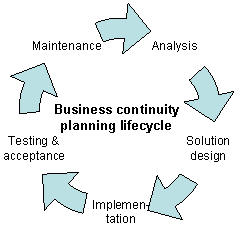
Business continuity may be defined as "the capability of an organization to continue the delivery of products or services at pre-defined acceptable levels following a disruptive incident", and business continuity planning is the process of creating systems of prevention and recovery to deal with potential threats to a company. In addition to prevention, the goal is to enable ongoing operations before and during execution of disaster recovery. Business continuity is the intended outcome of proper execution of both business continuity planning and disaster recovery.
In information technology, a backup, or data backup is a copy of computer data taken and stored elsewhere so that it may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form, referring to the process of doing so, is "back up", whereas the noun and adjective form is "backup". Backups can be used to recover data after its loss from data deletion or corruption, or to recover data from an earlier time. Backups provide a simple form of IT disaster recovery; however not all backup systems are able to reconstitute a computer system or other complex configuration such as a computer cluster, active directory server, or database server.
IT disaster recovery (also, simply disaster recovery (DR)) is the process of maintaining or reestablishing vital infrastructure and systems following a natural or human-induced disaster, such as a storm or battle. DR employs policies, tools, and procedures with a focus on IT systems supporting critical business functions. This involves keeping all essential aspects of a business functioning despite significant disruptive events; it can therefore be considered a subset of business continuity (BC). DR assumes that the primary site is not immediately recoverable and restores data and services to a secondary site.
Data loss is an error condition in information systems in which information is destroyed by failures or neglect in storage, transmission, or processing. Information systems implement backup and disaster recovery equipment and processes to prevent data loss or restore lost data. Data loss can also occur if the physical medium containing the data is lost or stolen.
A remote, online, or managed backup service, sometimes marketed as cloud backup or backup-as-a-service, is a service that provides users with a system for the backup, storage, and recovery of computer files. Online backup providers are companies that provide this type of service to end users. Such backup services are considered a form of cloud computing.
Given organizations' increasing dependency on information technology (IT) to run their operations, business continuity planning covers the entire organization, while disaster recovery focuses on IT.
Unitrends Inc., a Kaseya company, is an American company specializing in backup and business continuity.
Continuous data protection (CDP), also called continuous backup or real-time backup, refers to backup of computer data by automatically saving a copy of every change made to that data, essentially capturing every version of the data that the user saves. In its true form it allows the user or administrator to restore data to any point in time. The technique was patented by British entrepreneur Pete Malcolm in 1989 as "a backup system in which a copy [editor's emphasis] of every change made to a storage medium is recorded as the change occurs [editor's emphasis]."

Oracle Solaris Cluster is a high-availability cluster software product for Solaris, originally created by Sun Microsystems, which was acquired by Oracle Corporation in 2010. It is used to improve the availability of software services such as databases, file sharing on a network, electronic commerce websites, or other applications. Sun Cluster operates by having redundant computers or nodes where one or more computers continue to provide service if another fails. Nodes may be located in the same data center or on different continents.
A virtual tape library (VTL) is a data storage virtualization technology used typically for backup and recovery purposes. A VTL presents a storage component as tape libraries or tape drives for use with existing backup software.
Replication in computing involves sharing information so as to ensure consistency between redundant resources, such as software or hardware components, to improve reliability, fault-tolerance, or accessibility.

In data storage, disk mirroring is the replication of logical disk volumes onto separate physical hard disks in real time to ensure continuous availability. It is most commonly used in RAID 1. A mirrored volume is a complete logical representation of separate volume copies.
The IBM SAN Volume Controller (SVC) is a block storage virtualization appliance that belongs to the IBM System Storage product family. SVC implements an indirection, or "virtualization", layer in a Fibre Channel storage area network (SAN).
High availability (HA) is a characteristic of a system that aims to ensure an agreed level of operational performance, usually uptime, for a higher than normal period.
Hardware virtualization is the virtualization of computers as complete hardware platforms, certain logical abstractions of their componentry, or only the functionality required to run various operating systems. Virtualization emulates the hardware environment of its host architecture, allowing multiple OSes to run unmodified and in isolation. At its origins, the software that controlled virtualization was called a "control program", but the terms "hypervisor" or "virtual machine monitor" became preferred over time.
The subject of computer backups is rife with jargon and highly specialized terminology. This page is a glossary of backup terms that aims to clarify the meaning of such jargon and terminology.
A very large database, or VLDB, is a database that contains a very large amount of data, so much that it can require specialized architectural, management, processing and maintenance methodologies.
Disk-based backup refers to technology that allows one to back up large amounts of data to a disk storage unit. It is often supplemented by tape drives for data archival or replication to another facility for disaster recovery. Backup-to-disk is a popular in enterprise use for both technical and business reasons. Storage devices have gotten faster access time and higher storage capacity. There are different forms of disks used for back up, standard mechanical disks and solid state disks.
Software-defined storage (SDS) is a marketing term for computer data storage software for policy-based provisioning and management of data storage independent of the underlying hardware. Software-defined storage typically includes a form of storage virtualization to separate the storage hardware from the software that manages it. The software enabling a software-defined storage environment may also provide policy management for features such as data deduplication, replication, thin provisioning, snapshots and backup.

CloudEndure is a cloud computing company that develops business continuity software for disaster recovery, continuous backup, and live migration. CloudEndure is headquartered in the United States with R&D in Israel.



