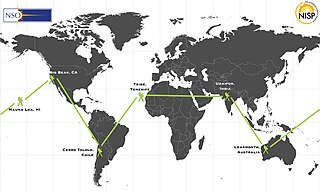
The Radio Solar Telescope Network (RSTN) is a network of solar observatories maintained and operated by the 557th Weather Wing, ACC. The RSTN consists of ground-based observatories in Australia, Italy, Massachusetts, and Hawaii.
The Radio Solar Telescope Network (RSTN) is a network of solar observatories maintained and operated by the 557th Weather Wing, ACC. The RSTN consists of ground-based observatories in Australia, Italy, Massachusetts, and Hawaii.
It became apparent in the early 1960s that certain space weather events might interfere with the stated U.S. objective of a crewed mission to the moon. In particular, the sun emits continuous electromagnetic energy and electrically charged particles, which can cause disturbances in the near-Earth environment and disrupt satellite communications.
Foremost among these concerns was the possibility of a geomagnetic storm of solar origin. Metric Type II radio bursts, signatures of coronal shock waves or coronal mass ejections, were known to be commonly associated with solar flares. The United States Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) was thus assigned the task of developing and validating a network of ground-based solar observatories. AFRL established a worldwide network of sweep frequency recorders from which estimates of the shock speed in the corona could be made. This network, called the Radio Solar Telescope Network (RSTN), uses a bandwidth from 25 MHz to 85 MHz.
The prototype was assembled and operated at the Sagamore Hill Solar Radio Observatory during the early 1960s. The Sagamore Hill Solar Radio Observatory began operating solar patrols in 1966. The Air Force Geophysics Laboratory (AFGL, currently Phillips Lab) transferred operation of the observatory to Detachment 2 of the 2nd Weather Group of the Air Force Weather Agency in October 1978. However, Phillips Lab continues to work in an advisory capacity to the observatory.
The mission of the solar observatories of the RSTN is to monitor solar flares, noise storms and other releases of energy from the sun, and when necessary, notify military and civilian personnel concerned with space, weather, power and communications in countries throughout the world.
The radio and optical observatories are operated by detachments of the 2nd Weather Group, as follows:
The RSTN is complemented in its real-time capability by a radio telescope operated from 25 MHz (the ionospheric cutoff) to 1,800 MHz by the Ionospheric Prediction Service at the Paul Wild Observatory in Culgoora, New South Wales, Australia.

The ionosphere is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about 48 km (30 mi) to 965 km (600 mi) above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. It also affects GPS signals that travel through this layer.

A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other solar phenomena. The occurrence of solar flares varies with the 11-year solar cycle.

Space weather is a branch of space physics and aeronomy, or heliophysics, concerned with the time varying conditions within the Solar System, including the solar wind, emphasizing the space surrounding the Earth, including conditions in the magnetosphere, ionosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. Space weather is distinct from, but conceptually related to, the terrestrial weather of the atmosphere of Earth. The term "space weather" was first used in the 1950s and came into common usage in the 1990s. Later, it was generalized to a "space climate" research discipline, which focuses on general behaviors of longer and larger-scale variabilities and effects.

A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave and/or cloud of magnetic field that interacts with the Earth's magnetic field.

Grote Reber was an American pioneer of radio astronomy, which combined his interests in amateur radio and amateur astronomy. He was instrumental in investigating and extending Karl Jansky's pioneering work, and conducted the first sky survey in the radio frequencies.

The Low-Frequency Array, or LOFAR, is a large radio telescope, with an antenna network located mainly in the Netherlands, and spreading across 7 other European countries as of 2019. Originally designed and built by ASTRON, the Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy, it was first opened by Queen Beatrix of The Netherlands in 2010, and has since been operated on behalf of the International LOFAR Telescope (ILT) partnership by ASTRON.

The Haleakalā Observatory, also known as the Haleakalā High Altitude Observatory Site, is Hawaii's first astronomical research observatory. It is located on the island of Maui and is owned by the Institute for Astronomy of the University of Hawaiʻi, which operates some of the facilities on the site and leases portions to other organizations. Tenants include the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) and the Las Cumbres Observatory Global Telescope Network (LCOGTN). At over 3,050 meters (10,010 ft) in altitude, the summit of Haleakalā is above one third of the Earths's troposphere and has excellent astronomical seeing conditions.

The Paul Wild Observatory, also known as the Narrabri Observatory and Culgoora Observatory, is an astronomical research facility located about 24 km west of Narrabri, New South Wales, Australia. It is the home of the Australia Telescope Compact Array, and the Culgoora Solar Observatory.

The 557th Weather Wing is a United States Air Force formation and its lead military meteorology center. It reports environmental situational awareness worldwide to the Air Force, the United States Army, joint warfighters, Unified Combatant Commands, the national intelligence community, and the Secretary of Defense. It is headquartered at Offutt Air Force Base, in Bellevue, Nebraska.
The Global Oscillation Network Group (GONG) is a worldwide network of six identical telescopes, designed to have 24/7 observations of the Sun. The network serves multiple purposes, including the provision of operation data for use in space weather prediction, and the study of solar internal structure and dynamics using helioseismology.

Haystack Observatory is a multidisciplinary radio science center, ionospheric observatory, and astronomical microwave observatory owned by Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). It is located in Westford, Massachusetts (US), approximately 45 kilometers (28 mi) northwest of Boston. Haystack was initially built by MIT's Lincoln Laboratory for the United States Air Force and was known as Haystack Microwave Research Facility. Construction began in 1960, and the antenna began operating in 1964. In 1970 the facility was transferred to MIT, which then formed the Northeast Radio Observatory Corporation (NEROC) with a number of other universities to operate the site as the Haystack Observatory. As of January 2012, a total of nine institutions participated in NEROC.

The Owens Valley Solar Array (OVSA), also known as Expanded Owens Valley Solar Array (EOVSA), is an astronomical radio telescope array, located at Owens Valley Radio Observatory (OVRO), near Big Pine, California, with main interests in studying the physics of the Sun. The instruments of the observatory are designed and employed specifically for studying the activities and phenomena of our solar system's sun. Other solar dedicated instruments operated on the site include the Solar Radio Burst Locator (SRBL), the FASR Subsystem Testbed (FST), and the Korean SRBL (KSRBL). The OVSA is operated by the New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT), which also operates the Big Bear Solar Observatory.

The 2nd Weather Squadron is an active United States Air Force unit assigned to the 2nd Weather Group of the 557th Weather Wing and is headquartered at Offutt Air Force Base, Nebraska. The squadron's mission is broad and includes the preparation of weather analysis for the intelligence community, observation of space weather, monitoring of volcanic ash, cloud analysis, production of weather broadcasts for the American Forces Network, as well as other tasks. The squadron's personnel is located at seven different sites worldwide.
The Sagamore Hill Solar Radio Observatory is a solar radio observatory located in Hamilton, Massachusetts, that operates on a daily basis to obtain scientific observations of the Sun. It is a functional component of the Radio Solar Telescope Network (RSTN).
The Solar Observing Optical Network (SOON) consists of three U.S. Air Force (USAF) Air Force Weather Agency (AFWA) solar observatories. AFWA operates a solar telescope at each site to monitor solar active regions at optical wavelengths. The National Geophysical Data Center (NGDC) archives histograms of intensity versus area every minute for the active regions. It also archives magnetograms of the magnetic field structure and tachograms of plasma velocities on an irregular schedule.

The POlarization Emission of Millimeter Activity at the Sun (POEMAS) is a solar patrol system composed of two radio telescopes with superheterodyne circular polarization receivers at 45 and 90 GHz. Since their half power beam width is around 1.4°, they observe the full sun. The acquisition system allows to gather 100 values per second at both frequencies and polarizations, with a sensitivity of around 20 solar flux units (SFU) (1 SFU ≡ 104 Jy). The telescope saw first light in November 2011, and showed excellent performance during two years, when it observed many flares. Since November 2013 is stopped for repairing. The main interest of POEMAS is the observation of solar flares in a frequency range where there are very few detectors and fill the gap between microwaves observed with the Radio Solar Telescope Network (1 to 15.4 GHz) and submillimeter observations of the Solar Submillimeter Telescope (212 and 405 GHz). Moreover, POEMAS is the only current telescope capable of carrying on circular polarization solar flare observations at 90 GHz. (Although, in principle, ALMA band 3 may also observe at 90 GHz with circular polarization).
The Space Safety Programme, formerly the Space Situational Awareness (SSA) programme, is the European Space Agency's (ESA) initiative to monitor hazards from space, determine their risk, make this data available to the appropriate authorities and where possible, mitigate the threat.

Solar phenomena are natural phenomena which occur within the atmosphere of the Sun. These phenomena take many forms, including solar wind, radio wave flux, solar flares, coronal mass ejections, coronal heating and sunspots.
Bruny Island Radio Specrometer, or BIRS, was a radio telescope on Bruny Island that was operated privately by Bill Erickson, who was then a research associate at the University of Tasmania. It was designed to measure relatively low frequency radio emissions from the sun; ranging from around 62 MHz down to the lowest possible frequencies that can penetrate the ionosphere, which typically fluctuates between 7 and 13 MHz, but can be as low as 3 MHz. Reliable measurements below 20 MHz are difficult to obtain with ground-based telescopes due to interference, both from local sources and distant ones. BIRS' main purpose was to detect and study coronal type II radio bursts, but has on occasion also measured radio bursts below 3 MHz believed to have originated from Jupiter. In January 2015, BIRS' sustained a hardware failure and has stopped publishing data.

The Nançay Radio Observatory, opened in 1956, is part of Paris Observatory, and also associated with the University of Orléans. It is located in the department of Cher in the Sologne region of France. The station consists of several instruments. Most iconic of these is the large decimetric radio telescope, which is one of the largest radio telescopes in the world. Long established are also the radio heliograph, a T-shaped array, and the decametric array operating at wavelengths between 3 m and 30 m.