Related Research Articles

Prenatal care, also known as antenatal care, is a type of preventive healthcare. It is provided in the form of medical checkups, consisting of recommendations on managing a healthy lifestyle and the provision of medical information such as maternal physiological changes in pregnancy, biological changes, and prenatal nutrition including prenatal vitamins, which prevents potential health problems throughout the course of the pregnancy and promotes the mother and child's health alike. The availability of routine prenatal care, including prenatal screening and diagnosis, has played a part in reducing the frequency of maternal death, miscarriages, birth defects, low birth weight, neonatal infections and other preventable health problems.

Fiona Juliet Stanley is an Australian epidemiologist noted for her public health work, her research into child and maternal health as well as birth disorders such as cerebral palsy. Stanley is the patron of the Telethon Kids Institute and a distinguished professorial fellow in the School of Paediatrics and Child Health at the University of Western Australia. From 1990 to December 2011 she was the founding director of Telethon Kids.
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can often result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term is in contrast to miscarriage, which is an early pregnancy loss, and Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, where the baby dies a short time after being born alive.
A cohort study is a particular form of longitudinal study that samples a cohort, performing a cross-section at intervals through time. It is a type of panel study where the individuals in the panel share a common characteristic.

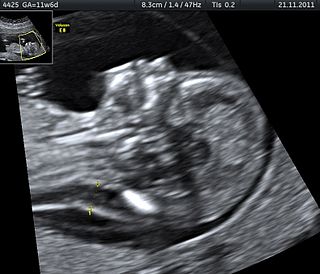
Obstetric ultrasonography, or prenatal ultrasound, is the use of medical ultrasonography in pregnancy, in which sound waves are used to create real-time visual images of the developing embryo or fetus in the uterus (womb). The procedure is a standard part of prenatal care in many countries, as it can provide a variety of information about the health of the mother, the timing and progress of the pregnancy, and the health and development of the embryo or fetus.
In obstetrics, gestational age is a measure of the age of a pregnancy taken from the beginning of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP), or the corresponding age of the gestation as estimated by a more accurate method, if available. Such methods include adding 14 days to a known duration since fertilization, or by obstetric ultrasonography. The popularity of using this measure of pregnancy is largely due to convenience: menstruation is usually noticed, while there is generally no convenient way to discern when fertilization or implantation occurred.

The Framingham Heart Study is a long-term, ongoing cardiovascular cohort study of residents of the city of Framingham, Massachusetts. The study began in 1948 with 5,209 adult subjects from Framingham, and is now on its third generation of participants. Prior to the study almost nothing was known about the epidemiology of hypertensive or arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Much of the now-common knowledge concerning heart disease, such as the effects of diet, exercise, and common medications such as aspirin, is based on this longitudinal study. It is a project of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, in collaboration with Boston University. Various health professionals from the hospitals and universities of Greater Boston staff the project.
A longitudinal study is a research design that involves repeated observations of the same variables over long periods of time. It is often a type of observational study, although it can also be structured as longitudinal randomized experiment.

Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Obstetrical bleeding is bleeding in pregnancy that occurs before, during, or after childbirth. Bleeding before childbirth is that which occurs after 24 weeks of pregnancy. Bleeding may be vaginal or less commonly into the abdominal cavity. Bleeding which occurs before 24 weeks is known as early pregnancy bleeding.
The Telethon Kids Institute is an Australian medical research institute focused on the prevention of paediatric disease and the development of improved treatments to improve the health and wellbeing of children. Telethon Kids has developed a particular focus on Aboriginal health and has more than 500 staff, post-graduate students and visiting scholars. Telethon Kids is located in the Perth suburb of Nedlands, in the Perth Children's Hospital building. Telethon Kids is an independent not-for-profit, non-government organisation with close affiliations with the University of Western Australia and the Perth Children's Hospital. It is named after the Channel Seven Perth Telethon.
Postterm pregnancy is when a woman has not yet delivered her baby after 42 weeks of gestation, two weeks beyond the typical 40-week duration of pregnancy. Postmature births carry risks for both the mother and the baby, including fetal malnutrition, meconium aspiration syndrome, and stillbirths. After the 42nd week of gestation, the placenta, which supplies the baby with nutrients and oxygen from the mother, starts aging and will eventually fail. Postterm pregnancy is a reason to induce labor.
The Joondalup Family Health Study (JFHS) will be an extensively characterized, community-based cohort study, which will investigate the complex interplay of environmental, lifestyle and genetic components that affect the risk of common conditions such as asthma, heart disease and diabetes. The Study will take place in Joondalup, Western Australia and will have a strong focus on families and the health of both children and adults.

James William Bruce Douglas was a British social researcher. Douglas was responsible for the National Survey of Health & Development that in turn led to other national birth cohort studies, such as the National Child Development Study, the 1970 British Cohort Study and the Millennium Cohort Study.

The Environmental Determinants of Islet Autoimmunity (ENDIA) Study is an Australian prospective pregnancy cohort study investigating the environmental triggers responsible for the autoimmune process that leads to type 1 diabetes. The study is led by Professor Jennifer Couper from the University of Adelaide in South Australia with collaborators from the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Monash University and Monash Medical Centre in Victoria, the University of NSW and the Children's Hospital at Westmead, the Royal Hospital for Women and St. George's Hospital in NSW, the University of Queensland and Mater Health Services in Queensland, and the University of Western Australia and Princess Margaret Hospital for Children in Western Australia.
The Raine Medical Research Foundation funds medical research in Western Australia. It was created from a bequest by Mary Raine to the University of Western Australia (UWA) following the death of her husband, Arnold Yeldham (Joe) Raine in 1957.

Melissa Anne Wake MBChB MD FRACP FAHMS is a New Zealand paediatrician and Scientific Director of the Generation Victoria initiative, aiming to create very large, parallel whole-of-state birth and parent cohorts in Victoria, Australia, for Open Science discovery and interventional research. She is Group Leader of the Murdoch Children's Research Institute’s Prevention Innovation Research Group and holds Professorial positions with the University of Melbourne and the University of Auckland.

The Pregnancy Outcome Prediction (POP) Study is a prospective cohort study of 4,512 women who have never given birth, recruited at the Rosie Hospital between January 2008 and July 2012.
Dame Lyn Susan Chitty is a British physician and Professor of Genetics and Fetal Medicine at University College London. She is the deputy director of the National Institute for Health and Care Research Great Ormond Street Hospital Biomedical Research Centre. She is the 2022 president of the International Society for Prenatal Diagnosis. Her research considers non-invasive prenatal diagnostics. She was made a Dame in the 2022 New Year Honours.
Annettee Olivia Nakimuli is a Ugandan obstetrician, gynecologist, medical researcher, academic and academic administrator. Since 17 February 2021, she serves as the Dean of Makerere University School of Medicine, the oldest medical school in East Africa. She concurrently serves as the Head of Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at the same medical school, a role she has served in since 2016. She is also the President of the East, Central and Southern Africa College of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
References
- ↑ "Long may kids' health study Raine | Health+Medicine". health.thewest.com.au. Archived from the original on 2017-12-27. Retrieved 2017-10-30.
- ↑ Wahlquist, Calla (September 30, 2015). "Researchers call for WHO review after one-seventh meet 'normal' sperm count". The Guardian . Archived from the original on 2017-12-27. Retrieved October 14, 2017.
- 1 2 "Perth researchers leading the way in preventing pre-term childbirth". ABC News. June 24, 2015. Archived from the original on 2016-12-24. Retrieved October 14, 2017.
- ↑ Straker, Leon; Mountain, Jenny; Jacques, Angela; White, Scott; Smith, Anne; Landau, Louis; Stanley, Fiona; Newnham, John; Pennell, Craig; Eastwood, Peter (2017). "Cohort Profile: The Western Australian Pregnancy Cohort (Raine) Study–Generation 2". International Journal of Epidemiology. 46 (5): 1384–1385j. doi:10.1093/ije/dyw308. PMC 5837608 . PMID 28064197.
- ↑ Newnham, J. P.; Evans, S. F.; Michael, C. A.; Stanley, F. J.; Landau, L. I. (9 October 1993). "Effects of frequent ultrasound during pregnancy: a randomised controlled trial". The Lancet. 342 (8876): 887–891. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(93)91944-H. PMID 8105165. S2CID 11763088.
- ↑ McKnight, Charlotte M.; Newnham, John P.; Stanley, Fiona J.; Mountain, Jenny A.; Landau, Louis I.; Beilin, Lawrence J.; Puddey, Ian B.; Pennell, Craig E.; Mackey, David A. (10 December 2012). "Birth of a cohort — the first 20 years of the Raine study". The Medical Journal of Australia. 197 (11): 608–610. doi:10.5694/mja12.10698. PMID 23230915. S2CID 43704496.