
The Railway Vehicle Preservation Society (Gesellschaft zur Erhaltung von Schienenfahrzeugen e.V. or GES) is one of the oldest societies in Germany that runs a museum railway. The headquarters of the GES is in Stuttgart.

The Railway Vehicle Preservation Society (Gesellschaft zur Erhaltung von Schienenfahrzeugen e.V. or GES) is one of the oldest societies in Germany that runs a museum railway. The headquarters of the GES is in Stuttgart.
The society was founded on 8 December 1965 by a group of tramway fans within the so-called Verkehrsfreunde Stuttgart society, that had signed up for the preservation and care of the last remaining railcar, no. 126, from the former Filderbahn as well as other historically valuable trams. After the Stuttgart Tram Company (Stuttgarter Straßenbahnen or SSB) had shown no interest in building up a museum collection and the Filderbahn railcar 126 could only be preserved by keeping it at Ludwigsburg, the GES turned at the end of the 1960s to the more promising theme of opening a railway. The engagement of the GES for the preservation and subsequent restoration of the Filderbahn wagon laid the foundation stone for the present-day collection of the Stuttgarter Historische Straßenbahnen .
The GES runs regular museum railway operations using the historical train consists Feuriger Elias ('Fiery Elias') and Sofazügle (literally: 'Little Sofa Train'). Due to the ban on steam locomotives issued by the Deutsche Bundesbahn between 1977 and 1985 the operations were restricted to private railway lines on the Strohgäubahn from Korntal-Münchingen to Weissach or the Tälesbahn between Nürtingen and Neuffen. The trains continue to have this as their there today. To begin with, special trips were also run on the WEG routes from Enz Nord to Enzweihingen and, up to 1982, on the Filderbahn between Stuttgart-Möhringen, Stuttgart-Vaihingen, Leinfelden and Neuhausen auf den Fildern. From 1985 specials were also offered on other routes in the Stuttgart area.


The GES has a cultural monument to the state of Baden-Württemberg: the Hohenzollern train. It comprises vehicles that were operated by the Hohenzollern Branch Line Company (Hohenzollerischen Kleinbahn Gesellschaft, from 1907 the Hohenzollerische Landesbahn). The majority of these are deployed in museum railway services on the Tälesbahn as part of the Sofazügle.
| Vehicle: | Manufacturer: | Built: | Status: |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steam locomotive 11 | Maschinenfabrik Esslingen | 1911 | Operational |
| Steam locomotive 16 (formerly KOE no. 11, DRG 92 442) | AEG | 1928 | Operational |
| Passenger coach 3 | Beuchelt & Co. | 1900 | Operational |
| Passenger coach 6 | Beuchelt & Co. | 1900 | Operational |
| Passenger coach 7 | Beuchelt & Co. | 1900 | Stored |
| Passenger coach 9 | Beuchelt & Co. | 1900 | Being restored |
| Passenger coach 21 | Waggonfabrik Rastatt | 1908 | Operational |
| Passenger coach 22 | Waggonfabrik Rastatt | 1908 | Operational |
| Passenger coach 24 | Waggonfabrik Rastatt | 1908 | Stored |
| Passenger coach 26 | Waggonfabrik Rastatt | 1908 | Stored |
| Luggage van 73 | Beuchelt & Co. | 1900 | Operational |
| Luggage van 74 | Beuchelt & Co. | 1900 | Being restored |
| Luggage van 77 | Beuchelt & Co. | 1900 | Operational |
| Number | Type/Builder | Built/class | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 3636 | MBA, later O&K | 1941 | Operational |
| 39 079 Stg | Spantenwagen [1] /ÖBB | 2nd class | Operational |
| 34 531 Stg | Spantenwagen/ÖBB | 2nd class | Operational |
| 39 692 Stg | Spantenwagen/ÖBB | Dining car | Operational |
| 39 439 Stg | Spantenwagen/ÖBB | 1st class | Operational |
| 39 433 Stg | Spantenwagen/ÖBB | 2nd class | Operational |
| 39 425 Stg | Spantenwagen/ÖBB | 2nd class | Operational |
| 114 535 Stg | Spantenwagen/ÖBB | Luggage van | Operational |
| 235 610 | Oppeln | G-Wagen | Operational |
| V100 1357 | Maschinenfabrik Esslingen | 1962 | Operational (with EMN Kornwestheim) |
The GES is[ when? ] working on restoring a Württemberg T 3 (K.W.St.E no. 930 and DRG no. 89 363).

Baden-Württemberg, commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants as of 2019 across a total area of nearly 35,752 km2 (13,804 sq mi), it is the third-largest German state by both area and population. As a federated state, Baden-Württemberg is a partly-sovereign parliamentary republic. The largest city in Baden-Württemberg is the state capital of Stuttgart, followed by Mannheim and Karlsruhe. Other major cities are Freiburg im Breisgau, Heidelberg, Heilbronn, Pforzheim, Reutlingen, Tübingen, and Ulm.

The Stuttgart Rack Railway is an electric rack railway in Stuttgart, Germany. It is the only urban rack railway in Germany, and one of only four rack railways operating in Germany, along with the Bavarian Zugspitze Railway, the Drachenfels Railway and the Wendelstein Railway.

Stuttgarter Straßenbahnen AG (SSB) is the principal public transport operating company in the German city of Stuttgart. The SSB is a member of the Verkehrs- und Tarifverbund Stuttgart (VVS), and operates the Stuttgart Stadtbahn, bus lines, a rack railway, and a funicular railway.

The Verkehrs- und Tarifverbund Stuttgart GmbH is a transport association that coordinates the local public transport in Stuttgart, the capital of Baden-Württemberg, as well as in the neighbouring districts of Böblingen, Esslingen, Ludwigsburg and Rems-Murr, and parts of Göppingen and Ostalbkreis. The network ensures uniform conditions of carriage and fare regulations as well as a coordinated timetable. It cooperates with the administrative districts and municipalities as well as the Verband Region Stuttgart.

Waggonfabrik Rastatt is a German public-limited company based in Rastatt in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southwestern Germany. Its chief products are tramway vehicles and railway coaches and wagons. The firm was founded in 1897 and built, for example, tramways for the Upper Rhine Railway Company, Karlsruhe Transport Company and Stuttgart Tramways. In its early days it also built rolling stock for the Grand Duchy of Baden State Railways.

Maschinenfabrik Esslingen (ME), was a German engineering firm that manufactured locomotives, tramways, railway wagons, roll-blocks, technical equipment for the railways,, bridges, steel structures, pumps and boilers.

The Ulm Railway Society is a German society for encouraging the preservation of historically valuable railway stock. It is based in the vicinity of Ulm, a city in the state of Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. The society was founded in 1969, has about 600 members and around 12 steam locomotives as well as numerous historical wagons.

The Württemberg T 3s were German steam locomotives with the Royal Württemberg State Railways delivered between 1891 and 1913.
The eurovapor is a European society of railway fans dedicated to the preservation of steam locomotives and historic railway vehicles.
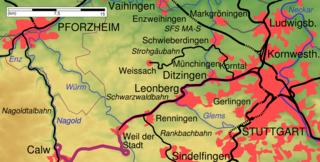
The Black Forest Railway —also known as the Württembergische Schwarzwaldbahn to distinguish it from the railway of the same name in Baden—is a railway line in southern Germany from Stuttgart to Calw, passing through the foothills of the Black Forest, that was opened in stages between 1868 and 1872.

The Krauss-Maffei ML 500 C industrial and works locomotive was built between 1954 and 1966 by Krauss-Maffei.
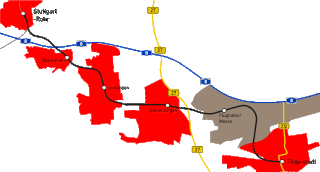
The Stuttgart-Rohr–Filderstadt line is an electrified, and mostly double-track line main railway in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It branches in the Stuttgart district of Rohr from the Stuttgart–Horb railway and runs via Oberaichen, Leinfelden, Echterdingen and Stuttgart Airport to Bernhausen, a district of Filderstadt. It is now part of the Stuttgart S-Bahn.

Filderstadt station is the end point of the railway from Stuttgart-Rohr. Line S 2 of the Stuttgart S-Bahn terminates here.

Vaihingen station is located on the Stuttgart–Horb railway in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is served by regional services and Stuttgart S-Bahn lines S1, S2 and S3. It is also a hub for public transport to the Filder plain.
The Upper Rhine Railway Company, was a railway infrastructure company and transport company based in Mannheim, Germany.

Neuwirtshaus (Porscheplatz) station is on the Stuttgart S-Bahn in the Stuttgart district of Zuffenhausen in the German state of Baden-Württemberg.

Obertürkheim station is located in the Stuttgart district of Obertürkheim in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located at the 9.3 kilometer mark of the Fils Valley Railway and is a station on the network of Stuttgart S-Bahn.The station building is a listed building, which now houses apartments and shops.

Echterdingen station is located in Leinfelden-Echterdingen at the 22.7 kilometre point of the Stuttgart-Rohr–Filderstadt railway in the German state of Baden-Württemberg and is a station on the Stuttgart S-Bahn network.

The Oberaargau-Jura Railways was a former railway company in Switzerland. It was created in 1958 from the merger of the Langenthal-Jura Railway with the Langenthal–Melchnau-Bahn. The name refers to the Oberaargau and the Swiss Jura. The OJB changed its name to Regionalverkehr Oberaargau on 2 July 1990.