
IEEE 802.11 is part of the IEEE 802 set of local area network (LAN) technical standards, and specifies the set of medium access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) protocols for implementing wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication. The standard and amendments provide the basis for wireless network products using the Wi-Fi brand and are the world's most widely used wireless computer networking standards. IEEE 802.11 is used in most home and office networks to allow laptops, printers, smartphones, and other devices to communicate with each other and access the Internet without connecting wires. IEEE 802.11 is also a basis for vehicle-based communication networks with IEEE 802.11p.

AirPort is a discontinued line of wireless routers and network cards developed by Apple Inc. using Wi-Fi protocols. In Japan, the line of products was marketed under the brand AirMac due to previous registration by I-O Data.

Wi-Fi is a family of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks, used globally in home and small office networks to link devices and to provide Internet access with wireless routers and wireless access points in public places such as coffee shops, hotels, libraries, and airports to provide visitors.
Atmel Corporation was a creator and manufacturer of semiconductors before being subsumed by Microchip Technology in 2016. Atmel was founded in 1984. The company focused on embedded systems built around microcontrollers. Its products included microcontrollers radio-frequency (RF) devices including Wi-Fi, EEPROM, and flash memory devices, symmetric and asymmetric security chips, touch sensors and controllers, and application-specific products. Atmel supplies its devices as standard products, application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), or application-specific standard product (ASSPs) depending on the requirements of its customers.

Nordic Semiconductor ASA was founded in 1983 and is a Norwegian fabless technology company with its headquarters in Trondheim, Norway. The company specializes in designing ultra-low-power wireless communication semiconductors and supporting software for engineers developing and manufacturing Internet of Things (IoT) products.
IEEE 802.11n-2009, or 802.11n, is a wireless-networking standard that uses multiple antennas to increase data rates. The Wi-Fi Alliance has also retroactively labelled the technology for the standard as Wi-Fi 4. It standardized support for multiple-input multiple-output, frame aggregation, and security improvements, among other features, and can be used in the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequency bands.

High-speed multimedia radio (HSMM) is the implementation of high-speed wireless TCP/IP data networks over amateur radio frequency allocations using commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) hardware such as 802.11 Wi-Fi access points. This is possible because the 802.11 unlicensed frequency bands partially overlap with amateur radio bands and ISM bands in many countries. Only licensed amateur radio operators may legally use amplifiers and high-gain antennas within amateur radio frequencies to increase the power and coverage of an 802.11 signal.
Qualcomm Atheros is a developer of semiconductor chips for network communications, particularly wireless chipsets. The company was founded under the name T-Span Systems in 1998 by experts in signal processing and VLSI design from Stanford University, the University of California, Berkeley, and private industry. The company was renamed Atheros Communications in 2000 and it completed an initial public offering in February 2004, trading on the NASDAQ under the symbol ATHR.
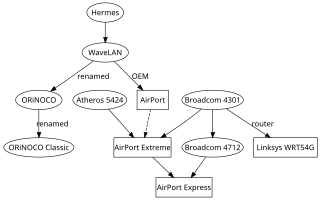
WaveLAN was a brand name for a family of wireless networking technology sold by NCR, AT&T, Lucent Technologies, and Agere Systems as well as being sold by other companies under OEM agreements. The WaveLAN name debuted on the market in 1990 and was in use until 2000, when Agere Systems renamed their products to ORiNOCO. WaveLAN laid the important foundation for the formation of IEEE 802.11 working group and the resultant creation of Wi-Fi.
Long-range Wi-Fi is used for low-cost, unregulated point-to-point computer network connections, as an alternative to other fixed wireless, cellular networks or satellite Internet access.
IEEE 802.11a-1999 or 802.11a was an amendment to the IEEE 802.11 wireless local network specifications that defined requirements for an orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) communication system. It was originally designed to support wireless communication in the unlicensed national information infrastructure (U-NII) bands as regulated in the United States by the Code of Federal Regulations, Title 47, Section 15.407.
IEEE 802.11b-1999 or 802.11b is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11 wireless networking specification that extends throughout up to 11 Mbit/s using the same 2.4 GHz band. A related amendment was incorporated into the IEEE 802.11-2007 standard.

An 802.15.4 radio module is a small device used to communicate wirelessly with other devices according to the IEEE 802.15.4 protocol.
Wi-Fi Direct is a Wi-Fi standard for peer-to-peer wireless connections that allows two devices to establish a direct Wi-Fi connection without an intermediary wireless access point, router, or Internet connection. Wi-Fi Direct is single-hop communication, rather than multi-hop communication like wireless ad hoc networks.
Linksys manufactures a series of network routers. Many models are shipped with Linux-based firmware and can run third-party firmware. The first model to support third-party firmware was the very popular Linksys WRT54G series.
Wilocity was a fabless semiconductor company based in California founded in 2007 developing 60 GHz multi-gigabit wireless chipsets for both the mobile computing platform and peripheral markets. Wilocity was founded in March 2007 by executives and engineers from Intel's Wi-Fi Centrino group. While Wilocity is based in California, most of its employees are in Israel. Based on the WiGig specification, Wilocity's Wireless PCI Express (wPCIe) technology enables multi-gigabit wireless for applications including I/O, networking and video.
IEEE 802.11ac-2013 or 802.11ac is a wireless networking standard in the IEEE 802.11 set of protocols, providing high-throughput wireless local area networks (WLANs) on the 5 GHz band. The standard has been retroactively labelled as Wi-Fi 5 by Wi-Fi Alliance.
IEEE 802.11ah is a wireless networking protocol published in 2017 called Wi-Fi HaLow as an amendment of the IEEE 802.11-2007 wireless networking standard. It uses 900 MHz license-exempt bands to provide extended-range Wi-Fi networks, compared to conventional Wi-Fi networks operating in the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz bands. It also benefits from lower energy consumption, allowing the creation of large groups of stations or sensors that cooperate to share signals, supporting the concept of the Internet of things (IoT). The protocol's low power consumption competes with Bluetooth, LoRa, and Zigbee, and has the added benefit of higher data rates and wider coverage range.

Banana Pi is a line of single-board computers produced by the Chinese company Shenzhen SINOVOIP Company, its spin-off Guangdong BiPai Technology Company, and supported by Hon Hai Technology (Foxconn). Its hardware design was influenced by the Raspberry Pi, and both lines use the same 40-pin I/O connector.

IEEE 802.11be, dubbed Extremely High Throughput (EHT), is the latest of the IEEE 802.11 standard, which is designated Wi-Fi 7. It has built upon 802.11ax, focusing on WLAN indoor and outdoor operation with stationary and pedestrian speeds in the 2.4, 5, and 6 GHz frequency bands.








