Related Research Articles

The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral to caudal axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets.

In many religious and philosophical traditions, the soul is the non-material essence of a person, which includes one's identity, personality, and memories, an immaterial aspect or essence of a living being that is believed to be able to survive physical death. The concept of the soul is generally applied to humans, although it can also be applied to other living or even non-living entities, as in animism.

World Brain is a collection of essays and addresses by the English science fiction pioneer, social reformer, evolutionary biologist and historian H. G. Wells, dating from the period of 1936–1938. Throughout the book, Wells describes his vision of the World Brain: a new, free, synthetic, authoritative, permanent "World Encyclopaedia" that could help world citizens make the best use of universal information resources and make the best contribution to world peace.

The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of three types of bone: cranial bones, facial bones, and ear ossicles. Two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium (braincase) and the viscerocranium that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans, these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton.

Neuropsychology is a branch of psychology concerned with how a person's cognition and behavior are related to the brain and the rest of the nervous system. Professionals in this branch of psychology focus on how injuries or illnesses of the brain affect cognitive and behavioral functions.
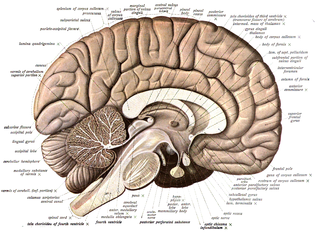
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems. Their neuroanatomy is therefore better understood. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord and the series of nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body. Breaking down and identifying specific parts of the nervous system has been crucial for figuring out how it operates. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or "lesions" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.
Neurophysiology is a branch of physiology and neuroscience that studies nervous system function rather than nervous system architecture. This area aids in the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological diseases. Historically, it has been dominated by electrophysiology—the electrical recording of neural activity ranging from the molar to the cellular, such as patch clamp, voltage clamp, extracellular single-unit recording and recording of local field potentials. However, since the neuron is an electrochemical machine, it is difficult to isolate electrical events from the metabolic and molecular processes that cause them. Thus, neurophysiologists currently utilise tools from chemistry, physics, and molecular biology to examine brain activity.
In philosophy and psychology, awareness is a perception or knowledge of something. The concept is often synonymous to consciousness. However, one can be aware of something without being explicitly conscious of it, such as in the case of blindsight.

Tomorrow Woman is a fictional character, an android in stories published in DC Comics. She debuted in JLA #5, and was created by Grant Morrison and Howard Porter. Within the DC Comics canon, she is created by the mad scientist super-villains Professor Ivo and T.O. Morrow. Given human-like physical characteristics and false memories of a human life, Tomorrow Woman believes herself to be a new superhero born with psionic abilities due to a "four-lobed brain". Her true purpose is to infiltrate and then kill the Justice League. In her first appearance, she says she exclusively has telekinetic abilities, but a later flashback issue of JLA: Tomorrow Woman (1998) reveals that she also has telepathic abilities.
Dunbar's number is a suggested cognitive limit to the number of people with whom one can maintain stable social relationships—relationships in which an individual knows who each person is and how each person relates to every other person.

Dinilysia is an extinct genus of snake from the Late Cretaceous (Coniacian) of South America. Dinilysia was a relatively large ambush predator, measuring approximately 2 m (6.6 ft) long. The skull morphology of Dinilysia is similar to boids, suggesting that it was able to consume large prey. Living in a desert-like environment, Dinilysia is likely a terrestrial or a semi-fossorial animal.
Wildbrain Entertainment, Inc. was an American entertainment company and animation studio that developed and produced television programming, motion pictures, commercial content, and licensed merchandise. Established in 1994, it maintained offices in Los Angeles, New York City, and San Francisco.
The Living Brain is the name of two supervillains appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. Created by writer Stan Lee and artist Steve Ditko, the original Living Brain first appears in The Amazing Spider-Man #8 and has made few subsequent appearances since.
"Locked In" is the nineteenth episode of the fifth season of House. It aired on Fox on March 30, 2009. Large portions of the episode are shown from the perspective of the patient, who retains consciousness but lacks the ability to move. After discovering the patient in an emergency room while being treated for injuries related to a motorbike crash, House's team move the patient to Princeton Plainsboro and attempts to diagnose him. During the course of treatment, the team discovers several medically relevant secrets about the patient. Other plot points focus on Wilson's attempts to discover why House was in Middletown, New York when he crashed, Wilson's new relationship, and the resolution of Taub's resignation from the previous episode.

The Transitional Learning Center(TLC) is a post-acute brain injury rehabilitation facility headquartered in the island city of Galveston, Texas. It was started by the non-profit Moody Foundation in 1982, in response to a brain injury suffered by a son of trustee Robert L. Moody. The center provides survivors of acute brain injury with rehabilitation services needed to help patients overcome their injuries and regain independence. In order to provide additional space for post-acute brain injury rehabilitation, in 2008 the center opened a branch facility in Lubbock, Texas, to help serve needs of people throughout the southwest United States. TLC Director of Neuropsychology, Dr. Dennis Zgaljardic, is a past president of the Houston Neuropsychological Society.

This article describes anatomical terminology that is used to describe the central and peripheral nervous systems - including the brain, brainstem, spinal cord, and nerves.
Cerebavis is an extinct genus of ornithurine dinosaurs that lived during the middle Cenomanian of the Late Cretaceous period, and is known from a single partial skull found in the Melovatskaya Formation of Volgograd Region in Russia. The skull was initially described as the fossilised brain of an enantiornithean by Russian palaeornithologist Evgeny Kurochkin and colleagues in 2006. Kurochkin and colleagues described Cerebavis as having a notable mixture of ancestral traits, such as a well-developed olfactory system, with derived traits of modern birds like a large cerebrum. At the same time, they identified various unusual and unique features not seen in the brains of reptiles or birds. These include well-developed auditory tubercles on the midbrain, as well as a prominent parietal organ compared to living birds or Archaeopteryx between them.

Lego DC Super Hero Girls: Brain Drain is a 2017 American animated superhero comedy film based on the DC Super Hero Girls franchise, produced by Warner Bros. Animation. It is the third film in the DC Super Hero Girls franchise, as well as the first in the series to be based on the DC Super Hero Girls brand of Lego. It was digitally released on July 25, 2017, and was followed by a DVD release on August 8. The film premiered on Cartoon Network in the US on November 19 the same year.
Symbiosis (mutualism) appears in fiction, especially science fiction, as a plot device. It is distinguished from parasitism in fiction, a similar theme, by the mutual benefit to the organisms involved, whereas the parasite inflicts harm on its host.
Brain drain from Nigeria, nicknamed Japa is the exodus of middle-class and highly skilled Nigerians which has been occurring in waves since the late 1980s to early 1990s. This trend was initially restricted to certain professions but has now become free for all with the introduction of visa programs in order to fill workforce gaps in developed nations. This was sparked by an economic downturn following a period of economic boom in the 1970s and 1980s propelled by the discovery of oil wells in Nigeria.
References
- ↑ Towards A Living Encyclopædia: A Contribution to Mr Wells's New Encyclopædism. London: Andrew Dakers Ltd., 1941.
- ↑ Library Trends, Vol. 42, No. 4, Spring 1994, pp. 585–90. Retrieved 29 November 2010 from http://hdl.handle.net/2142/7925