
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor. Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist.

Head and neck cancer develops from tissues in the lip and oral cavity (mouth), larynx (throat), salivary glands, nose, sinuses or the skin of the face. The most common types of head and neck cancers occur in the lip, mouth, and larynx. Symptoms predominantly include a sore that does not heal or a change in the voice. Some may experience a sore throat that does not go away. In those with advanced disease, there may be unusual bleeding, facial pain, numbness or swelling, and visible lumps on the outside of the neck or oral cavity. Given the location of these cancers, trouble breathing may also be present.

In the field of medical treatment, proton therapy, or proton radiotherapy, is a type of particle therapy that uses a beam of protons to irradiate diseased tissue, most often to treat cancer. The chief advantage of proton therapy over other types of external beam radiotherapy is that the dose of protons is deposited over a narrow range of depth, which results in minimal entry, exit, or scattered radiation dose to healthy nearby tissues.
Adjuvant therapy, also known as adjunct therapy, adjuvant care, or augmentation therapy, is therapy that is given in addition to the primary or initial therapy to maximize its effectiveness. The surgeries and complex treatment regimens used in cancer therapy have led the term to be used mainly to describe adjuvant cancer treatments. An example of such adjuvant therapy is the additional treatment usually given after surgery where all detectable disease has been removed, but where there remains a statistical risk of relapse due to the presence of undetected disease. If known disease is left behind following surgery, then further treatment is not technically adjuvant.

Tirapazamine (SR-[[4233]]) is an experimental anticancer drug that is activated to a toxic radical only at very low levels of oxygen (hypoxia). Such levels are common in human solid tumors, a phenomenon known as tumor hypoxia. Thus, tirapazamine is activated to its toxic form preferentially in the hypoxic areas of solid tumors. Cells in these regions are resistant to killing by radiotherapy and most anticancer drugs. Thus the combination of tirapazamine with conventional anticancer treatments is particularly effective. As of 2006, tirapazamine is undergoing phase III testing in patients with head and neck cancer and gynecological cancer, and similar trials are being undertaken for other solid tumor types.

Anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC), also known as anaplastic thyroid carcinoma, is an aggressive form of thyroid cancer characterized by uncontrolled growth of cells in the thyroid gland. This form of cancer generally carries a very poor prognosis due to its aggressive behavior and resistance to cancer treatments. The cells of anaplastic thyroid cancer are highly abnormal and usually no longer resemble the original thyroid cells and have poor differentiation.
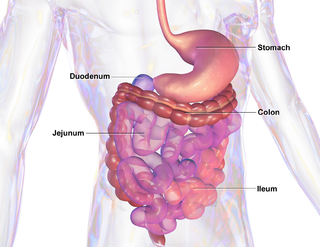
Mucositis is the painful inflammation and ulceration of the mucous membranes lining the digestive tract, usually as an adverse effect of chemotherapy and radiotherapy treatment for cancer. Mucositis can occur anywhere along the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, but oral mucositis refers to the particular inflammation and ulceration that occurs in the mouth. Oral mucositis is a common and often debilitating complication of cancer treatment.

The Regional Cancer Centre (RCC) at Thiruvananthapuram is a cancer care hospital and research centre. RCC was established in 1981 by the Government of Kerala and the Government of India. It is located in the Thiruvananthapuram Medical College campus in Thiruvananthapuram, the capital city of the state of Kerala. It was established as an expansion of the Radiation Therapy / Radiotherapy department of Medical College Trivandrum. It is a tertiary care center for the managements of all types of cancers. The clinics are mainly on Haematology, Lymphoreticular, soft tissue, bone, head and neck, breast, CNS, gynaecological, urinary, chest, gastro, paediatric oncology and thyroid.

Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), or nasopharynx cancer, is the most common cancer originating in the nasopharynx, most commonly in the postero-lateral nasopharynx or pharyngeal recess, accounting for 50% of cases. NPC occurs in children and adults. NPC differs significantly from other cancers of the head and neck in its occurrence, causes, clinical behavior, and treatment. It is vastly more common in certain regions of East Asia and Africa than elsewhere, with viral, dietary and genetic factors implicated in its causation. It is most common in males. It is a squamous cell carcinoma of an undifferentiated type. Squamous epithelial cells are a flat type of cell found in the skin and the membranes that line some body cavities. Differentiation means how different the cancer cells are from normal cells. Undifferentiated cells are cells that do not have their mature features or functions.

Cancer and Leukemia Group B is a cancer research cooperative group in the United States.

Fast neutron therapy utilizes high energy neutrons typically between 50 and 70 MeV to treat cancer. Most fast neutron therapy beams are produced by reactors, cyclotrons (d+Be) and linear accelerators. Neutron therapy is currently available in Germany, Russia, South Africa and the United States. In the United States, one treatment center is operational, in Seattle, Washington. The Seattle center uses a cyclotron which produces a proton beam impinging upon a beryllium target.
The University of Maryland Marlene and Stewart Greenebaum Comprehensive Cancer Center (UMGCCC) is a National Cancer Institute (NCI)-designated comprehensive cancer center located in Baltimore, Maryland.

Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an oncologist.

Human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal cancer, is a cancer of the throat caused by the human papillomavirus type 16 virus (HPV16). In the past, cancer of the oropharynx (throat) was associated with the use of alcohol or tobacco or both, but the majority of cases are now associated with the HPV virus, acquired by having oral contact with the genitals of a person who has a genital HPV infection. Risk factors include having a large number of sexual partners, a history of oral-genital sex or anal–oral sex, having a female partner with a history of either an abnormal Pap smear or cervical dysplasia, having chronic periodontitis, and, among men, younger age at first intercourse and a history of genital warts. HPV-positive OPC is considered a separate disease from HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancer.

Nanobiotix is a biotechnology company that uses nanomedicine to develop new radiotherapy techniques for cancer patients. The company is headquartered in Paris, with additional corporate offices in New York and Massachusetts.
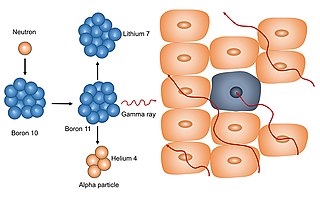
Neutron capture therapy (NCT) is a radio-therapeutic modality for treating locally invasive malignant tumors such as primary brain tumors, recurrent cancers of the head and neck region, and cutaneous and extracutaneous melanomas. It is a two-step procedure: first, the patient is injected with a tumor-localizing drug containing the non-radioactive isotope boron-10 (10B), which has a high propensity to capture low energy "thermal" neutrons. The neutron cross section of 10B is 1,000 times greater than that of the other elements, such as nitrogen, hydrogen, and oxygen, that are present in tissues. In the second step, the patient is radiated with epithermal neutrons, the sources of which in the past have been nuclear reactors and now are accelerators that produce higher energy epithermal neutrons. After losing energy as they penetrate tissue, the resultant low energy "thermal" neutrons are captured by the 10B atoms. The resulting decay reaction yields high-energy alpha particles that kill the cancer cells that have taken up sufficient quantities of 10B. All of the clinical experience to date with NCT has been with the non-radioactive isotope boron-10, and hence this radio-therapeutic modality is known as boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). The use of another non-radioactive isotope, such as gadolinium (Gd), has been limited to experimental animal studies and has not been used clinically. BNCT has been evaluated clinically as an alternative to conventional radiation therapy for the treatment of malignant brain tumors such as glioblastomas, which presently are incurable, and more recently, locally advanced recurrent cancers of the head and neck region and, much less frequently, superficial melanomas primarily involving the skin and genital region.
Professor Minesh P Mehta, MD, FASTRO, is an American radiation oncologist and physician-scientist of Indian origin, Ugandan birth, Zambian Schooling and American Training, who contributed to the field of oncology for more than two and half decades.
Christopher M. Nutting is a British Professor of Clinical Oncology and medical consultant, specializing in head and neck cancers, who has helped develop Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT), an advanced form of Radiation therapy.

Nancy Y. Lee is a Taiwanese-born American physician and the vice-chair of the Department of Radiation Oncology in Memorial Sloan Kettering's Department of Medicine.
Deborah Watkins Bruner is an American researcher, clinical trialist, and academic. She is the senior vice president for research at Emory University. Her research focus is on patient reported outcomes, symptom management across cancer sites, sexuality after cancer treatment, and effectiveness of radiotherapy modalities. Bruner's research has been continually funding since 1998, with total funding of her research exceeding $180 million. She is ranked among the top five percent of all National Institutes of Health-funded investigators worldwide since 2012, according to the Blue Ridge Institute for Medical Research.















