
A watch is a portable timepiece intended to be carried or worn by a person. It is designed to keep a consistent movement despite the motions caused by the person's activities. A wristwatch is designed to be worn around the wrist, attached by a watch strap or other type of bracelet, including metal bands, leather straps, or any other kind of bracelet. A pocket watch is designed for a person to carry in a pocket, often attached to a chain.
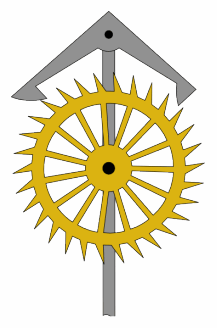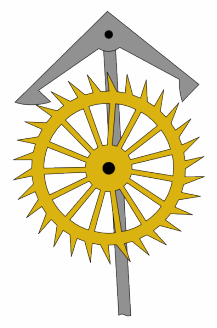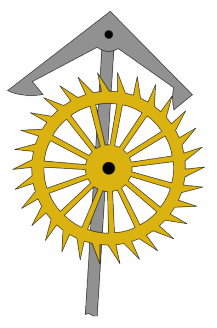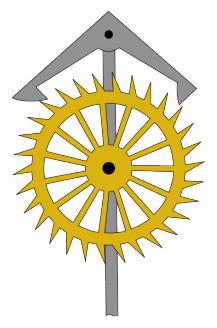
An escapement is a mechanical linkage in mechanical watches and clocks that gives impulses to the timekeeping element and periodically releases the gear train to move forward, advancing the clock's hands. The impulse action transfers energy to the clock's timekeeping element to replace the energy lost to friction during its cycle and keep the timekeeper oscillating. The escapement is driven by force from a coiled spring or a suspended weight, transmitted through the timepiece's gear train. Each swing of the pendulum or balance wheel releases a tooth of the escapement's escape wheel, allowing the clock's gear train to advance or "escape" by a fixed amount. This regular periodic advancement moves the clock's hands forward at a steady rate. At the same time, the tooth gives the timekeeping element a push, before another tooth catches on the escapement's pallet, returning the escapement to its "locked" state. The sudden stopping of the escapement's tooth is what generates the characteristic "ticking" sound heard in operating mechanical clocks and watches.

The Waltham Watch Company, also known as the American Waltham Watch Co. and the American Watch Co., was a company that produced about 40 million watches, clocks, speedometers, compasses, time delay fuses, and other precision instruments in the United States of America between 1850 and 1957. The company's historic 19th-century manufacturing facilities in Waltham, Massachusetts have been preserved as the American Waltham Watch Company Historic District.

Aaron Lufkin Dennison was an American watchmaker and businessman who founded a number of companies.

Webster Clay Ball was a jeweler and watchmaker born in Fredericktown, Ohio, who founded the Ball Watch Company. When Standard Time was adopted in 1883, he was the first jeweler to use time signals from the United States Naval Observatory, bringing accurate time to Cleveland.

A pocket watch is a watch that is made to be carried in a pocket, as opposed to a wristwatch, which is strapped to the wrist.

The Elgin National Watch Company, commonly known as Elgin Watch Company, was a major US watch maker from 1864 to 1968. The company sold watches under the names Elgin, Lord Elgin, and Lady Elgin.

ETA SA Manufacture Horlogère Suisse designs and manufactures quartz watches and both hand-wound and automatic-winding mechanical ébauches and movements. Commonly referred to as ETA, the company is headquartered in Grenchen, Switzerland, and is a wholly owned subsidiary of The Swatch Group.

A balance wheel, or balance, is the timekeeping device used in mechanical watches and small clocks, analogous to the pendulum in a pendulum clock. It is a weighted wheel that rotates back and forth, being returned toward its center position by a spiral torsion spring, known as the balance spring or hairspring. It is driven by the escapement, which transforms the rotating motion of the watch gear train into impulses delivered to the balance wheel. Each swing of the wheel allows the gear train to advance a set amount, moving the hands forward. The balance wheel and hairspring together form a harmonic oscillator, which due to resonance oscillates preferentially at a certain rate, its resonant frequency or "beat", and resists oscillating at other rates. The combination of the mass of the balance wheel and the elasticity of the spring keep the time between each oscillation or "tick" very constant, accounting for its nearly universal use as the timekeeper in mechanical watches to the present. From its invention in the 14th century until tuning fork and quartz movements became available in the 1960s, virtually every portable timekeeping device used some form of balance wheel.

In horology, a tourbillon is an addition to the mechanics of a watch escapement to increase accuracy, it was developed by the Swiss-French watchmaker Abraham-Louis Breguet and patented by Breguet on 26 June 1801. In a tourbillon the escapement and balance wheel are mounted in a rotating cage, with the goal of eliminating errors of poise in the balance giving a uniform weight.

John Arnold was an English watchmaker and inventor.

The Hamilton Watch Company is a Swiss manufacturer of wristwatches based in Bienne, Switzerland. Founded in 1892 as an American firm, the Hamilton Watch Company ended American manufacture in 1969. Through a series of mergers and acquisitions, the Hamilton Watch Company eventually became integrated into the Swatch Group, the world's largest watch manufacturing and marketing conglomerate.

The history of watches began in 16th-century Europe, where watches evolved from portable spring-driven clocks, which first appeared in the 15th century.

A mechanical watch is a watch that uses a clockwork mechanism to measure the passage of time, as opposed to quartz watches which function using the vibration modes of a piezoelectric quartz tuning fork, or radio watches, which are quartz watches synchronized to an atomic clock via radio waves. A mechanical watch is driven by a mainspring which must be wound either periodically by hand or via a self-winding mechanism. Its force is transmitted through a series of gears to power the balance wheel, a weighted wheel which oscillates back and forth at a constant rate. A device called an escapement releases the watch's wheels to move forward a small amount with each swing of the balance wheel, moving the watch's hands forward at a constant rate. The escapement is what makes the 'ticking' sound which is heard in an operating mechanical watch. Mechanical watches evolved in Europe in the 17th century from spring powered clocks, which appeared in the 15th century.

A marine chronometer is a precision timepiece that is carried on a ship and employed in the determination of the ship's position by celestial navigation. It is used to determine longitude by comparing Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), and the time at the current location found from observations of celestial bodies. When first developed in the 18th century, it was a major technical achievement, as accurate knowledge of the time over a long sea voyage was vital for effective navigation, lacking electronic or communications aids. The first true chronometer was the life work of one man, John Harrison, spanning 31 years of persistent experimentation and testing that revolutionized naval navigation.

A chronometer is an extraordinarily accurate mechanical timepiece, with an original focus on the needs of maritime navigation. In Switzerland, timepieces certified by the Contrôle Officiel Suisse des Chronomètres (COSC) may be marked as Certified Chronometer or Officially Certified Chronometer. Outside Switzerland, equivalent bodies, such as the Japan Chronometer Inspection Institute, have in the past certified timepieces to similar standards, although use of the term has not always been strictly controlled.

Gallet (ˈgæl.eɪ) is a historic Swiss manufacturer of high-end timepieces for professional, military, sports, racing, and aviation use. Gallet is the world's oldest clock making house with history dating back to Humbertus Gallet, a clock maker who became a citizen of Geneva in 1466. The Gallet & Cie name was officially registered by Julien Gallet (1806–1849) in 1826, who moved the family business from Geneva to La Chaux-de-Fonds, Switzerland. Prior to this date, operations commenced under the name of each of the Gallet family patriarchs.
Regina pocket watches were a brand of pocket watches made by Omega that were popular in the early 1900s. The name Regina Pocket Watch was originally trademarked by LOUIS MAIER in Bienne Switzerland in 1888. The name was then trademarked by Omega in 1911, indicating that they bought the company at that time. The faces and mechanisms were imported into New York and assembled with cases in Ontario, for sale mostly in Canada.
















