corp is a fabless semiconductor company situated in the Hsinchu Science Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan. Realtek was founded in October 1987 and subsequently listed on the Taiwan Stock Exchange in 1998. Realtek currently manufactures and sells a variety of microchips globally and its product lines broadly fall into three categories: communications network ICs, computer peripheral ICs, and multimedia ICs. As of 2019, Realtek employs 5,000 people, of whom 78% work in research and development.

Wireless network cards for computers require control software to make them function. This is a list of the status of some open-source drivers for 802.11 wireless network cards.

Broadcom Inc. is an American multinational designer, developer, manufacturer, and global supplier of a wide range of semiconductor and infrastructure software products. Broadcom's product offerings serve the data center, networking, software, broadband, wireless, storage, and industrial markets. As of 2022, some 78 percent of Broadcom's revenue was coming from its semiconductor-based products and 22 percent from its infrastructure software products and services.
Tensilica was a company based in Silicon Valley in the semiconductor intellectual property core business. It is now a part of Cadence Design Systems.
The Realtek Remote Control Protocol (RRCP), developed by Realtek, is an application layer protocol, running directly over Ethernet frames. The main idea behind this protocol is to allow direct access to the internal register of an Ethernet switch controller (ASIC) over an Ethernet network itself. This approach allows to avoid cost of including a processor, RAM, flash memory, etc. in a managed Ethernet switch. Instead, all "intelligence" is targeted to reside in a nearby computer, running special RRCP-aware Ethernet switch management software.
The Apricot Picobook Pro is the first product of the reformed Apricot Computers. It is a netbook based on the VIA NanoBook, first shown to the press on October 15 2008.
Wi-Fi Direct is a Wi-Fi standard for peer-to-peer wireless connections that allows two devices to establish a direct Wi-Fi connection without an intermediary wireless access point, router, or Internet connection. Wi-Fi Direct is single-hop communication, rather than multi-hop communication like wireless ad hoc networks.

Redpine Signals is a fabless semiconductor company that started its operation in 2001. The company makes chipsets and system-level products for wireless networks. It serves the Internet of Things and wireless embedded systems market, enabling all volume levels of chipsets and modules.

Amlogic Inc. is a fabless semiconductor company that was founded on March 14, 1995 in Santa Clara, California and is predominantly focused on designing and selling system on a chip integrated circuits. Like most fabless companies in the industry, the company outsources the actual manufacturing of its chips to third-party independent chip manufacturers such as TSMC. Its main target applications as of 2021 are entertainment devices such as Android TV-based devices and IPTV/OTT set-top boxes, media dongles, smart TVs and tablets. It has offices in Shanghai, Shenzhen, Beijing, Xi'an, Chengdu, Hefei, Nanjing, Qingdao, Taipei, Hong Kong, Seoul, Mumbai, London, Munich, Indianapolis, Milan, Novi Sad and Santa Clara, California.

NodeMCU is a low-cost open source IoT platform. It initially included firmware which runs on the ESP8266 Wi-Fi SoC from Espressif Systems, and hardware which was based on the ESP-12 module. Later, support for the ESP32 32-bit MCU was added.

The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi microchip, with built-in TCP/IP networking software, and microcontroller capability, produced by Espressif Systems in Shanghai, China.
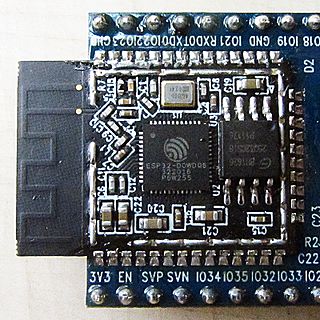
ESP32 is a series of low-cost, low-power system on a chip microcontrollers with integrated Wi-Fi and dual-mode Bluetooth. The ESP32 series employs either a Tensilica Xtensa LX6 microprocessor in both dual-core and single-core variations, Xtensa LX7 dual-core microprocessor or a single-core RISC-V microprocessor and includes built-in antenna switches, RF balun, power amplifier, low-noise receive amplifier, filters, and power-management modules. ESP32 is created and developed by Espressif Systems, a Shanghai-based Chinese company, and is manufactured by TSMC using their 40 nm process. It is a successor to the ESP8266 Microcontroller.
ESP Easy is a free and open source MCU firmware for the Internet of things (IoT). and originally developed by the LetsControlIt.com community. It runs on ESP8266 Wi-Fi based MCU platforms for IoT from Espressif Systems. The name "ESP Easy," by default, refers to the firmware rather than the hardware on which it runs. At a low level, the ESP Easy firmware works the same as the NodeMCU firmware and also provides a very simple operating system on the ESP8266. The main difference between ESP Easy firmware and NodeMCU firmware is that the former is designed as a high-level toolbox that just works out-of-the-box for a pre-defined set of sensors and actuators. Users simply hook up and read/control over simple web requests without having to write any code at all themselves, including firmware upgrades using OTA updates.

MySensors is a free and open source DIY software framework for wireless IoT devices allowing devices to communicate using radio transmitters. The library was originally developed for the Arduino platform.
Mongoose OS is an Internet of Things (IoT) Firmware Development Framework available under Apache License Version 2.0. It supports low power, connected microcontrollers such as: ESP32, ESP8266, TI CC3200, TI CC3220, STM32. Its purpose is to be a complete environment for prototyping, development and managing connected devices.
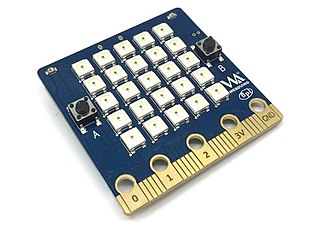
The BPI Bit is an ESP32 with Xtensa 32bit LX6 single/dual-core processor based embedded system
IEEE 802.11be, dubbed Extremely High Throughput (EHT), is the next amendment of the IEEE 802.11 standard, which will be designated Wi-Fi 7. It will build upon 802.11ax, focusing on WLAN indoor and outdoor operation with stationary and pedestrian speeds in the 2.4, 5, and 6 GHz frequency bands. Speeds are expected to reach a theoretical maximum of 46 Gbit/s, although actual results will be much lower.
Kr00k is a security vulnerability that allows some WPA2 encrypted WiFi traffic to be decrypted. The vulnerability was originally discovered by security company ESET in 2019 and assigned CVE-2019-15126 on August 17, 2019. ESET estimates that this vulnerability affects over a billion devices.
References
- ↑ "An Alternative to ESP8266? Realtek RTL8710 ARM Cortex-M3 WiFi IoT Modules Sell for $2 and Up". cnx-software.com. Retrieved 4 March 2017.
- ↑ By. "New Chip Alert: RTL8710, A Cheaper ESP8266 Competitor". hackaday.com. Retrieved 4 March 2017.