A Trombe wall is a massive equator-facing wall that is painted a dark color in order to absorb thermal energy from incident sunlight and covered with a glass on the outside with an insulating air-gap between the wall and the glaze. A Trombe wall is a passive solar building design strategy that adopts the concept of indirect-gain, where sunlight first strikes a solar energy collection surface which covers thermal mass located between the Sun and the space. The sunlight absorbed by the mass is converted to thermal energy (heat) and then transferred into the living space.
Environmental design is the process of addressing surrounding environmental parameters when devising plans, programs, policies, buildings, or products. It seeks to create spaces that will enhance the natural, social, cultural and physical environment of particular areas. Classical prudent design may have always considered environmental factors; however, the environmental movement beginning in the 1940s has made the concept more explicit.

Pierre Francis Koenig was an American architect and a Professor of Architecture at the University of Southern California. He taught at the USC School of Architecture from 1964 until his death in 2004. He was the director of the undergraduate building science program from 1980 to 2004. He lectured widely at other universities, and received more than 20 awards for his work. The architecture of Pierre Koenig was the subject of the book "Pierre Koenig" written by James Steele in 1998. Also in 1998, Koenig was elevated to "Distinguished Professor" after 35 years on the USC faculty. He received the USC Distinguished Alumni Award and the Gold Medal from the Los Angeles chapter of the American Institute of Architects.

Steve Baer is an American inventor and pioneer of passive solar technology. Baer helped popularize the use of Zomes. He took a number of solar power patents, wrote a number of books and publicized his work. Baer served on the board of directors of the U.S. Section of the International Solar Energy Society, and on the board of the New Mexico Solar Energy Association. He was the founder, chairman of the board, president, and director of research at Zomeworks Corporation.

Passive house is a voluntary standard for energy efficiency in a building, which reduces the building's ecological footprint. It results in ultra-low energy buildings that require little energy for space heating or cooling. A similar standard, MINERGIE-P, is used in Switzerland. The standard is not confined to residential properties; several office buildings, schools, kindergartens and a supermarket have also been constructed to the standard. Passive design is not an attachment or supplement to architectural design, but a design process that integrates with architectural design. Although it is principally applied to new buildings, it has also been used for refurbishments.

Sustainable architecture is architecture that seeks to minimize the negative environmental impact of buildings through improved efficiency and moderation in the use of materials, energy, development space and the ecosystem at large. Sustainable architecture uses a conscious approach to energy and ecological conservation in the design of the built environment.

A Zero Energy Building (ZEB), also known as a Net Zero Energy (NZE) building, or a Zero Net Energy (ZNE) building, is a building with net zero energy consumption, meaning the total amount of energy used by the building on an annual basis is equal to the amount of renewable energy created on the site or in other definitions by renewable energy sources offsite, using technology such as heat pumps, high efficiency windows and insulation, and solar panels. The goal is that these buildings contribute less overall greenhouse gas to the atmosphere during operations than similar non-ZNE buildings. They do at times consume non-renewable energy and produce greenhouse gases, but at other times reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas production elsewhere by the same amount. Zero-energy buildings are not only driven by a want to have less of an impact on the environment, but they are also driven by money. Tax breaks as well as savings on energy costs make Zero-energy buildings financially viable. A similar concept approved and implemented by the European Union and other agreeing countries is nearly Zero Energy Building (nZEB), with the goal of having all new buildings in the region under nZEB standards by 2020.
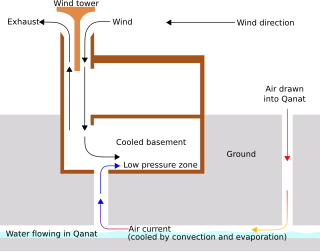
Passive cooling is a building design approach that focuses on heat gain control and heat dissipation in a building in order to improve the indoor thermal comfort with low or no energy consumption. This approach works either by preventing heat from entering the interior or by removing heat from the building.
The passive solar design of buildings includes consideration of their orientation to the sun and their thermal mass, factors which have been incorporated to a greater or lesser extent in vernacular architecture for thousands of years. Ancient Greeks, Romans, and Chinese were the first to refine and develop the basic principles of passive solar design, but European technological advances were largely abandoned after the Fall of Rome. It was not until the 20th century that interest in the principles of passive solar design had a resurgence in Europe and the U.S.A., with architects such as George F. Keck and Frank Lloyd Wright. In the 21st century, worldwide endeavours to reduce power consumption have kept the interest in passive solar technology alive.
A double envelope house is a passive solar house design which collects solar energy in a solarium and passively allows the warm air to circulate around the house between two sets of walls, a double building envelope. This design is from 1975 by Lee Porter Butler in the United States.

John Ingle Yellott was an American engineer recognized as a pioneer in passive solar energy, and an inventor with many patents to his credit. In his honor the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Solar Division confers a biannual "John I. Yellott Award" which "recognizes ASME members who have demonstrated sustained leadership within the Solar Energy Division, have a reputation for performing high-quality solar energy research and have made significant contributions to solar engineering through education, state or federal government service or in the private sector."
Richard Steven "Dick" Levine is an American environmental architect, solar energy and sustainability pioneer, and professor at the University of Kentucky. He is one of the early solar energy innovators in the U.S., a holder of U.S. patents on structural systems and solar energy applications, and the architect of a number of award winning solar buildings including his widely published Raven Run Solar House (1974). Levine is co-director of the Center for Sustainable Cities at the University of Kentucky. His contributions to sustainable urban planning are in both the theory and practice of the sustainable city-region. He has over 150 publications on solar energy and sustainability research, conducted in Italy, Austria, China and the Middle East.
The USC School of Architecture (USCArchitecture) is the architecture school at the University of Southern California. Located in Los Angeles, California, it is one of the university's twenty-two professional schools, offering both undergraduate and graduate degrees in the fields of architecture, building science, landscape architecture and heritage conservation.
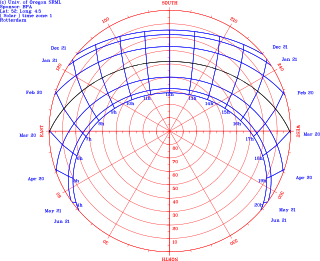
Solar access is the ability of one property to continue to receive sunlight across property lines without obstruction from another’s property. Solar access is calculated using a sun path diagram. Sun is the source of our vision and energy. Its movements inform our perception of time and space. Access to sun is essential to energy conservation and to the quality of our lives.
Kenneth L. Haggard is an American architect, educator, and solar pioneer who has designed more than 300 buildings and seen more than 200 built. He is a licensed architect in California and Florida. He and his partner Polly Cooper were awarded the American Solar Energy Society Passive Solar Pioneer Award in 1996. They have been leaders in both passive solar architecture and the rediscovery of straw bale building.
Ken-ichi Kimura is a Japanese environmental architect.

Douglas E. Noble is an American architect and tenured faculty member at the USC School of Architecture. He is a fellow of the American Institute of Architects. He is known for his work in four overlapping arenas: Architectural Computing, Building Science, Architecture Education, and Design Theories and Methods. He received the ACSA/AIAS New Faculty Teaching Award in 1995, and the ACSA Creative Achievement Award in 2013 He was named among the "10 most admired educators" in architecture in 2010 and was twice more selected as a "most admired educator" in 2015 and 2018 He is the recipient of the 2017 American Institute of Architects Los Angeles Chapter Presidential Honor as educator of the year.

Karen M. Kensek is on the faculty of the USC School of Architecture at the University of Southern California. She is a leading figure in architectural computing, focusing on analytical building information modeling and building science.

Marc Eugene Schiler is a professor of the USC School of Architecture at the University of Southern California. He is a Fellow of the American Solar Energy Society and a winner of the Passive Solar Pioneer award in 2015. Schiler completed an undergraduate degree in architecture at USC School of Architecture and a Master of Architecture at Cornell University. He was an Assistant Professor of Architecture and Landscape Architecture at Cornell for four years prior to returning to USC in 1982. He was invited for a year to do research at the EMPA. He served as a Fulbright Senior Scholar to the Middle East in 2002-2003 at the Technion – Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa and the Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Sede Boqer. He has published more than 100 peer-reviewed scientific papers and authored or edited six books on environmental controls.












