Related Research Articles

General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a packet oriented mobile data standard on the 2G and 3G cellular communication network's global system for mobile communications (GSM). GPRS was established by European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) in response to the earlier CDPD and i-mode packet-switched cellular technologies. It is now maintained by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).
The Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a third generation mobile cellular system for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed and maintained by the 3GPP, UMTS is a component of the International Telecommunication Union IMT-2000 standard set and compares with the CDMA2000 standard set for networks based on the competing cdmaOne technology. UMTS uses wideband code-division multiple access (W-CDMA) radio access technology to offer greater spectral efficiency and bandwidth to mobile network operators.
Enhanced 911, E-911 or E911 is a system used in North America to automatically provide the caller's location to 911 dispatchers. 911 is the universal emergency telephone number in the region. In the European Union, a similar system exists known as E112 and known as eCall when called by a vehicle.

A SIM card is an integrated circuit (IC) intended to securely store the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number and its related key, which are used to identify and authenticate subscribers on mobile telephony devices. Technically the actual physical card is known as a universal integrated circuit card (UICC); this smart card is usually made of PVC with embedded contacts and semiconductors, with the SIM as its primary component. In practise the term "SIM card" refers to the entire unit and not simply the IC.
The GPRS core network is the central part of the general packet radio service (GPRS) which allows 2G, 3G and WCDMA mobile networks to transmit IP packets to external networks such as the Internet. The GPRS system is an integrated part of the GSM network switching subsystem.
Network switching subsystem (NSS) is the component of a GSM system that carries out call out and mobility management functions for mobile phones roaming on the network of base stations. It is owned and deployed by mobile phone operators and allows mobile devices to communicate with each other and telephones in the wider public switched telephone network (PSTN). The architecture contains specific features and functions which are needed because the phones are not fixed in one location.
The IP Multimedia Subsystem or IP Multimedia Core Network Subsystem (IMS) is a standardised architectural framework for delivering IP multimedia services. Historically, mobile phones have provided voice call services over a circuit-switched-style network, rather than strictly over an IP packet-switched network. Alternative methods of delivering voice (VoIP) or other multimedia services have become available on smartphones, but they have not become standardized across the industry. IMS is an architectural framework that provides such standardization.
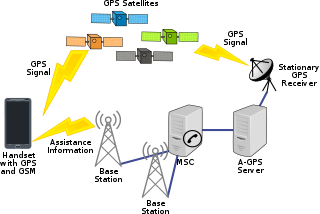
Assisted GNSS (A-GNSS) is a GNSS augmentation system that often significantly improves the startup performance—i.e., time-to-first-fix (TTFF)—of a global navigation satellite system (GNSS). A-GNSS works by providing the necessary data to the device via a radio network instead of the slow satellite link, essentially "warming up" the receiver for a fix. When applied to GPS, it is known as assisted GPS or augmented GPS. Other local names include A-GANSS for Galileo and A-Beidou for BeiDou.
Authentication and Key Agreement (AKA) is a security protocol used in 3G networks. AKA is also used for one-time password generation mechanism for digest access authentication. AKA is a challenge–response based mechanism that uses symmetric cryptography.

Mobile phone tracking is a process for identifying the location of a mobile phone, whether stationary or moving. Localization may be effected by a number of technologies, such as the multilateration of radio signals between (several) cell towers of the network and the phone or by simply using GNSS. To locate a mobile phone using multilateration of mobile radio signals, the phone must emit at least the idle signal to contact nearby antenna towers and does not require an active call. The Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) is based on the phone's signal strength to nearby antenna masts.
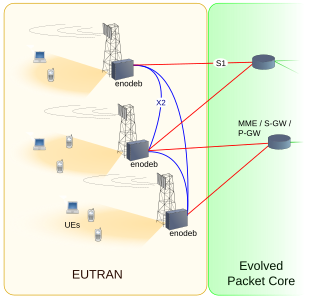
E-UTRA is the air interface of 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Long Term Evolution (LTE) upgrade path for mobile networks. It is an acronym for Evolved Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) Terrestrial Radio Access, also referred to as the 3GPP work item on the Long Term Evolution (LTE) also known as the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) in early drafts of the 3GPP LTE specification. E-UTRAN is the initialism of Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network and is the combination of E-UTRA, user equipment (UE), and E-UTRAN Node B or Evolved Node B (eNodeB).
Generic Access Network (GAN) is a protocol that extends mobile voice, data and multimedia applications over IP networks. Unlicensed Mobile Access (UMA) is the commercial name used by mobile carriers for external IP access into their core networks. The latest generation system is named Wi-Fi calling or VoWiFi by a number of handset manufacturers, including Apple and Samsung, a move that is being mirrored by carriers like T-Mobile US and Vodafone. The service is dependent on IMS, IPsec, IWLAN and ePDG.

In telecommunications, a femtocell is a small, low-power cellular base station, typically designed for use in a home or small business. A broader term which is more widespread in the industry is small cell, with femtocell as a subset. It connects to the service provider's network via broadband ; current designs typically support four to eight simultaneously active mobile phones in a residential setting depending on version number and femtocell hardware, and eight to sixteen mobile phones in enterprise settings. A femtocell allows service providers to extend service coverage indoors or at the cell edge, especially where access would otherwise be limited or unavailable. Although much attention is focused on WCDMA, the concept is applicable to all standards, including GSM, CDMA2000, TD-SCDMA, WiMAX and LTE solutions.
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receivers, using the GPS, GLONASS, Galileo or BeiDou system, are used in many applications. The first systems were developed in the 20th century, mainly to help military personnel find their way, but location awareness soon found many civilian applications.

Generic Bootstrapping Architecture (GBA) is a technology that enables the authentication of a user. This authentication is possible if the user owns a valid identity on an HLR or on an HSS.
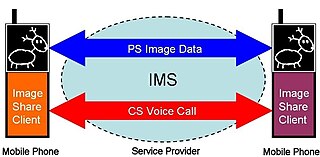
Image Share is a service for sharing images between users during a mobile phone call. It has been specified for use in a 3GPP-compliant cellular network by the GSM Association in the PRD IR.79 Image Share Interoperability Specification.
Enhanced Observed Time Difference (E-OTD) is a standard for the location of mobile telephones. The location method works by multilateration. The standardisation was first carried out for GSM by the GSM standard committees in LCS Release 98 and Release 99. The standardisation was continued for 3G and WCDMA mobile telephones by 3GPP.
For mobile telecommunications, the Charging Data Record (CDR) is, in 3GPP parlance, a formatted collection of information about a chargeable telecommunication event.
The Mobile Location Protocol (MLP) is an application-level protocol for receiving the position of Mobile Stations independent of underlying network technology.
OTDOA is a positioning feature introduced in rel9 E-UTRA. It's a multilateration method in which the User Equipment (UE) measures the time difference between some specific signals from several eNodeBs and reports these time differences to a specific device in the network. The ESMLC based on these time differences and knowledge of the enodeBs locations calculates the UEs' position.