
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican state of ancient Rome. It included territory around the Mediterranean in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. The adoption of Christianity as the state church in 380 and the fall of the Western Roman Empire conventionally marks the end of classical antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages.

The cuisine of ancient Rome changed greatly over the duration of the civilization's existence. Dietary habits were affected by the political changes from kingdom to republic to empire, and Roman trading with foreigners along with the empire's enormous expansion exposed Romans to many new foods, provincial culinary habits and cooking methods.

The Samnites were an ancient Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy.

Peter Robert Lamont Brown is an Irish historian. He is the Rollins Professor of History Emeritus at Princeton University. Brown is credited with having brought coherence to the field of Late Antiquity, and is often regarded as the inventor of said field. His work has concerned, in particular, the religious culture of the later Roman Empire and early medieval Europe, and the relation between religion and society.
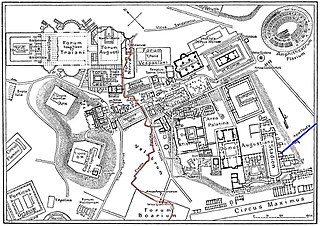
The Cloaca Maxima was one of the world's earliest sewage systems. Its name derives from Cloacina, a Roman goddess. Built during either the Roman Kingdom or early Roman Republic, it was constructed in Ancient Rome in order to drain local marshes and remove waste from the city. It carried effluent to the River Tiber, which ran beside the city. The sewer started at the Forum Augustum and ended at the Ponte Rotto and Ponte Palatino. It began as an open air canal, but it developed into a much larger sewer over the course of time. Agrippa renovated and reconstructed much of the sewer. This would not be the only development in the sewers. By the first century CE all eleven Roman aqueducts were connected to the sewer. After the Roman Empire fell the sewer still was used. By the 19th century, it became a tourist attraction. Some parts of the sewer are still used today. Whilst still being used, it was highly valued as a sacred symbol of Roman culture, and Roman engineering.

Michael Grant was an English classicist, numismatist, and author of numerous books on ancient history. His 1956 translation of Tacitus's Annals of Imperial Rome remains a standard of the work. Having studied and held a number of academic posts in the United Kingdom and the Middle East, he retired early to devote himself fully to writing. He once described himself as "one of the very few freelancers in the field of ancient history: a rare phenomenon". As a populariser, his hallmarks were his prolific output and his unwillingness to oversimplify or talk down to his readership. He published over 70 works.

Dame Winifred Mary Beard, is an English scholar of Ancient Rome. She is a trustee of the British Museum and formerly held a personal professorship of Classics at the University of Cambridge. She is a fellow of Newnham College, Cambridge, and Royal Academy of Arts Professor of Ancient Literature.
Andrew Frederic Wallace-Hadrill, is a British ancient historian, classical archaeologist, and academic. He is Professor of Roman Studies and Director of Research in the Faculty of Classics at the University of Cambridge. He was Director of the British School at Rome between 1995 and 2009, and Master of Sidney Sussex College, Cambridge from August 2009 to July 2013.

In Ancient Rome the month of March was the traditional start of the campaign season, and the Tubilustrium was a ceremony to make the army fit for war. The ceremony involved sacred trumpets called tubae.
Glen Warren Bowersock is a historian of ancient Greece, Rome and the Near East, and former Chairman of Harvard’s classics department.

The Villa Poppaea is an ancient luxurious Roman seaside villa located in Torre Annunziata between Naples and Sorrento, in Southern Italy. It is also called the Villa Oplontis or Oplontis Villa A. as it was situated in the ancient Roman town of Oplontis.

The Temple of Isis is a Roman temple dedicated to the Egyptian goddess Isis. This small and almost intact temple was one of the first discoveries during the excavation of Pompeii in 1764. Its role as a Hellenized Egyptian temple in a Roman colony was fully confirmed with an inscription detailed by Francisco la Vega on July 20, 1765. Original paintings and sculptures can be seen at the Museo Archaeologico in Naples; the site itself remains on the Via del Tempio di Iside. In the aftermath of the temple's discovery many well-known artists and illustrators swarmed to the site.
Edith Hall, is a British scholar of classics, specialising in ancient Greek literature and cultural history, and professor in the Department of Classics and Ancient History at Durham University. She is a Fellow of the British Academy. From 2006 until 2011 she held a Chair at Royal Holloway, University of London, where she founded and directed the Centre for the Reception of Greece and Rome until November 2011. She resigned over a dispute regarding funding for classics after leading a public campaign, which was successful, to prevent cuts to or the closure of the Royal Holloway Classics department. Until 2022, she was a professor at the Department of Classics at King's College London. She also co-founded and is Consultant Director of the Archive of Performances of Greek and Roman Drama at Oxford University, Chair of the Gilbert Murray Trust, and Judge on the Stephen Spender Prize for poetry translation. Her prizewinning doctoral thesis was awarded at Oxford. In 2012 she was awarded a Humboldt Research Prize to study ancient Greek theatre in the Black Sea, and in 2014 she was elected to the Academy of Europe. She lives in Cambridgeshire.

Pompeii was an ancient city located in what is now the comune of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area, was buried under 4 to 6 m of volcanic ash and pumice in the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD.

In Roman timekeeping, a day was divided into periods according to the available technology. Initially, the day was divided into two parts: the ante meridiem and the post meridiem. With the advent of the sundial circa 263 BC, the period of the natural day from sunrise to sunset was divided into twelve hours.
Lawrence Richardson Jr. was an American Classicist and ancient historian educated at Yale University who was a member of the faculty of classics at Duke University from 1966 to 1991. He was married to the Classical archaeologist Emeline Hill Richardson. Richardson received numerous fellowships, including a Fulbright, a Guggenheim, and support from the American Council of Learned Societies. He was a Fellow of the American Academy in Rome (1950) and field director of the AAR's Cosa excavations (1952–1955). He was a Resident of the American Academy in Rome (1979), and served as the American Academy in Rome’s Mellon Professor-in-Charge of the School of Classical Studies (1981). In 2012 he was awarded the Gold Medal of the Archaeological Institute of America.
Mary Harlow, is an English archaeologist and classical scholar. Her research focuses on various aspects of Roman social history―such as age, family, dress and textiles―and their impact on the formation of ancient identity. Her approach strongly promotes interdisciplinary methods, using source materials to accompany the study of Roman dress.

Several non-native societies had an influence on Ancient Pompeian culture. Historians’ interpretation of artefacts, preserved by the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79, identify that such foreign influences came largely from Greek and Hellenistic cultures of the Eastern Mediterranean, including Egypt. Greek influences were transmitted to Pompeii via the Greek colonies in Magna Graecia, which were formed in the 8th century BC. Hellenistic influences originated from Roman commerce, and later conquest of Egypt from the 2nd century BC.
Steven J. R. Ellis is an Australian classicist and archaeologist, and a professor of classics at the University of Cincinnati. His research focuses on Roman cities and archaeological methodologies, and he is widely known for his archaeological excavations at Pompeii. Ellis won the Rome Prize in 2012-2013. In 2018, Ellis wrote the book called The Roman Retail Revolution, published with Oxford University Press.
Michael SquireFBA is a British art historian and classicist. He became the Laurence Professor of Classical Archaeology in the University of Cambridge in 2022. He is a Senior Research Fellow at Trinity College, and was elected Fellow of the British Academy in 2022.












