
Pepin Iof Landen, also called the Elder or the Old, was the Mayor of the palace of Austrasia under the Merovingian King Dagobert I from 623 to 629. He was also the Mayor for Sigebert III from 639 until his death.

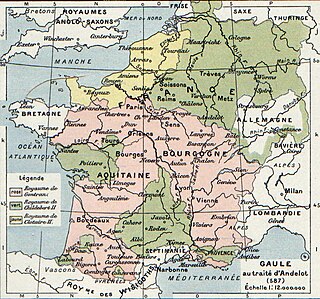
Austrasia was the northeastern kingdom within the core of the Frankish Empire during the Early Middle Ages, centring on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers. It included the original Frankish-ruled territories within what had been the northernmost part of Roman Gaul, and cities such as Cologne, Trier and Metz. It also stretched beyond the old Roman borders on the Rhine into Frankish areas which had never been formally under Roman rule. It came into being as a part of the Frankish Empire founded by Clovis I (481–511). At the same time, the initial powerbase of Clovis himself was the more Romanized part of northern Gaul, lying southwest of Austrasia, which came to be known as Neustria.

Chlothar II, sometimes called "the Young", was king of the Franks, ruling Neustria (584–629), Burgundy (613–629) and Austrasia (613–623).

Neustria was the western part of the Kingdom of the Franks during the Early Middle Ages, in contrast to the eastern Frankish kingdom, Austrasia. It initially included land between the Loire and the Silva Carbonaria, in the north of present-day France, with Paris, Orléans, Tours, Soissons as its main cities.

Chilperic I was the king of Neustria from 561 to his death. He was one of the sons of the Frankish king Clotaire I and Queen Aregund.

Chlothar III was King of the Franks, ruling in Neustria and Burgundy from 657 to his death. He also briefly ruled Austrasia.

Childebert II (c.570–596) was the Merovingian king of Austrasia from 575 until his death in March 596, and the king of Burgundy from 592 to his death, as the adopted son of his uncle Guntram.
Under the Merovingian dynasty, the mayor of the palace or majordomo. (Latin: maior palatii or maior domus) was the manager of the household of the Frankish king. He was the head of the Merovingian administrative ladder and orchestrated the operation of the entire court. He was appointed by the king from among the magnates, the most powerful families. Austrasia, Neustria and Burgundy had their own mayor of the palace. After Chlothar II, who ruled over the entire Frankish Kingdom, had ordered the execution of Warnachar, the mayor of Burgundy, the magnates of Burgundy declared in 626 not to want their own mayor anymore; see Fredegar IV.54. This declaration marks the effective end of the Burgundian court and the beginning of the Neustrian-Burgundian political alliance against Austrasian influence. The Austrasian magnates revolted and the Battle of Tertry of 687 became the Austrasian victory with Pepin of Herstal as their leader and the new mayor of the palace.

The Kingdom of the Franks, also known as the Frankish Kingdom, the Frankish Empire or Francia, was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Frankish Merovingian and Carolingian dynasties during the Early Middle Ages. Francia was among the last surviving Germanic kingdoms from the Migration Period era.

Sigebert I was a Frankish king of Austrasia from the death of his father in 561 to his own death. He was the third surviving son out of four of Clotaire I and Ingund. His reign found him mostly occupied with a successful civil war against his half-brother, Chilperic.

Sigebert III was the Merovingian king of Austrasia from 633 to his death around 656. He was described as the first Merovingian roi fainéant —do-nothing king—, in effect the mayor of the palace ruling the kingdom throughout his reign. However he lived a pious Christian life and was later sanctified, being remembered as Saint Sigebert of Austrasia in the Roman Catholic Church and Eastern Orthodox Church.
Brunhilda was queen consort of Austrasia, part of Francia, by marriage to the Merovingian king Sigebert I of Austrasia, and regent for her son, grandson and great-grandson.

Charibert II, a son of Clotaire II and his junior wife Sichilde, was briefly King of Aquitaine from 629 to his death, with his capital at Toulouse. There are no direct statements about when Charibert was born exactly, the only known fact being that he was "a few years younger" than his half-brother Dagobert. His father Clotaire evidently had a bigamous marriage and he was the offspring of the junior wife.

Sigebert II (601–613) or Sigisbert II, was the illegitimate son of Theuderic II, from whom he inherited the kingdoms of Burgundy and Austrasia in 613. However, he fell under the influence of his great-grandmother, Brunhilda.
Theuderic II, king of Burgundy (595–613) and Austrasia (612–613), was the second son of Childebert II. At his father's death in 595, he received Guntram's kingdom of Burgundy, with its capital at Orléans, while his elder brother, Theudebert II, received their father's kingdom of Austrasia, with its capital at Metz. He also received the lordship of the cities (civitates) of Toulouse, Agen, Nantes, Angers, Saintes, Angoulême, Périgueux, Blois, Chartres, and Le Mans. During his minority, and later, he reigned under the guidance of his grandmother Brunhilda, evicted from Austrasia by his brother Theudebert II.

Audoin, venerated as Saint Audoin, was a Frankish bishop, courtier, hagiographer and saint. He authored Vita Sancti Eligii which outlines the life and deeds of Eligius, his close friend and companion in the royal court and the Church.
Warnachar was the mayor of the palace of Burgundy (617-626) and briefly Austrasia (612-617). He began his career as the regent during Theuderic II's minority (596-c.604). In 612, when Theuderic became king of Austrasia, he became mayor of the palace. In 613, he allied with King Clotaire II of Neustria, feeling that the young Sigebert II should not be under the hated Brunhilda's influence. He betrayed Brunhilda into Clotaire's hands by instructing the army not to oppose the invading Neustrian. When Clotaire then became sole king of the Franks, he left Warnachar in power in Austrasia briefly, but confirmed at Bonneuil-sur-Marne, in 617, Warnachar's function in Burgundy until his death in 626. His son, Godinus, succeeded him.
Godinus succeeded his father Warnachar as mayor of the palace of Burgundy in 626 and held that post until 627. He married his stepmother Bertha and the king, Clotaire II, hunted him down for this. He fled to the court of Dagobert I, the king's son, in Austrasia, but Clotaire found him in Chartres and executed him.

Saint Chlodulf was bishop of Metz approximately from 657 to 697.

Reuil-en-Brie is a commune in the Seine-et-Marne department in the Île-de-France region in north-central France.















