Reach-in ovens are meant for different industrial applications that may need uniform temperature throughout. The ovens normally use horizontal re-circulating air to ensure the uniform temperature, and can use fans that circulate air, creating the airflow. Reach-in ovens can be used in numerous production and laboratory applications, including curing, drying, sterilizing, aging, and other process-critical applications.

Temperature is a physical quantity expressing hot and cold. It is measured with a thermometer calibrated in one or more temperature scales. The most commonly used scales are the Celsius scale, Fahrenheit scale, and Kelvin scale. The kelvin is the unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), in which temperature is one of the seven fundamental base quantities. The Kelvin scale is widely used in science and technology.

A laboratory is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed.
Reach-in ovens are considered a type of industrial batch oven. Other types of batch ovens are bench/laboratory, burn in, laboratory, walk in/truck in, and clean process.
Batch ovens are a type of furnace used for thermal processing. They are used in numerous production and laboratory applications, including curing, drying, sterilizing, aging, and other process-critical applications. Sizes can vary depending on what type of thermal processing application is needed. Batch ovens are used mainly for single batch thermal processing. Cabinet and bench ovens are smaller batch ovens, and walk in/drive in ovens are larger and to be used for more variations of industrial applications.
Laboratory ovens are ovens for high-forced volume thermal convection applications. These ovens generally provide uniform temperatures throughout. Process applications for laboratory ovens can be for annealing, die-bond curing, drying, Polyimide baking, sterilizing, and other industrial laboratory functions. Typical sizes are from one cubic foot to 0.9 cubic metres (32 cu ft) with temperatures that can be over 340 degrees Celsius.
A clean process oven is a type of industrial batch oven that is ideal for high-temperature applications, such as curing Polyimide, and annealing thin and film waters. Clean process ovens may be for air atmospheres, or inert atmospheres for oxidation-sensitive materials. Temperatures can be over 525 degrees Celsius.

Distillation is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation. Distillation may result in essentially complete separation, or it may be a partial separation that increases the concentration of selected components in the mixture. In either case, the process exploits differences in the volatility of the mixture's components. In industrial chemistry, distillation is a unit operation of practically universal importance, but it is a physical separation process, not a chemical reaction.

A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber, a type of oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete some process, such as hardening, drying, or chemical changes. Kilns have been used for millennia to turn objects made from clay into pottery, tiles and bricks. Various industries use rotary kilns for pyroprocessing—to calcinate ores, to calcinate limestone to lime for cement, and to transform many other materials.
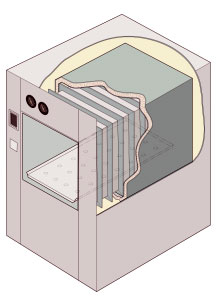
An autoclave is a pressure chamber used to carry out industrial processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure different from ambient air pressure. Autoclaves are used in medical applications to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis. Industrial autoclaves are used in industrial applications, especially regarding composites.

A convection oven is an oven that has fans to circulate air around food, using the convection mechanism to cook food faster than a conventional oven. Convection ovens are also used for non-food, industrial applications.

Crystallization is the process by which a solid forms, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some of the ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposition directly from a gas. Attributes of the resulting crystal depend largely on factors such as temperature, air pressure, and in the case of liquid crystals, time of fluid evaporation.

Dielectric heating, also known as electronic heating, radio frequency heating, and high-frequency heating, is the process in which a radio frequency (RF) alternating electric field, or radio wave or microwave electromagnetic radiation heats a dielectric material. At higher frequencies, this heating is caused by molecular dipole rotation within the dielectric.
Powder coating is a type of coating that is applied as a free-flowing, dry powder. The main difference between a conventional liquid paint and a powder coating is that the powder coating does not require a solvent to keep the binder and filler parts in coating and is then cured under heat to allow it to flow and form a "skin". The powder may be a thermoplastic or a thermoset polymer. It is usually used to create a hard finish that is tougher than conventional paint. Powder coating is mainly used for coating of metals, such as household appliances, aluminium extrusions, drum hardware and automobile and bicycle parts. Newer technologies allow other materials, such as MDF, to be powder coated using different methods. The powder coating process was invented around 1945 by Daniel Gustin US Patent 2538562.
A vacuum furnace is a type of furnace in which the product in the furnace is surrounded by a vacuum during processing. The absence of air or other gases prevents oxidation, heat loss from the product through convection, and removes a source of contamination. This enables the furnace to heat materials to temperatures as high as 3,000 °C (5,432 °F) with select materials. Maximum furnace temperatures and vacuum levels depend on melting points and vapor pressures of heated materials. Vacuum furnaces are used to carry out processes such as annealing, brazing, sintering and heat treatment with high consistency and low contamination.
The Air Movement and Control Association International, Inc. (AMCA) is a long-established American trade body that sets standards for Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) equipment. It is best known for its ratings in fan balance and vibration, aerodynamic performance, air density, speed and efficiency.
Burn-in ovens are designed for dynamic and static burn-in of integrated circuits and other electronic devices, including laser diodes. Typical sizes are from under ten to over 30 cubic feet (0.85 m3), with air or nitrogen configurations. Operating temperatures can go over 260 °C (500 °F), and can use both single and multiple temperature settings.

Industrial ovens are heated chambers used for a variety of industrial applications, including drying, curing, or baking components, parts or final products. Industrial ovens can be used for large or small volume applications, in batches or continuously with a conveyor line, and a variety of temperature ranges, sizes and configurations.

In systems involving heat transfer, a condenser is a device or unit used to condense a substance from its gaseous to its liquid state, by cooling it. In so doing, the latent heat is given up by the substance and transferred to the surrounding environment. Condensers can be made according to numerous designs, and come in many sizes ranging from rather small (hand-held) to very large. For example, a refrigerator uses a condenser to get rid of heat extracted from the interior of the unit to the outside air. Condensers are used in air conditioning, industrial chemical processes such as distillation, steam power plants and other heat-exchange systems. Use of cooling water or surrounding air as the coolant is common in many condensers.

Basting is a cooking technique that involves cooking meat with either its own juices or some type of preparation such as a sauce or marinade. The meat is left to cook, then periodically coated with the juice.

Hot air ovens are electrical devices which use dry heat to sterilize. They were originally developed by Pasteur. Generally, they can be operated from 50 to 300 °C, using a thermostat to control the temperature. Their double walled insulation keeps the heat in and conserves energy, the inner layer being a poor conductor and outer layer being metallic. There is also an air filled space in between to aid insulation. An air circulating fan helps in uniform distribution of the heat. These are fitted with the adjustable wire mesh plated trays or aluminium trays and may have an on/off rocker switch, as well as indicators and controls for temperature and holding time. The capacities of these ovens vary. Power supply needs vary from country to country, depending on the voltage and frequency (hertz) used. Temperature sensitive tapes or biological indicators using bacterial spores can be used as controls, to test for the efficacy of the device during use.

A water bath is laboratory equipment made from a container filled with heated water. It is used to incubate samples in water at a constant temperature over a long period of time. All water baths have a digital or an analogue interface to allow users to set a desired temperature. Utilisations include warming of reagents, melting of substrates or incubation of cell cultures. It is also used to enable certain chemical reactions to occur at high temperature. Water bath is a preferred heat source for heating flammable chemicals instead of an open flame to prevent ignition. Different types of water baths are used depending on application. For all water baths, it can be used up to 99.9 °C. When temperature is above 100 °C, alternative methods such as oil bath, silicone bath or sand bath may be used.

A high-volume low-speed (HVLS) fan is a type of mechanical fan greater than 7 feet (2.1 m) in diameter. HVLS fans are generally ceiling fans although some are pole mounted. HVLS fans move slowly and distribute large amounts of air at low rotational speed– hence the name "high volume, low speed."













