Springhill mining disaster may refer to any of three deadly Canadian mining disasters that occurred in 1891, 1956, and 1958 in different mines within the Springhill coalfield, near the town of Springhill in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia. In the 1891 accident, 125 died; in 1956, 39 were killed; and in 1958, there were 75 miners killed.
A mining accident is an accident that occurs during the process of mining minerals or metals. Thousands of miners die from mining accidents each year, especially from underground coal mining, although accidents also occur in hard rock mining. Coal mining is considered much more hazardous than hard rock mining due to flat-lying rock strata, generally incompetent rock, the presence of methane gas, and coal dust. Most of the deaths these days occur in developing countries, and rural parts of developed countries where safety measures are not practiced as fully. A mining disaster is an incident where there are five or more fatalities.
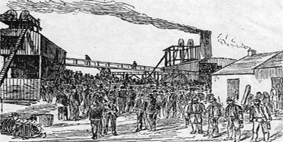
The Blantyre mining disaster, which happened on the morning of 22 October 1877, in Blantyre, Scotland, was Scotland's worst ever mining accident. Pits No. 2 and No. 3 of William Dixon's Blantyre Colliery were the site of an explosion which killed 207 miners, possibly more, with the youngest being a boy of 11. It was known that firedamp was present in the pit and it is likely that this was ignited by a naked flame. The accident left 92 widows and 250 fatherless children.

Moura is a rural town and locality in the Shire of Banana in Central Queensland, Australia. It services the surrounding coal mining and rural activities. It is situated approximately 65 kilometres (40 mi) west of Biloela on the Dawson Highway, 186 kilometres (116 mi) west of the port city of Gladstone, and 171 kilometres (106 mi) south west of Rockhampton. As of the 2021 census, the locality of Moura had a population of 1,993 people.

The Senghenydd colliery disaster, also known as the Senghenydd explosion, occurred at the Universal Colliery in Senghenydd, near Caerphilly, Glamorgan, Wales, on 14 October 1913. The explosion, which killed 439 miners and a rescuer, is the worst mining accident in the United Kingdom. Universal Colliery, on the South Wales Coalfield, extracted steam coal, which was much in demand. Some of the region's coal seams contained high quantities of firedamp, a highly explosive gas consisting of methane and hydrogen.

The Cherry Mine disaster was a fire which occurred at the Cherry Mine, a coal mine outside Cherry, Illinois, on November 13, 1909. The fire, which killed 259 men and boys, is the third most deadly mine disaster in American coal mining history.

Mine rescue or mines rescue is the specialised job of rescuing miners and others who have become trapped or injured in underground mines because of mining accidents, roof falls or floods and disasters such as explosions.

Mining in Australia has long been a significant primary sector industry and contributor to the Australian economy by providing export income, royalty payments and employment. Historically, mining booms have also encouraged population growth via immigration to Australia, particularly the gold rushes of the 1850s. Many different ores, gems and minerals have been mined in the past and a wide variety are still mined throughout the country.

Redding is a village within the Falkirk council area in Central Scotland. The village is 2.1 miles (3.4 km) southeast of Falkirk, 1.9 miles (3.1 km) south-southwest of Grangemouth and 1 mile (1.6 km) west of Polmont.

California is a former pit village in the Falkirk council area of Scotland. It lies between Shieldhill and Avonbridge on the uplands which form the southern edge of the council area.

The Knockshinnoch disaster was a mining accident that occurred in September 1950 in the village of New Cumnock, Ayrshire, Scotland. A glaciated lake filled with liquid peat and moss flooded pit workings, trapping more than a hundred miners underground. For several days rescue teams worked non-stop to reach the trapped men. Most were eventually rescued three days later, but 13 died. The disaster was an international media event.

The Eglinton Castle estate was situated at Irvine, on the outskirts of Kilwinning, North Ayrshire, Scotland in the former district of Cunninghame. Eglinton Castle, was once home to the Montgomeries, Earls of Eglinton and chiefs of the Clan Montgomery. Eglinton Country Park now occupies part of the site.

The Avondale Mine disaster was a massive fire at the Avondale Colliery near Plymouth Township, Pennsylvania, on September 6, 1869. It caused the death of 110 workers. It started when the wooden lining of the mine shaft caught fire and ignited the coal breaker built directly overhead. The shaft was the only entrance and exit to the mine, and the fire trapped and suffocated 108 of the workers. It was the greatest mine disaster to that point in American history.
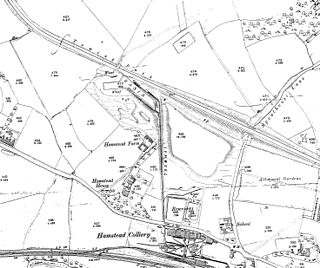
Hamstead Colliery in Hamstead, England, produced coal between 1878 and 1965, by mining the South Staffordshire 'Thick' coal seam. It suffered a major fire in 1908 in which 26 men died.

The Forest of Dean Coalfield, underlying the Forest of Dean, in west Gloucestershire, is one of the smaller coalfields in the British Isles, although intensive mining during the 19th and 20th centuries has had enormous influence on the landscape, history, culture, and economy of the area.
The Tarenni Colliery and its associated workings, are a series of coal mines and pits located between the villages of Godre'r Graig and Cilybebyll located in the valley of the River Tawe, in Neath Port Talbot county borough, South Wales.
Sir William Galloway was a Scottish mining engineer, professor and industrialist.
The Diglake Colliery Disaster, was a coal-mining disaster at what was Audley Colliery in Bignall End, North Staffordshire, on 14 January 1895. A flood of water rushed into the mine and caused the deaths of 77 miners. Only three bodies were recovered, with efforts to retrieve the dead hampered by floodwater. 73 bodies are still entombed underground.