
Ralph Roberts was an American automotive designer who worked for the Chrysler Corporation during the 1930s and 1940s.

Ralph Roberts was an American automotive designer who worked for the Chrysler Corporation during the 1930s and 1940s.
Although a designer Roberts joined the founders of design practice LeBaron in 1921 to look after administration. The founders left but he remained in the practice which grew to manufacture car bodies and was taken over in 1927 by Briggs. Roberts moved to Briggs along with LeBaron. [1]
Roberts spent much of the second half of the 1930s in England setting up the Briggs Manufacturing Company plant for the bodies for Ford Dagenham.

Jack Wills of Pasadena California brought in Roberts and formed Wills and Roberts Manufacturing Company (WiRo or WilRo) in 1942 to make plastic housings for Aerojet and fiberglass droppable boats using one of the first polyester resins — Lamitex —and Owens-Corning Fiberglas. [2] Postwar Roberts designed and built a clay model in 1946 for a fibreglass body later briefly made and sold as the Skorpion car. [3]

Stellantis North America ) is one of the "Big Three" automobile manufacturers in the United States, headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan. It is the American subsidiary of the multinational automotive company Stellantis. In addition to the Chrysler brand, Stellantis North America sells vehicles worldwide under the Dodge, Jeep, and Ram nameplates. It also includes Mopar, its automotive parts and accessories division, and SRT, its performance automobile division.

Simca was a French automaker, founded in November 1934 by Fiat S.p.A. and directed from July 1935 to May 1963 by Italian Henri Pigozzi. Simca was affiliated with Fiat and, after Simca bought Ford's French subsidiary, became increasingly controlled by Chrysler. In 1970, Simca became a brand of the Chrysler's European business, ending its period as an independent company. Simca disappeared in 1978, when Chrysler divested its European operations to another French automaker, PSA Peugeot Citroën. PSA replaced the Simca brand with Talbot after a short period when some models were badged as Simca-Talbots.

Imperial was the Chrysler Corporation's luxury automobile brand from 1955 to 1975, and again from 1981 to 1983.

The K-car platform was a key automotive design platform introduced by Chrysler Corporation for the 1981 model year, featuring a transverse engine, front-wheel drive, independent front and semi-independent rear suspension configuration—a stark departure from the company's previous reliance on solid axle, rear-drive unibody configurations during the 1970s. Derived from Chrysler's L-cars, the Plymouth Horizon and Dodge Omni, the platform was developed just as the company faltered in the market, at first underpinning a modest range of compact/mid-size sedans and wagons—and eventually underpinning nearly fifty different models, including all-wheel drive variants—and playing a vital role in the company's subsequent resurgence.

Chrysler's TC by Maserati is a jointly developed car by Chrysler and Maserati. It was positioned as a grand tourer and introduced at the 1986 Los Angeles Auto Show. It is a "Q" body built on a modified second generation Chrysler K platform. After two years of development delays, the TC became available in late-1988 and a total of 7,300 units were manufactured in Milan, Italy through 1990. All cars sold as 1991 models were manufactured in 1990.

The Chrysler LeBaron, also known as the Imperial LeBaron, is a line of automobiles built by Chrysler from 1931-1941 and from 1955-1995. The model was introduced in 1931, with a body manufactured by LeBaron, and competed with other luxury cars of the era such as Lincoln and Packard. After purchasing LeBaron with its parent Briggs Manufacturing Company, Chrysler introduced the luxury make Imperial in 1955, and sold automobiles under the name Imperial LeBaron until 1975. Chrysler discontinued the Imperial brand in 1975, and reintroduced the Chrysler LeBaron in 1977 to what was then Chrysler's lowest priced model.

The Chrysler Imperial, introduced in 1926, was Chrysler's top-of-the-line vehicle for much of its history. Models were produced with the Chrysler name until 1954, after which it became a standalone brand; and again from 1990 to 1993. The company positioned the cars as a prestige marque to rival Cadillac, Continental, Lincoln, Duesenberg, Pierce Arrow, Cord, and Packard. According to Antique Automobile, "The adjective ‘imperial’ according to Webster's Dictionary means sovereign, supreme, superior or of unusual size or excellence. The word imperial thus justly befits Chrysler's highest priced model."

The Newport was a name used by Chrysler for both a hardtop body designation and also for its lowest priced model between 1961 and 1981. Chrysler first used the Newport name on a 1940 show car, of which five vehicles were produced. The Newport continued the tradition of a large, comfortable luxurious coupe and sedan, while offering a modestly priced product in comparison to the Chrysler New Yorker and Chrysler Imperial. The Newport gradually replaced the Chrysler Windsor which originally replaced the Chrysler Royal. The Newport was initially the brand name for the Windsor with a hardtop body style, then was used for coupes, sedans and station wagons in later decades.
Dietrich Inc. was an American coachbuilder founded in 1925 by Raymond H. Dietrich (1894–1980), co-founder of LeBaron Incorporated in New York City. He was a close friend to Edsel Ford who supported him by talking the owner of the J W Murray Manufacturing Co into partly financing the venture. Murray was itself a vendor of standard bodies to the Ford Motor Company, and hoped for an in-house source for designing and building custom bodies for luxury cars. Dietrich himself held 50% of the stock.

The Chrysler Executive was a car offered by the American automobile producer Chrysler from 1983 through 1986 during the malaise era of American automobile manufacture. The Executive was a stretched version of the Chrysler LeBaron aimed at the then booming market segment of limousines. Chrysler chose to use the stretched wheelbase E-body instead of the M-body platform used by the rear-wheel-drive Chrysler Fifth Avenue.

The Plymouth Belmont was a 1954 concept sports car built by Plymouth. It were the first plastic-bodied cars by the Chrysler Corporation. The Belmont seated two and used a V8 engine, that produced up to 150 hp (112 kW). It was originally painted in a light blue metallic, it was painted red later. It was 191.5" long. Had it ever become a production model, its main competitors would have been the Chevrolet Corvette and the Ford Thunderbird.
The Cunningham C7 Grand Touring car was an American limited production high performance luxury sports coupe. It was first introduced to the public at the 2001 North American International Auto Show.

LeBaron Incorporated was an American design business from 1920 and also a coachbuilder from 1924 until 1953.

Theodore Wells Pietsch II was an American automobile stylist and industrial designer who, with little formal education, managed to launch a career in automobile design that took him over a period of 38 years to nearly every major automobile company in the nation.
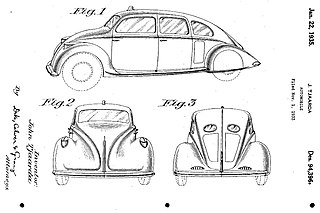
Johan "Jan" Tjaarda (1897–1962), later known as John Tjaarda van Sterkenburg, was a Dutch product and automotive designer and stylist in the United States.

Frederick Morrell Zeder was an American automotive industry engineer and a member of the Automotive Hall of Fame. He made material contributions to Allis-Chalmers and Studebaker. Along with Carl Breer and Owen Skelton, he was one of the core engineering team that formed the present-day Chrysler Corporation. His innovations included rubber motor mounts that contributed to Chrysler's success. He was the first president of Chrysler's Institute of Engineering.
Briggs Manufacturing was an American, Detroit-based manufacturer of automobile bodies for Ford Motor Company, Chrysler Corporation and other U.S. and European automobile manufacturers.
Briggs Swift Cunningham II was an American entrepreneur and sportsman. He is best known for skippering the yacht Columbia to victory in the 1958 America's Cup race, and for his efforts as a driver, team owner, and constructor in sports car racing, including the 24 Hours of Le Mans.
The B. S. Cunningham Company was an automobile company established by Briggs Cunningham. It produced six different models in very small numbers, primarily to be raced at the 24 Hours of Le Mans.
William Robinson was an American automobile designer for numerous American companies, notably Chrysler as creative designer from 1948 to 1980 and Briggs Manufacturing Company. In a second career, Robinson taught design for twenty-two years at the College of Creative Studies.