
Captain George Vancouver was a British officer of the Royal Navy best known for his 1791–95 expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern Pacific Coast regions, including the coasts of what are now the American states of Alaska, Washington, and Oregon, as well as the province of British Columbia in Canada. He also explored the Hawaiian Islands and the southwest coast of Australia.

The Strait of Georgia or the Georgia Strait is an arm of the Pacific Ocean between Vancouver Island and the extreme southwestern mainland coast of British Columbia, Canada and the extreme northwestern mainland coast of Washington, United States. It is approximately 240 kilometres (150 mi) long and varies in width from 20 to 58 kilometres. Along with the Strait of Juan de Fuca and Puget Sound, it is a constituent part of the Salish Sea. Archipelagos and narrow channels mark each end of the Strait of Georgia, the Gulf Islands and San Juan Islands in the south, and the Discovery Islands in the north. The main channels to the south are Boundary Pass, Haro Strait and Rosario Strait, which connect the Strait of Georgia to the Strait of Juan de Fuca. In the north, Discovery Passage is the main channel connecting the Strait of Georgia to Johnstone Strait. The strait is a major navigation channel on the west coast of North America, owing to the presence of the port of Vancouver, and also due to its role as the southern entrance to the intracoastal route known as the Inside Passage.

Queen Charlotte Sound is a sound of the Pacific Ocean in British Columbia, Canada, between Vancouver Island in the south and Haida Gwaii in the north. It merges with Hecate Strait in the north and Queen Charlotte Strait in the south.

Lynn Canal is an inlet into the mainland of southeast Alaska.

William Robert Broughton was a British naval officer in the late 18th century. As a lieutenant in the Royal Navy, he commanded HMS Chatham as part of the Vancouver Expedition, a voyage of exploration through the Pacific Ocean led by Captain George Vancouver in the early 1790s.

Lincoln Island is a wooded island in Lynn Canal in Alaska, United States. Located at 58°29′41″N134°59′40″W, the island is one kilometer northwest of larger Shelter Island and some 200 meters southeast of smaller Ralston Island. It is part of the Juneau City and Borough. The first European to sight the island was Joseph Whidbey, master of HMS Discovery during George Vancouver's 1791–1795 expedition, in 1794. It was named in 1868 by Commander R. W. Meade, USN, presumably for Abraham Lincoln.
Zarembo Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago of southeastern Alaska, United States. It lies directly south of Mitkof Island and northwest of Etolin Island. To the northwest is Kupreanof Island and to the southwest is Prince of Wales Island. It has a land area of 183.14 square miles, making it the 34th largest island in the United States. It has no permanent resident population. It was first charted in 1793 by James Johnstone, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791-95 expedition. He only charted its north, west, and south coasts, not realizing it was an island. The island is named after Dionysius Zarembo, a Polish employee of the Russian American Company and explorer of Alaska. Usually known as Dionysius Zarembo, he was captain of the Russian-American Company ship Chichagof during the foundation of the Redoubt San Dionisio, named for his name-saint, a fortification at present-day Wrangell which was established to forestall encroachment on the Stikine region by the Hudson's Bay Company.
The Vancouver Expedition (1791–1795) was a four-and-a-half-year voyage of exploration and diplomacy, commanded by Captain George Vancouver of the Royal Navy. The British expedition circumnavigated the globe and made contact with five continents. The expedition at various times included between two and four vessels, and up to 153 men, all but six of whom returned home safely.
Couverden Island is a small island located at the western entrance of Lynn Canal in Alaska. The first European to see it was Joseph Whidbey in 1794, master of the Discovery during George Vancouver's 1792-1794 exploration of the Pacific Northwest. The south point of the island was named by Vancouver Point Couverden, "which I called after the seat of my ancestors". The name was apparently later transferred to the island. The island is located in Haines Borough in southeastern Alaska.
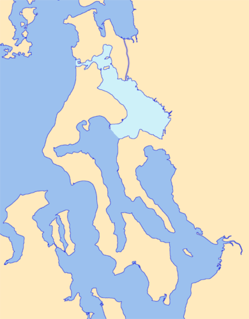
Skagit Bay is a bay and strait located in the U.S. state of Washington. It is part of the Whidbey Island Basin of Puget Sound. The Skagit River empties into Skagit Bay. To the south, Skagit Bay connects with the rest of Puget Sound via Saratoga Passage and Possession Sound. The boundary between Saratoga Passage and Skagit Bay is between Polnell Point on Whidbey Island and Rocky Point on Camano Island. To the northwest, Skagit Bay connects to the Strait of Juan de Fuca via the narrow strait of Deception Pass. A third waterway, the Swinomish Channel, connects Skagit Bay with Padilla Bay to the north.
Fillmore Island is an island in Southeast Alaska, United States. The island lies between Fillmore Inlet and Pearse Canal. The island was charted by George Vancouver in 1793, who sailed around it and proved its insular nature. It was named in 1885 by the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey after Ensign John Hudson Fillmore, USN.
Bell Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago in Southeast Alaska, United States. It is 14 kilometres (8.7 mi) long, lying in Behm Canal, north of Revillagigedo Island. George Vancouver first visited the island on August 12, 1793, in the evening dining on its south coast. He suspected that it was an island, but this was not proven until later in the same month, when Joseph Whidbey, master of HMS Discovery, charted its entire coastline. Vancouver later named it "Bell's Island" after one of his crew, Midshipman Bell.
Ernest Sound is a strait in Southeast Alaska, U.S.A. It extends 48 kilometres (30 mi) southwest, from the mouth of Bradfield Canal to Clarence Strait, separating Wrangell and Etolin Islands from the mainland. It was first traversed and charted in 1793 by James Johnstone, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791-95 expedition. Vancouver later named it "Prince Ernest's Sound", after Prince Ernest, Duke of Cumberland.
The Narrows is a channel in Southeast Alaska, U.S.A. It is the shortest and narrowest stretch of waterway separating Wrangell Island from the mainland, connecting Blake Channel and Eastern Passage. It was named in 1917 by the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey. It was first traversed and charted in 1793 by James Johnstone, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791-95 expedition.
Eastern Passage is a channel in Southeast Alaska, U.S.A. It extends southeast 29 kilometres (18 mi) from the mouth of the Stikine River to The Narrows, separating the northeastern half of Wrangell Island from the mainland. It was named in 1877 by William Healy Dall of the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey. It was first traversed and charted in 1793 by James Johnstone, one of George Vancouver's officers during his 1791-95 expedition.

Shelter Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago, southeast of Lincoln Island and northwest of Juneau, Alaska, U.S. It trends northwest between Favorite and Saginaw channels. It was named in 1869 by Commander R. W. Meade of the United States Navy. The first European to sight the island was Joseph Whidbey, master of HMS Discovery during George Vancouver's 1791–95 expedition, in 1794.
Favorite Channel is a channel in Southeast Alaska, northwest of Juneau, Alaska, United States. It is 25 kilometres (16 mi) long, extending northwest from Stephens Passage to Lynn Canal, separating Lincoln and Shelter islands from the mainland to the east. It was named in 1880 by U.S. Navy officers after the 80-foot (24 m) steamboat Favorite, which was chartered by the Navy for surveying work in Alaska, later being used to carry out trading and fishing for the herring plant at Killisnoo. The first European to traverse and chart the channel was Joseph Whidbey, master of HMS Discovery during George Vancouver's 1791–95 expedition, in 1794.

The Glass Peninsula is a peninsula extending southeast from Admiralty Island, between Seymour Canal and Stephens Passage, Southeast Alaska, United States. It was named by the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey for United States Navy Commander Henry Glass, who had made surveys in the area in 1881. It was first charted in 1794 by Joseph Whidbey, master of HMS Discovery, during George Vancouver's 1791–1795 expedition.
Tiedeman Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago, east of Admiralty Island, about two-thirds up from the entrance of Seymour Canal, Southeast Alaska, United States. To its north is Swan Island. It was named by William Healy Dall of the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey, and published in the 1883 Coast Pilot. The first European to discover and chart the island was Joseph Whidbey, master of HMS Discovery during George Vancouver's 1791–1795 expedition, in 1794.
Sullivan Island is an island in Lynn Canal, southwest of Chilkat Island, Southeast Alaska, United States. It was named in 1869 by Commander R.W. Meade, USN, for the master of the schooner Louisa Downs, which had wrecked on the island in 1867. The Tlingit name for the island is "Schikuk". The first European to discover and chart the island was Joseph Whidbey, master of HMS Discovery during George Vancouver's 1791–1795 expedition, in 1794.












