Related Research Articles

Mabo v Queensland is a landmark decision of the High Court of Australia that recognised the existence of Native Title in Australia. It was brought by Eddie Mabo against the State of Queensland and decided on 3 June 1992. The case is notable for being the first in Australia to recognise pre-colonial land interests of Indigenous Australians within the common law of Australia.

Wik Peoples v The State of Queensland is a decision of the High Court of Australia delivered on 23 December 1996 on whether statutory leases extinguish native title rights. The court found that the statutory pastoral leases under consideration by the court did not bestow rights of exclusive possession on the leaseholder. As a result, native title rights could co-exist depending on the terms and nature of the particular pastoral lease. Where there was a conflict of rights, the rights under the pastoral lease would extinguish the remaining native title rights.
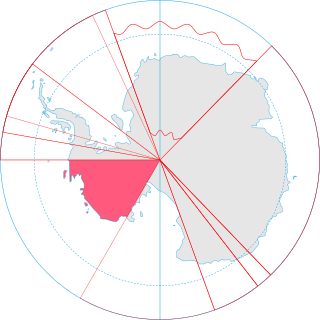
Terra nullius is a Latin expression meaning "nobody's land". It was a principle sometimes used in international law to justify claims that territory may be acquired by a state's occupation of it. There are currently three territories said to be terra nullius: Bir Tawil, pockets of land near the Danube due to the Croatia–Serbia border dispute, and parts of Antarctica, principally Marie Byrd Land.

Edward Koiki Mabo was an Indigenous Australian man from the Torres Strait Islands known for his role in campaigning for Indigenous land rights in Australia, in particular the landmark decision of the High Court of Australia that recognised that indigenous rights to land had continued after the British Crown acquired sovereignty and that the international law doctrine of terra nullius was not applicable to Australian domestic law. High court judges considering the case Mabo v Queensland found in favour of Mabo, which led to the Native Title Act 1993 and established native title in Australia, officially recognising the rights of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people in Australia.

Australian Indigenous sovereignty, also recently termed Blak sovereignty, refers to various rights claimed by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples over parts or all of Australia. Such rights are said to derive from Indigenous peoples' occupation and ownership of Australia prior to colonisation and through their continuing spiritual connection to land. Indigenous sovereignty is not explicitly recognised in the Australian Constitution or under Australian law.

Sir Francis Gerard Brennan was an Australian lawyer and jurist who served as the 10th Chief Justice of Australia. As a judge in the High Court of Australia, he wrote the lead judgement on the Mabo decision, which gave rise to the Native Title Act.

In common law systems, land tenure, from the French verb "tenir" means "to hold", is the legal regime in which land owned by an individual is possessed by someone else who is said to "hold" the land, based on an agreement between both individuals. It determines who can use land, for how long and under what conditions. Tenure may be based both on official laws and policies, and on informal local customs. In other words, land tenure implies a system according to which land is held by an individual or the actual tiller of the land but this person does not have legal ownership. It determines the holder's rights and responsibilities in connection with their holding. The sovereign monarch, known in England as The Crown, held land in its own right. All land holders are either its tenants or sub-tenants. Tenure signifies a legal relationship between tenant and lord, arranging the duties and rights of tenant and lord in relationship to the land. Over history, many different forms of land tenure, i.e., ways of holding land, have been established.
Native title is the designation given to the common law doctrine of Aboriginal title in Australia, which is the recognition by Australian law that Indigenous Australians have rights and interests to their land that derive from their traditional laws and customs. The concept recognises that in certain cases there was and is a continued beneficial legal interest in land held by Indigenous peoples which survived the acquisition of radical title to the land by the Crown at the time of sovereignty. Native title can co-exist with non-Aboriginal proprietary rights and in some cases different Aboriginal groups can exercise their native title over the same land.

Mabo v Queensland , was a significant court case decided in the High Court of Australia on 8 December 1988. It found that the Queensland Coast Islands Declaratory Act 1985, which attempted to retrospectively abolish native title rights, was not valid according to the Racial Discrimination Act 1975.
Native title legislation in Australia includes legislation by Commonwealth, state, and territory parliaments of Australia which codifies and modifies common law regarding native title in Australia.
Indigenous land rights are the rights of Indigenous peoples to land and natural resources therein, either individually or collectively, mostly in colonised countries. Land and resource-related rights are of fundamental importance to Indigenous peoples for a range of reasons, including: the religious significance of the land, self-determination, identity, and economic factors. Land is a major economic asset, and in some Indigenous societies, using natural resources of land and sea form the basis of their household economy, so the demand for ownership derives from the need to ensure their access to these resources. Land can also be an important instrument of inheritance or a symbol of social status. In many Indigenous societies, such as among the many Aboriginal Australian peoples, the land is an essential part of their spirituality and belief systems.

Milirrpum v Nabalco Pty Ltd, also known as the Gove land rights case because its subject was land known as the Gove Peninsula in the Northern Territory, was the first litigation on native title in Australia, and the first significant legal case for Aboriginal land rights in Australia, decided on 27 April 1971.

The Native Title Act 1993(Cth) is a law passed by the Australian Parliament, the purpose of which is "to provide a national system for the recognition and protection of native title and for its co-existence with the national land management system". The Act was passed by the Keating government following the High Court's decision in Mabo v Queensland (No 2) (1992). The Act commenced operation on 1 January 1994.

Aboriginal title is a common law doctrine that the land rights of indigenous peoples to customary tenure persist after the assumption of sovereignty under settler colonialism. The requirements of proof for the recognition of aboriginal title, the content of aboriginal title, the methods of extinguishing aboriginal title, and the availability of compensation in the case of extinguishment vary significantly by jurisdiction. Nearly all jurisdictions are in agreement that aboriginal title is inalienable, and that it may be held either individually or collectively.

Yarmirr v Northern Territory was an Australian court case, decided in 2001. It was an application for the determination of native title to seas, sea-bed and sub-soil, over an area in the Northern Territory, ultimately determined on appeal to the High Court of Australia.

A lord paramount is a term of art in feudal law describing an overlord who holds his own fief from no superior lord. It thus describes a person who holds allodial title, owing no socage or feudal obligations such as military service. This was distinguished from a mesne lord who held his own fief from a superior.
Indigenous Australian customary law refers to the legal systems and practices uniquely belonging to Indigenous Australians of Australia, that is, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people.
Indigenous land rights in Australia, also known as Aboriginal land rights in Australia, are the rights and interests in land of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people in Australia; the term may also include the struggle for those rights. Connection to the land and waters is vital in Australian Aboriginal culture and to that of Torres Strait Islander people, and there has been a long battle to gain legal and moral recognition of ownership of the lands and waters occupied by the many peoples prior to colonisation of Australia starting in 1788, and the annexation of the Torres Strait Islands by the colony of Queensland in the 1870s.
The Sagong Tasi case was a landmark land rights case in Malaysia, in which the courts ruled against the Selangor State in favour of the Temuan-Orang Asli plaintiffs.

Mabo: Life of an Island Man is a 1997 Australian documentary film on the life of Indigenous Australian land rights campaigner Eddie Koiki Mabo.
References
- ↑ Williams, David V. (15 April 2021). "Radical Title of the Crown and Aboriginal Title: North America 1763, New South Wales 1788, and New Zealand 1840". Common Law, Civil Law, and Colonial Law. Cambridge University Press. p. 260–285. doi:10.1017/9781108955195.011.
- ↑ Bartlett, Richard (2020). Native Title in Australia (4 ed.). LexisNexis Butterworths. pp. 274–276. ISBN 978-0409350920.
- ↑ Mabo v Queensland (No 2) [1992] HCA 23 at para 50-1, (1992) 175 CLR 1(3 June 1992), High Court.