
Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty.

Hadrian was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. He was born in Italica, a Roman municipium founded by Italic settlers in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the gens Aelia, the Aeli Hadriani, came from the town of Hadria. His father was of senatorial rank and was a first cousin of Emperor Trajan. Hadrian married Trajan's grand-niece Vibia Sabina early in his career before Trajan became emperor and possibly at the behest of Trajan's wife Pompeia Plotina. Plotina and Trajan's close friend and adviser Lucius Licinius Sura were well disposed towards Hadrian. When Trajan died, his widow claimed that he had nominated Hadrian as emperor immediately before his death.

A merchant is a person who trades in commodities produced by other people, especially one who trades with foreign countries. Historically, a merchant is anyone who is involved in business or trade. Merchants have operated for as long as industry, commerce, and trade have existed. In 16th-century Europe, two different terms for merchants emerged: meerseniers referred to local traders and koopman referred to merchants who operated on a global stage, importing and exporting goods over vast distances and offering added-value services such as credit and finance.

Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus, was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his death in AD 68. He was adopted by the Roman emperor Claudius at the age of 13 and succeeded him on the throne. Nero was popular with the members of his Praetorian Guard and lower-class commoners in Rome and its provinces, but he was deeply resented by the Roman aristocracy. Most contemporary sources describe him as tyrannical, self-indulgent, and debauched. After being declared a public enemy by the Roman Senate, he committed suicide at age 30.

The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. In the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of 7,641 islands which are broadly categorized in three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. The Philippines is bounded by the South China Sea to the west, the Philippine Sea to the east, and the Celebes Sea to the south. It shares maritime borders with Taiwan to the north, Japan to the northeast, Palau to the east and southeast, Indonesia to the south, Malaysia to the southwest, Vietnam to the west, and China to the northwest. It is the world's thirteenth-most-populous country, with diverse ethnicities and cultures. Manila is the country's capital, and its largest city is Quezon City; both are within Metro Manila.

Rome is the capital city of Italy. It is also the capital of the Lazio region, the centre of the Metropolitan City of Rome, and a special comune named Comune di Roma Capitale. With 2,860,009 residents in 1,285 km2 (496.1 sq mi), Rome is the country's most populated comune and the third most populous city in the European Union by population within city limits. The Metropolitan City of Rome, with a population of 4,355,725 residents, is the most populous metropolitan city in Italy. Its metropolitan area is the third-most populous within Italy. Rome is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, within Lazio (Latium), along the shores of the Tiber. Vatican City is an independent country inside the city boundaries of Rome, the only existing example of a country within a city. Rome is often referred to as the City of Seven Hills due to its geographic location, and also as the "Eternal City". Rome is generally considered to be the "cradle of Western civilization and Christian culture", and the centre of the Catholic Church.

The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The imperial seat moved from Rome to Byzantium and following the capture of the city of Rome in AD 476, it became its sole capital as Constantinople. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western Roman Empire to Germanic kings conventionally marks the end of classical antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. Because of these events, along with the prevalence of Greek instead of Latin, some historians distinguish the medieval Roman Empire that remained in the Eastern provinces as the Byzantine Empire.

Trajan was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared optimus princeps by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presided over one of the greatest military expansions in Roman history and led the empire to attain its greatest territorial extent by the time of his death. He is also known for his philanthropic rule, overseeing extensive public building programs and implementing social welfare policies, which earned him his enduring reputation as the second of the Five Good Emperors who presided over an era of peace within the Empire and prosperity in the Mediterranean world.

In ancient Rome, the Vestal Virgins or Vestals were priestesses of Vesta, virgin goddess of Rome's sacred hearth and its flame.
Career Development or Career Development Planning refers to the process an individual may undergo to evolve their occupational status. It is the process of making decisions for long term learning, to align personal needs of physical or psychological fulfillment with career advancement opportunities. Career Development can also refer to the total encompassment of an individual's work-related experiences, leading up to the occupational role they may hold within an organization.

Vastu shastra is a traditional Indian system of architecture based on ancient texts that describe principles of design, layout, measurements, ground preparation, space arrangement, and spatial geometry. The designs aim to integrate architecture with nature, the relative functions of various parts of the structure, and ancient beliefs utilising geometric patterns (yantra), symmetry, and directional alignments.

The ancient Romans were the first civilization to build large, permanent bridges. Early Roman bridges used techniques introduced by Etruscan immigrants, but the Romans improved those skills, developing and enhancing methods such as arches and keystones. There were three major types of Roman bridge: wooden, pontoon, and stone. Early Roman bridges were wooden, but by the 2nd century stone was being used. Stone bridges used the arch as their basic structure, and most used concrete, the first use of this material in bridge-building.

The Samnites were an ancient Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy.

A warehouse is a building for storing goods. Warehouses are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport businesses, customs, etc. They are usually large plain buildings in industrial parks on the outskirts of cities, towns, or villages.

The pyramid of Cestius is a Roman Era pyramid in Rome, Italy, near the Porta San Paolo and the Protestant Cemetery. It was built as a tomb for Gaius Cestius, a member of the Epulones religious corporation. It stands at a fork between two ancient roads, the Via Ostiensis and another road that ran west to the Tiber along the approximate line of the modern Via Marmorata. Due to its incorporation into the city's fortifications, it is today one of the best-preserved ancient buildings in Rome.
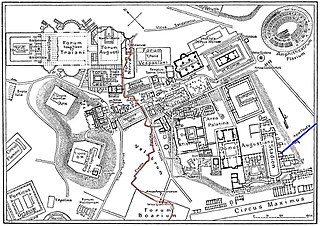
The Cloaca Maxima was one of the world's earliest sewage systems. Its name derives from Cloacina, a Roman goddess. Built during either the Roman Kingdom or early Roman Republic, it was constructed in Ancient Rome in order to drain local marshes and remove waste from the city. It carried effluent to the River Tiber, which ran beside the city. The sewer started at the Forum Augustum and ended at the Ponte Rotto and Ponte Palatino. It began as an open air canal, but it developed into a much larger sewer over the course of time. Agrippa renovated and reconstructed much of the sewer. This would not be the only development in the sewers. By the first century CE all eleven Roman aqueducts were connected to the sewer. After the Roman Empire fell the sewer still was used. By the 1800s it became a tourist attraction. Some parts of the sewer are still used today. Whilst still being used it was highly valued as a sacred symbol of Roman culture, and Roman engineering.

In Roman architecture, an insula was one of two things: either a kind of apartment building, or a city block. This article deals with the former definition, that of a type of apartment building.

The Comitium was the original open-air public meeting space of Ancient Rome, and had major religious and prophetic significance. The name comes from the Latin word for "assembly". The Comitium location at the northwest corner of the Roman Forum was later lost in the city's growth and development, but was rediscovered and excavated by archaeologists at the turn of the twentieth century. Some of Rome's earliest monuments; including the speaking platform known as the Rostra, the Columna Maenia, the Graecostasis and the Tabula Valeria were part of or associated with the Comitium.

East Asia is the easternmost region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. Hong Kong and Macau, two small coastal quasi-dependent territories located in the south of China, are officially highly autonomous but are under Chinese sovereignty. Japan, Taiwan, South Korea, Mainland China, Hong Kong, and Macau are among the world's largest and most prosperous economies. East Asia borders Siberia and the Russian Far East to the north, Southeast Asia to the south, South Asia to the southwest, and Central Asia to the west. To the east is the Pacific Ocean and to the southeast is Micronesia.

The Roman architectural revolution, also known as the concrete revolution, is the name sometimes given to the widespread use in Roman architecture of the previously little-used architectural forms of the arch, vault, and dome. For the first time in history, their potential was fully exploited in the construction of a wide range of civil engineering structures, public buildings, and military facilities. These included amphitheatres, aqueducts, baths, bridges, circuses, dams, roads, and temples.



















