
India is the second most populated country in the world with nearly a fifth of the world's population. According to the 2017 revision of the World Population Prospects, the population stood at 1,324,171,354.
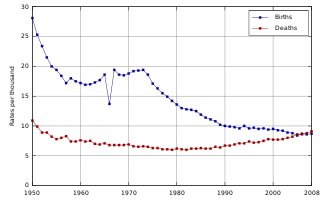
The demographic features of the population of Japan include population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects regarding the population.
This article is about the demographic features of the population of Jamaica, including population density, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

In biology, a population is all the organisms of the same group or species, which live in a particular geographical area, and have the capability of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is potentially possible between any pair within the area, and where the probability of interbreeding is greater than the probability of cross-breeding with individuals from other areas.
This article contains demographic features of the United Arab Emirates (UAE), including population density, vital statistics, immigration and emigration data, ethnicity, education levels, religions practiced, and languages spoken within the UAE.

Demography is the statistical study of populations, especially human beings. As a very general science, it can analyze any kind of dynamic living population, i.e., one that changes over time or space. Demography encompasses the study of the size, structure, and distribution of these populations, and spatial or temporal changes in them in response to birth, migration, aging, and death. Based on the demographic research of the earth, earth's population up to the year 2050 and 2100 can be estimated by demographers. Demographics are quantifiable characteristics of a given population.

Demographic transition (DT) is the transition from high birth and death rates to lower birth and death rates as a country or region develops from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system. The theory was proposed in 1929 by the American demographer Warren Thompson, who observed changes, or transitions, in birth and death rates in industrialized societies over the previous 200 years. Most developed countries have completed the demographic transition and have low birth rates; most developing countries are in the process of this transition. The major (relative) exceptions are some poor countries, mainly in sub-Saharan Africa and some Middle Eastern countries, which are poor or affected by government policy or civil strife, notably, Pakistan, Palestinian territories, Yemen, and Afghanistan.

Alfred Sauvy was a demographer, anthropologist and historian of the French economy. Sauvy coined the term Third World in reference to countries that were unaligned with either the Communist Soviet bloc or the Capitalist NATO bloc during the Cold War. In an article published in the French magazine, L'Observateur on August 14, 1952, Sauvy said:

The world's core Jewish population was estimated at 14,511,000 in April 2018, up from 14.41 million in 2016. Demographer Sergio DellaPergola proposes an "extended" Jewish population, including people identifying as partly Jewish and non-Jews with Jewish parents, numbering 17.3 million globally, and an "enlarged" Jewish population figure that also includes non-Jewish members of Jewish households totaling 20.2 million. Additionally, the total number of people who hold or are eligible for Israeli citizenship under the Law of Return — defined as anyone with at least one Jewish grandparent, and who does not profess any other religion — is estimated at around 23 million, of which 6.6 million were living in Israel as of 2015. Figures for these expanded categories are less precise than for the core Jewish population.
Natalism is a belief that promotes the reproduction of sentient life.
The term comes from the Latin adjective for "birth", nātālis.

Population geography is a division of human geography. It is the study of the ways in which spatial variations in the distribution, composition, migration, and growth of populations are related to the nature of places. Population geography involves demography in a geographical perspective. It focuses on the characteristics of population distributions that change in a spatial context. This often involves factors such as where populations are found and how the size and composition of these populations is regulated by the demographic processes of fertility, mortality, and migration. Contributions to population geography are cross-disciplinary because geographical epistemologies related to environment, place and space have been developed at various times. Related disciplines include geography, demography, sociology, and economics.
A social issue is a problem that influences a considerable number of individuals within a society. It is often the consequence of factors extending beyond an individual's control, and is the source of a conflicting opinion on the grounds of what is perceived as a morally just personal life or societal order. Social issues are distinguished from economic issues; however, some issues have both social and economic aspects. There are also issues that don't fall into either category, such as warfare.
Kingsley Davis was an internationally recognized American sociologist and demographer. He was identified by the American Philosophical Society as one of the most outstanding social scientists of the twentieth century, and was a Hoover Institution senior research fellow.
The French Institute for Demographic Studies (INED) is a French research institute specializing in demography and population studies in general.

The Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research (MPIDR) is located in Rostock, Germany. It was founded in 1996 by James Vaupel and moved into new buildings in Rostock in 2002. It is one of approximately 80 institutes of the Max Planck Society.

Demographic history is the reconstructed record of human population in the past. Given the lack of population records prior to the 1950s, there are many gaps in our record of demographic history. Historical demographers must make do with estimates. models and extrapolations. For the methodology, see Historical demography

The aging of Europe, also known as the greying of Europe, is a demographic phenomenon in Europe characterised by a decrease in fertility, a decrease in mortality rate, and a higher life expectancy among European populations. Low birth rates and higher life expectancy contribute to the transformation of Europe's population pyramid shape. The most significant change is the transition towards a much older population structure, resulting in a decrease in the proportion of the working age while the number of the retired population increases. The total number of the older population is projected to increase greatly within the coming decades, with rising proportions of the post-war baby-boom generations reaching retirement. This will cause a high burden on the working age population as they provide for the increasing number of the older population.

In demographics, the world population is the total number of humans currently living, and was estimated to have reached 7.7 billion people as of April 2019. It took over 200,000 years of human history for the world's population to reach 1 billion; and only 200 years more to reach 7 billion.
The International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) serves as a regional Institute for Training and Research in Population Studies for the ESCAP region. It was established in Mumbai in July 1956; until July 1970, it was known as the Demographic Training and Research Center (DTRC), and until 1985, it was known as the International Institute for Population Studies (IIPS). The Institute was re-designated to its present title in 1985 to facilitate the expansion of its academic activities and was declared as a 'Deemed University' on 19 August 1985 under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956 by the Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India. The recognition has facilitated the award of recognized degrees by the Institute itself and paved the way for further expansion of the Institute as an academic institution.The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MOHFW), Government of India has designated IIPS as the nodal agency, responsible for providing coordination and technical guidance for the National Family Health Survey (NFHS).

The University of Michigan Institute for Social Research (ISR) is one of the largest academic social research and survey organization in the world, established in 1949. ISR includes more than 250 scientists from many academic disciplines – including political science, psychology, sociology, economics, demography, history, anthropology, and statistics. It has been said to be "the premier center for survey research methodology in the world."











