
Assistive technology (AT) is a term for assistive, adaptive, and rehabilitative devices for people with disabilities and the elderly. Disabled people often have difficulty performing activities of daily living (ADLs) independently, or even with assistance. ADLs are self-care activities that include toileting, mobility (ambulation), eating, bathing, dressing, grooming, and personal device care. Assistive technology can ameliorate the effects of disabilities that limit the ability to perform ADLs. Assistive technology promotes greater independence by enabling people to perform tasks they were formerly unable to accomplish, or had great difficulty accomplishing, by providing enhancements to, or changing methods of interacting with, the technology needed to accomplish such tasks. For example, wheelchairs provide independent mobility for those who cannot walk, while assistive eating devices can enable people who cannot feed themselves to do so. Due to assistive technology, disabled people have an opportunity of a more positive and easygoing lifestyle, with an increase in "social participation", "security and control", and a greater chance to "reduce institutional costs without significantly increasing household expenses." In schools, assistive technology can be critical in allowing students with disabilities to access the general education curriculum. Students who experience challenges writing or keyboarding, for example, can use voice recognition software instead. Assistive technologies assist people who are recovering from strokes and people who have sustained injuries that affect their daily tasks.

Parasports are sports played by people with a disability, including physical and intellectual disabilities. Some parasports are forms of adapted physical activities from existing non-disabled sports, while others have been specifically created for persons with a disability and do not have a non-disabled equivalent. Disability exists in four categories: physical, mental, permanent and temporary. At a competitive level, disability sport classifications are applied to allow people of varying abilities to face similar opposition.

In medicine, a prosthesis, or a prosthetic implant, is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through physical trauma, disease, or a condition present at birth. Prostheses are intended to restore the normal functions of the missing body part. Amputee rehabilitation is primarily coordinated by a physiatrist as part of an inter-disciplinary team consisting of physiatrists, prosthetists, nurses, physical therapists, and occupational therapists. Prostheses can be created by hand or with computer-aided design (CAD), a software interface that helps creators design and analyze the creation with computer-generated 2-D and 3-D graphics as well as analysis and optimization tools.

Occupational therapy (OT) is a healthcare profession that involves the use of assessment and intervention to develop, recover, or maintain the meaningful activities, or occupations, of individuals, groups, or communities. The field of OT consists of health care practitioners trained and educated to improve mental and physical performance. Occupational therapists specialize in teaching, educating, and supporting participation in any activity that occupies an individual's time. It is an independent health profession sometimes categorized as an allied health profession and consists of occupational therapists (OTs) and occupational therapy assistants (OTAs). While OTs and OTAs have different roles, they both work with people who want to improve their mental and or physical health, disabilities, injuries, or impairments.
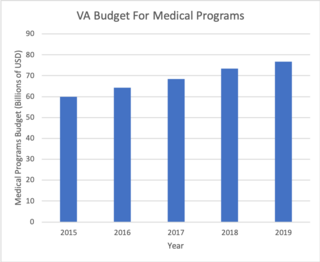
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) is the component of the United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) led by the Under Secretary of Veterans Affairs for Health that implements the healthcare program of the VA through a nationalized healthcare service in the United States, providing healthcare and healthcare-adjacent services to veterans through the administration and operation of 146 VA Medical Centers (VAMC) with integrated outpatient clinics, 772 Community Based Outpatient Clinics (CBOC), and 134 VA Community Living Centers Programs. It is the largest division in the department, and second largest in the entire federal government, employing over 350,000 employees. All VA hospitals, clinics and medical centers are owned by and operated by the Department of Veterans Affairs, and all of the staff employed in VA hospitals are federal employees. Because of this, veterans that qualify for VHA healthcare do not pay premiums or deductibles for their healthcare but may have to make copayments depending on the medical procedure. VHA is not a part of the US Department of Defense Military Health System.
Peer support occurs when people provide knowledge, experience, emotional, social or practical help to each other. It commonly refers to an initiative consisting of trained supporters, and can take a number of forms such as peer mentoring, reflective listening, or counseling. Peer support is also used to refer to initiatives where colleagues, members of self-help organizations and others meet, in person or online, as equals to give each other connection and support on a reciprocal basis.

Telerehabilitation (or e-rehabilitation is the delivery of rehabilitation services over telecommunication networks and the internet. Telerehabilitation allows patients to interact with providers remotely and can be used both to assess patients and to deliver therapy. Fields of medicine that utilize telerehabilitation include: physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech-language pathology, audiology, and psychology. Therapy sessions can be individual or community-based. Types of therapy available include motor training exercises, speech therapy, virtual reality, robotic therapy, goal setting, and group exercise.
Rehabilitation engineering is the systematic application of engineering sciences to design, develop, adapt, test, evaluate, apply, and distribute technological solutions to problems confronted by individuals with disabilities. These individuals may have experienced a spinal cord injury, brain trauma, or any other debilitating injury or disease. Functional areas addressed through rehabilitation engineering may include mobility, communications, hearing, vision, and cognition, and activities associated with employment, independent living, education, and integration into the community.

The Paralyzed Veterans of America was established in 1946 with the goal of serving the needs of disabled veterans. The organization was created to assist members, such as veterans of the armed forces living with spinal cord injuries or diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS) or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in living with increased independence and dignity.
Polytrauma and multiple trauma are medical terms describing the condition of a person who has been subjected to multiple traumatic injuries, such as a serious head injury in addition to a serious burn. The term is defined via an Injury Severity Score (ISS) equal to or greater than 16. It has become a commonly applied term by US military physicians in describing the seriously injured soldiers returning from Operation Iraqi Freedom in Iraq and Operation Enduring Freedom in Afghanistan. The term is generic, however, and has been in use for a long time for any case involving multiple trauma.
Cognitive orthotics are software-based personal reminder systems for people with cognitive impairment, such as memory loss. Individuals with cognitive impairments frequently encounter substantial challenges in developing independence skills, including vocational abilities and daily living activities. Individuals with mild intellectual disabilities typically attain adequate skills for independence.[1] Conversely, those categorized as moderately intellectually disabled seldom reach this degree of autonomy.[1] Historically, training programs for individuals with moderate intellectual disabilities have served as the traditional means to instill and support independent living skills.[1] However, the effectiveness of these programs has shown varying degrees of success.[1] Many daily routine tasks involve a series of steps, and even if each step is simple, the quantity of steps can make the process challenging for an individual with cognitive impairments.[1] A mistake in any step or an error in the sequence can lead to the entire process being deemed unacceptable.[1] For over thirty years, computers have been utilized in the rehabilitation of individuals with brain injuries. Initially, researchers delved into the potential of developing a "prosthetic memory." However, by the early 1980s, the focus shifted towards addressing brain dysfunction through repetitive practice. Only a few psychologists were developing rehabilitation software for individuals with traumatic brain injury (TBI), resulting in a scarcity of available programs.[3] Cognitive rehabilitation specialists opted for commercially available computer games that were visually appealing, engaging, repetitive, and entertaining, theorizing their potential remedial effects on neuropsychological dysfunction.[3] The outcomes of initial computer-based rehabilitation interventions were restricted and, in several aspects, fell short of expectations.[3] While repetitive practice improved performance in the specific task practiced, this effect did not extend to other tasks.[3]
Supported employment refers to service provisions wherein people with disabilities, including intellectual disabilities, mental health, and traumatic brain injury, among others, are assisted with obtaining and maintaining employment. Supported employment is considered to be one form of employment in which wages are expected, together with benefits from an employer in a competitive workplace, though some versions refer to disability agency paid employment. Companies such as Skilcraft in the United States are an example of "supported employment" which is defined in law for state and federal reimbursements.

Paul Wehman is a professor of counseling and special education at the School of Education, Virginia Commonwealth University. He also is Director of the Rehabilitation Research and Training Center.

Vocational rehabilitation, also abbreviated VR or voc rehab, is a process which enables persons with functional, psychological, developmental, cognitive, and emotional disabilities, impairments or health disabilities to overcome barriers to accessing, maintaining, or returning to employment or other useful occupations.
The Veterans Health Administration Office of Research and Development (ORD) is the research and development agency of the Veterans Health Administration in the United States Department of Veterans Affairs. The department focuses on biomedical and health care research for the care of veterans and wounded soldiers, and has a budget of $1.018 billion in the requested 2012 budget, in addition to $710 million derived from federal and non-federal grants from other agencies.
The Chronic Effects of Neurotrauma Consortium (CENC) is a federally funded research project devised to address the long-term effects of mild traumatic brain injury in military service personnel (SMs) and Veterans. Announced by President Barack Obama on August 20, 2013, the CENC was one of two major initiatives developed in response to the injuries incurred by U.S. service personnel during Operation Enduring Freedom and Operation Iraqi Freedom. The project is jointly funded in the amount of $62.175 million by the Department of Defense (DoD) and the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). The CENC is led by Dr. David X. Cifu of the Virginia Commonwealth University.
Robert S. Gailey Jr., PT, PhD, FAPTA, is an American physical therapist; professor at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Department of Physical Therapy; and the Director of the Neil Spielholz Functional Outcomes Research & Evaluation Center. His research efforts include amputee rehabilitation, prosthetic gait, and functional assessment. He developed the Amputee Mobility Predictor (AMP), an outcome measure designed to evaluate the ambulatory potential of lower-limb amputees with and without the use of a prosthesis. In 2002, he was appointed as a Special Advisor to the United States Department of Defense for amputee rehabilitation. In the aftermath of the 2010 Haiti earthquake, he served as the rehabilitation coordinator for Project Medishare.

The Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Health Care System (VAHCS) is network of hospital and outpatient clinics based in Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA. It belongs to the VISN23 VA Midwest Health Care Network managed by the Veterans Health Administration of the Department of Veterans Affairs. The Minneapolis VAHCS provides healthcare for United States military veterans in areas such as medicine, surgery, psychiatry, physical medicine and rehabilitation, neurology, oncology, dentistry, geriatrics and extended care. As a teaching hospital, it operates comprehensive training programs for multiple treatment specialties. The Minneapolis VAHCS also hosts one of the largest research programs of any VA health care system and maintains research affiliations with the University of Minnesota.

Alison Nenos Cernich is an American neuropsychologist specializing in traumatic brain injury and computerized neuropsychological assessment. She is the deputy director of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Cernich was previously deputy director of the Defense Centers of Excellence for Psychological Health and Traumatic Brain Injury, assistant professor of neurology at University of Maryland School of Medicine, and chief of neuropsychology at the VA Maryland Health Care System.

Margaret Joan Giannini was an American physician and a specialist in assistive technology and rehabilitation. She was the first director of the National Institute of Disability Rehabilitation Research (NIDRR).











