HCL Sametime Premium is a client–server application and middleware platform that provides real-time, unified communications and collaboration for enterprises. Those capabilities include presence information, enterprise instant messaging, web conferencing, community collaboration, and telephony capabilities and integration. Currently it is developed and sold by HCL Software, a division of Indian company HCL Technologies, until 2019 by the Lotus Software division of IBM.
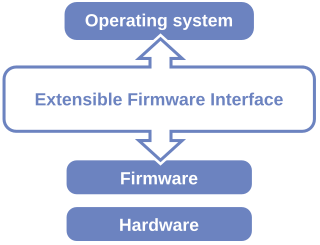
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is a publicly available specification that defines a software interface between an operating system and platform firmware. UEFI replaces the legacy Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) firmware interface originally present in all IBM PC-compatible personal computers, with most UEFI firmware implementations providing support for legacy BIOS services. UEFI can support remote diagnostics and repair of computers, even with no operating system installed.
Wind River Systems, also known as Wind River, is an Alameda, California–based company, subsidiary of Aptiv PLC. The company develops embedded system and cloud software consisting of real-time operating systems software, industry-specific software, simulation technology, development tools and middleware.
The Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) is a set of computer interface specifications for an autonomous computer subsystem that provides management and monitoring capabilities independently of the host system's CPU, firmware and operating system. IPMI defines a set of interfaces used by system administrators for out-of-band management of computer systems and monitoring of their operation. For example, IPMI provides a way to manage a computer that may be powered off or otherwise unresponsive by using a network connection to the hardware rather than to an operating system or login shell. Another use case may be installing a custom operating system remotely. Without IPMI, installing a custom operating system may require an administrator to be physically present near the computer, insert a DVD or a USB flash drive containing the OS installer and complete the installation process using a monitor and a keyboard. Using IPMI, an administrator can mount an ISO image, simulate an installer DVD, and perform the installation remotely.

SUSE is a German-based multinational open-source software company that develops and sells Linux products to business customers. Founded in 1992, it was the first company to market Linux for enterprise. It is the developer of SUSE Linux Enterprise and the primary sponsor of the community-supported openSUSE Project, which develops the openSUSE Linux distribution. While the openSUSE "Tumbleweed" variation is an upstream distribution for both the "Leap" variation and SUSE Linux Enterprise distribution, its branded "Leap" variation is part of a direct upgrade path to the enterprise version, which effectively makes openSUSE Leap a non-commercial version of its enterprise product.

Marratech was a Swedish company that made software for e-meetings. It was acquired by Google in 2007.

Windows IoT, formerly Windows Embedded, is a family of operating systems from Microsoft designed for use in embedded systems. Microsoft currently has three different subfamilies of operating systems for embedded devices targeting a wide market, ranging from small-footprint, real-time devices to point of sale (POS) devices like kiosks. Windows Embedded operating systems are available to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), who make it available to end users preloaded with their hardware, in addition to volume license customers in some cases.

Award Software International Inc. was a BIOS manufacturer founded in 1983, by Rene Vishney and Bob Stillman in San Jose, California. In 1984 the company moved its international headquarters to Los Gatos, California, United States.

IGEL Technology is a German multinational software company best known for their "Next generation edge operating system" which is purpose-built for secure access to cloud workspaces such as Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) and/or Desktop as a Service.
IntervalZero, Inc. develops hard real-time software and its symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) enabled RTX and RTX64 software transform the Microsoft Windows general-purpose operating system (GPOS) into a real-time operating system (RTOS).
Open Systems International, Inc. (OSI) is an automation software company headquartered in Medina, Minnesota, with international offices in Canada, Colombia, Spain, India, Dubai, Australia, Singapore, and China. Founded in 1992, OSI is privately held and employee - owned. The company’s systems are used for the real-time management and optimization of production, transport, and delivery networks for utilities in the electric, oil & gas, transportation, and water industries. OSI is one of the few U.S.-based companies in the operational technology (OT) industry, and has always developed its technology exclusively in the USA, without outsourcing or offshoring. The company's core real-time OT platform has been successfully implemented at more than 550 installations worldwide.

Auriga is a software R&D and IT outsourcing services provider. The company is a privately held C-corporation, incorporated in the US in 1993. Auriga is recognized as one of the Top-100 leading outsourcing software R&D providers worldwide. Headquartered in Boston, MA with 600+ employees, seven development centers, 13+ embedded testing R&D labs and 100+ projects yearly for medical device, automobile and construction tools manufacturers, telecom and power management companies, chip manufacturers, consumer electronics, digital health, semiconductors, retail & logistics, software vendors (ISVs) and hardware manufacturers (OEMs), industrial automation, etc.

TenAsys is a privately owned company providing real-time software and services based on the x86 Intel Architecture and Microsoft Windows operating system.

Elron Electronic Industries is an Israeli technology holding company based in Tel Aviv; since 1962 the company has been involved in setting up, funding and developing over 30 companies and is considered one of the foundation stones of the high-tech industry in Israel. The company's sectors of interest include clean technology, software, semiconductors, medical technology, telecommunications, defence and aerospace. Today, the combined annual revenues of the companies established by Elron are approximately $5 billion.
The ETAS Group is a German company which designs tools for the development of embedded systems for the automotive industry and other sectors of the embedded industry. ETAS is 100-percent subsidiary of Robert Bosch GmbH.

Wyse was an independent American manufacturer of cloud computing systems. As of 2012, Wyse is a subsidiary of Dell. Wyse are best remembered for their video terminal line introduced in the 1980s, which competed with the market-leading Digital. They also had a successful line of IBM PC compatible workstations in the mid-to-late 1980s. But starting late in the decade, Wyse were outcompeted by companies such as eventual parent Dell. Current products include thin client hardware and software as well as desktop virtualization solutions. Other products include cloud software-supporting desktop computers, laptops, and mobile devices. Dell Cloud Client Computing is partnered with IT vendors such as Citrix, IBM, Microsoft, and VMware.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise and its predecessor entities have a long history of developing and selling networking products. Today it offers campus and small business networking products through its wholly owned company Aruba Networks which was acquired in 2015. Prior to this, HP Networking was the entity within HP offering networking products.

Zylog Systems Limited (ZSL) is an international information technology company publicly listed on the National Stock Exchange of India (NSE) & Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). Zylog is headquartered in Chennai, India and Edison, New Jersey, United States.

Stratix is a family of FPGA products developed by Intel, Programmable Solutions Group. Other current product lines include e.g. Arria and Cyclone families.

Rhonda Software is a privately held camera design company that specializes in embedded solutions in digital image processing. Rhonda's solutions are used in action cameras, virtual reality (VR) cameras, wearable video recorders, dashcams, drone cameras.












